 Flux Used in Various Scientific Disciplines
Flux Used in Various Scientific Disciplines
Physics - The flow or movement of something through a surface or within a medium. In electromagnetism, magnetic flux is the measure of the strength of a magnetic field through a given surface. In fluid dynamics, flux refers to the rate of flow of a fluid.
Mathematics - In calculus, the flow of a vector field through a surface. It's calculated as the surface integral of the vector field over the surface. This is used in physics and engineering, such as electromagnetism, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer.
Biology - The movement of substances (such as ions or molecules) across a membrane or within a biological system. For example, the flux of ions across a cell membrane is crucial for various cellular functions like nerve impulses or muscle contractions.
Chemistry - The rate of flow of a substance, particularly in processes like chemical reactions or diffusion. It's often used to describe the movement of atoms, ions, or molecules within a system.
Geology - The transfer of matter or energy through Earth's systems, such as the movement of magma through the Earth's crust or the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface.
In each of these contexts, flux describes some kind of flow, transfer, or movement, though the specifics can vary depending on the discipline.
Flux in Physics
Flux in physics is the flow or transfer of a particular quantity through a surface, and it is a used in various branches of physics to describe and analyze physical phenomena. Here are some common types of flux in physics:
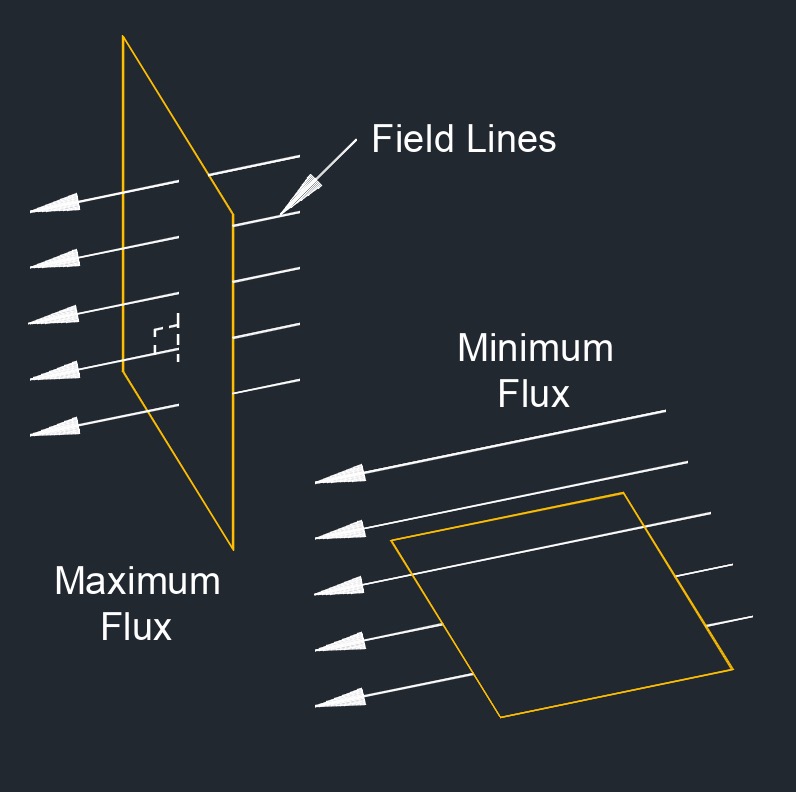
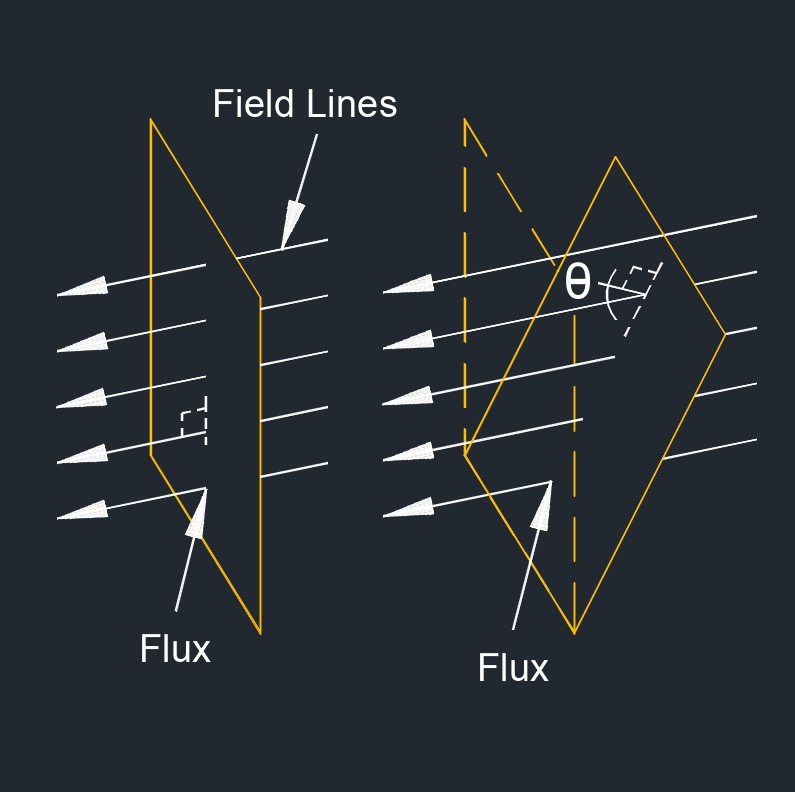
Magnetic Flux - This is a measure of the quantity of magnetic field passing through a surface. It is calculated as the product of the magnetic field strength and the area perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Electric Flux - A measure of the electric field passing through a surface. It is calculated as the product of the electric field strength and the area perpendicular to the electric field.
Heat Flux - The rate of heat transfer per unit area. It is a measure of the amount of heat energy transferred through a surface in a given time.
Fluid Flux - The rate of flow of a fluid through a surface. It is often used in fluid dynamics to describe the flow of liquids or gases through a specified area.
Flux Density in Physics
