Algebric Difference in Grade Formula |
||
|
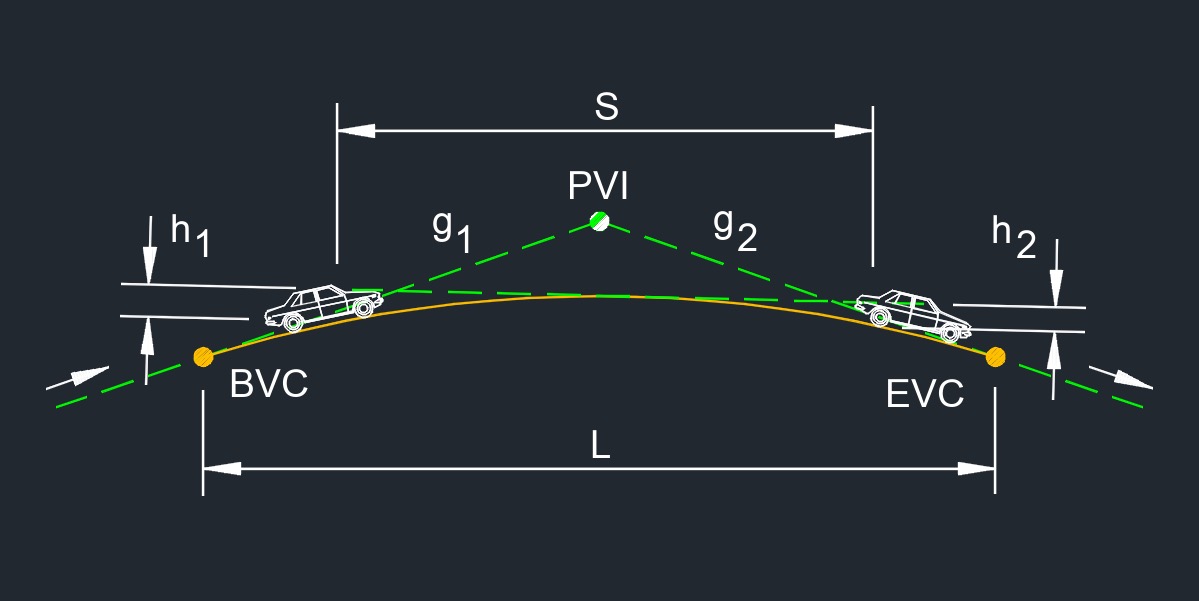
\( A \;=\; g_2 - g_1 \) (Algebric Difference in Grade) \( g_2 \;=\; A + g_1 \) \( g_1 \;=\; g_2 - A \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = Algebric Difference in Grade (%) | \(dimensionless\) | \(dimensionless\) |
| \( g_2 \) = Tangent Grade of a Slope Given in % | \(dimensionless\) | \(dimensionless\) |
| \( g_1 \) = Tangent Grade of a Slope Given in % | \(dimensionless\) | \(dimensionless\) |
The algebraic difference in grade, abbreviated as A, a dimensionless number, refers to the difference between two grades, taking into account their signs or directions. It is commonly used when working with signed numbers or vectors. The algebraic difference takes into consideration whether the grades are positive or negative and calculates the result accordingly.
To find the algebraic difference in grade, you subtract one grade from the other, considering the signs. Here are a few scenarios:
- If both grades are positive -
- If the first grade is larger than the second grade, the algebraic difference will be positive.
- If the second grade is larger than the first grade, the algebraic difference will be negative.
- If both grades are negative -
- If the first grade is larger (in magnitude) than the second grade, the algebraic difference will be negative.
- If the second grade is larger (in magnitude) than the first grade, the algebraic difference will be positive.
- If one grade is positive and the other is negative -
- The algebraic difference will depend on the magnitudes of the grades and their signs.
- If the positive grade is larger (in magnitude) than the absolute value of the negative grade, the algebraic difference will be positive.
- If the absolute value of the negative grade is larger than the positive grade, the algebraic difference will be negative.
Remember that the algebraic difference considers both the numerical difference and the signs of the grades. It helps provide a more complete understanding of the relative positions or directions of the grades involved.
