Mechanical Properties
 Mechanical properties are the characteristics of a material that describe how it responds to applied forces or loads. These properties are crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of materials under various conditions, and they play a fundamental role in the design and analysis of structures and components. These are types of stress that the metal has to withstand and resist. Some of the properties are creep, ductility, hardness, elastic and inelastic, stress and strain, tensile stress and shear strength.
Mechanical properties are the characteristics of a material that describe how it responds to applied forces or loads. These properties are crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of materials under various conditions, and they play a fundamental role in the design and analysis of structures and components. These are types of stress that the metal has to withstand and resist. Some of the properties are creep, ductility, hardness, elastic and inelastic, stress and strain, tensile stress and shear strength.
Common Mechanical Properties
Stress - Force applied per unit area.
Strain - Deformation or change in length relative to the original length.
Elastic Modulus - Measures the stiffness or rigidity of a material.
Shear Modulus - Describes the material's response to shear stress.
Bulk Modulus - Measures a material's resistance to uniform compression.
Poisson's Ratio - Ratio of transverse contraction strain to longitudinal extension strain.
Tensile Strength - Maximum stress a material can withstand under tension.
Compressive Strength - Maximum stress a material can withstand under compression.
Hardness - Measures a material's resistance to localized deformation, often by indentation or scratching.
Ductility - The ability of a material to undergo significant plastic deformation before rupture or fracture.
Brittleness - The tendency of a material to fracture with little or no plastic deformation.
These mechanical properties are needed for engineers and material scientists to select appropriate materials for specific applications and to design structures that can withstand the expected forces and environmental conditions. The properties can vary significantly among different materials, and the appropriate choice depends on the intended use and operating conditions.
Mechanical Properties of a Material
The mechanical properties of materials are characteristics that describe how a material responds to applied forces or loads. These properties are essential for engineers and designers when selecting materials for specific applications.
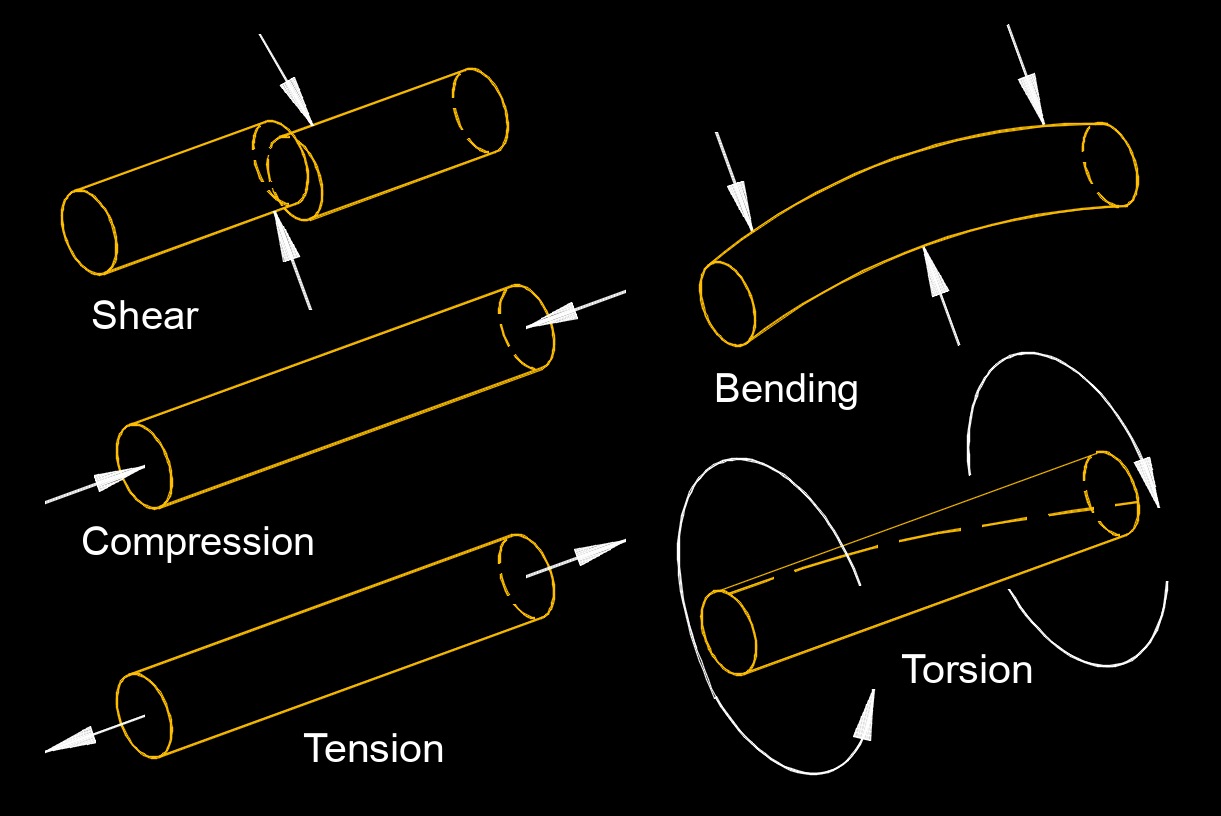
Shear - It is the deformation in which layers of a material slide past each other in response to parallel forces acting in opposite directions. This occurs when a force is applied tangentially or parallel to the surface of an object or material.
Compression - The force (pressure) acting on a material. Compression is the process of reducing the volume or increasing the density of a substance, typically by applying external forces. It involves the application of pressure to compress or squeeze a material, resulting in a decrease in its volume.
Tension - It's the force that is transmitted through a flexible or stretched object when it is pulled or stretched. It is a type of force that acts along the length of the object and is responsible for maintaining its shape and integrity.
Bending - The deformation of a material under the influence of an external force. This is particularly significant in the study of mechanics and materials science. When a force is applied to an object, it can cause the object to undergo bending, resulting in a change in its shape.
Torsion - It is the twisting or rotational deformation of an object when subjected to a torque or twisting force. This force causes the object to twist about its longitudinal axis. It is the stress of twisting of an object due to applied torque between both ends of an object.