Flux density, also called flux density field or field strength, is the amount of flux passing through a unit area perpendicular to the direction of flux flow. It's a measure of the intensity of the field at a given point in space. These concepts are used to understanding and quantifying electromagnetic fields, which are needed in various areas of physics and engineering, including electrical engineering, electronics, telecommunications, and materials science. Depending on the context, flux density can refer to different types of fields:
Magnetic Flux Density - It measures the strength of a magnetic field. It quantifies how much magnetic flux (the total magnetic field passing through a given area) is present per unit area.
Electric Flux Density - It measures the electric flux (total electric field passing through a given area) per unit area.
Measuring Flux Density
The methods for measuring flux density in physics vary depending on the type of flux density being measured, magnetic flux density or electric flux density. When performing measurements, it's important to calibrate the instruments properly, account for any external interference, and ensure that measurements are taken consistently and accurately. Additionally, consider the specific properties of the material or medium being measured, as these may affect the measurement technique and accuracy.
Measuring Magnetic Flux Density
- Magnetic Field Probe - Use a calibrated magnetic field probe or sensor, such as a Hall effect sensor, fluxgate magnetometer, or magnetoresistive sensor. These devices can directly measure the magnetic field strength at a specific point in space.
- Hall Effect Measurement - The Hall effect can be used to measure magnetic fields indirectly. A Hall sensor is placed in the magnetic field, and the voltage produced across it is proportional to the magnetic field strength.
- Magnetometer - Magnetometers are instruments specifically designed to measure magnetic fields. They can provide accurate measurements of magnetic flux density over a range of magnitudes and are often used in research and engineering applications.
Measuring Electric Flux Density
- Electric Field Probe - Use an electric field probe or sensor, such as a capacitive probe or a field mill. These devices can directly measure the electric field strength at a specific point in space.
- Dielectric Constant and Capacitance - Electric flux density is related to the electric field and the permittivity of the material. Therefore, by measuring the elect field and knowing the permittivity of the material, you can calculate the electric flux density.
- Boundary Integral Methods - In some cases, particularly in experimental setups or simulations, flux density can be indirectly determined by measuring the boundary conditions and using boundary integral methods to calculate the flux density within a material.
