Weight of Soil
Weight of Soil Formula |
||
|
\( W_s \;=\; \dfrac{ W }{ 1 + w }\) (Weight of Soil) \( W \;=\; W_s \cdot \left( 1 + w \right) \) \( w \;=\; \dfrac{ W - W_s }{ W_s }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( W_s \) = Weight of Soil | \(lbf\) | \(N\) |
| \( W \) = Total Weight | \(lbf\) | \(N\) |
| \( w \) = Water Content | \(dimensionless\) | \(dimensionless\) |
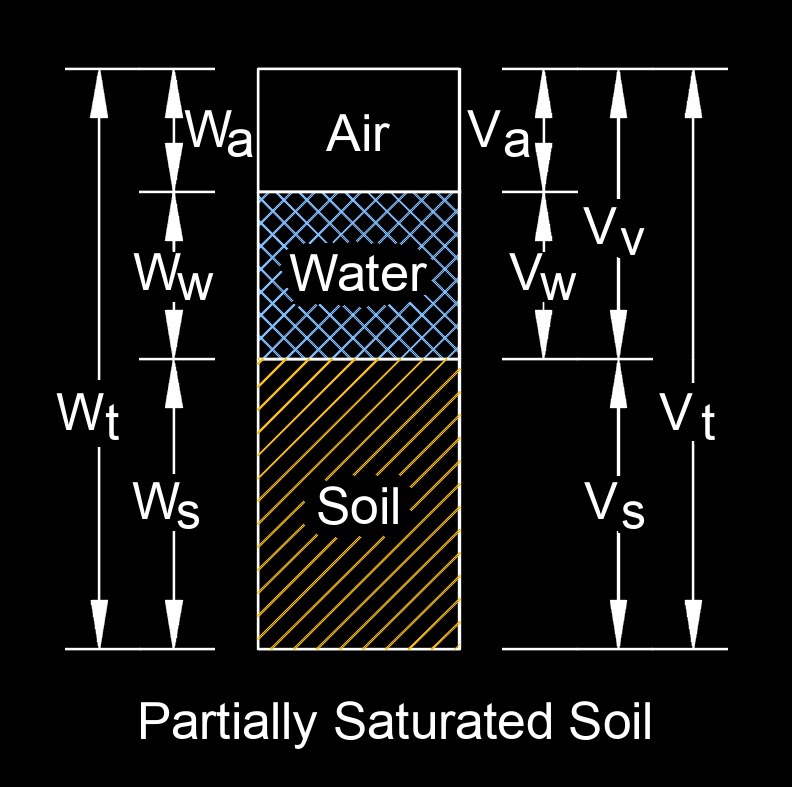
The weight of soil depends on several factors, including its volume, density, and moisture content.
Volume - The volume of soil refers to the amount of space it occupies.
Density - Soil density is the mass of soil per unit volume. The density of soil can vary widely depending on its composition, texture, and moisture content. For example, sandy soils tend to have lower densities, while clayey soils have higher densities.
Moisture Content - The moisture content of soil also affects its weight. Soil can contain varying amounts of water, and the weight of the water needs to be considered when calculating the total weight of the soil. Moisture content is typically expressed as a percentage of the soil's total weight.
To calculate the weight of a specific volume of soil, you need to know the density of the soil and its moisture content, if applicable. Keep in mind that the density of soil can change over time due to compaction, settling, and other factors, so precise measurements may require laboratory testing.

