Hydrostatic Pressure for Drilling
Hydrostatic Pressure (Mud Weight \(\;lbm/gal\)) Formula |
||
|
\( HP \;=\; 0.052 \cdot MW \cdot TVD \) (Hydrostatic Pressure) \( MW \;=\; \dfrac{ HP }{ 0.052 \cdot TVD }\) \( TVD \;=\; \dfrac{ HP }{ 0.052 \cdot MW }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( HP \) = Hydrostatic Pressure (psi) | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | - |
| \( MW \) = Mud Weight (ppg) | \(lbm\;/\;gal\) | - |
| \( TVD \) = True Vertical Dept | \(ft\) | - |
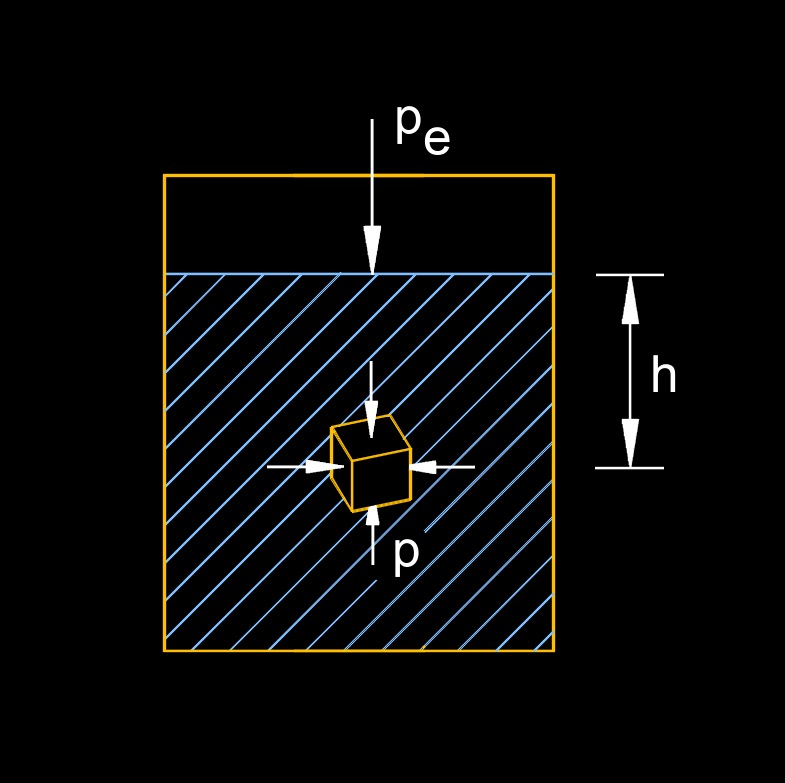 Hydrostatic pressure, abbreviated as HP, is the pressure a fluid exerts on an immersed object floating at a certain depth in a liquid. It is a concept in fluid mechanics and is related to the density of the fluid and the height of the fluid column.
Hydrostatic pressure, abbreviated as HP, is the pressure a fluid exerts on an immersed object floating at a certain depth in a liquid. It is a concept in fluid mechanics and is related to the density of the fluid and the height of the fluid column.
Key Points about Hydrostatic Pressure
- It increases with the depth of the fluid. The deeper you go in a fluid, the higher the hydrostatic pressure becomes.
- It depends on the density of the fluid. Denser fluids exert greater hydrostatic pressure for a given depth.
- It is directly proportional to the depth of the fluid. If you double the depth, you will double the hydrostatic pressure.
- Hydrostatic pressure is a scalar quantity, which means it has magnitude but no direction. It acts equally in all directions at a specific depth in a fluid.
Hydrostatic Pressure (Pressure Gradient \(\;psi/ft\)) Formula |
||
|
\( HP \;=\; PG \cdot TVD \) (Hydrostatic Pressure) \( PG \;=\; \dfrac{ HP }{ TVD }\) \( TVD \;=\; \dfrac{ HP }{ PG }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( HP \) = Hydrostatic Pressure (psi) | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | - |
| \( PG \) = Pressure Gradient | \(psi\;/\;ft\) | - |
| \( TVD \) = True Vertical Depth | \(ft\) | - |
Hydrostatic Pressure (Mud Weight \(\;lbf/ft^3\)) Formula |
||
|
\( HP \;=\; 0.006944 \cdot MW \cdot TVD \) (Hydrostatic Pressure) \( MW \;=\; \dfrac{ HP }{ 0.006944 \cdot TVD }\) \( TVD \;=\; \dfrac{ HP }{ 0.006944 \cdot MW} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( HP \) = Hydrostatic Pressure (psi) | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | - |
| \( MW \) = Mud Weight | \(lbf\;/\;ft^3\) | - |
| \( TVD \) = True Vertical Depth | \(ft\) | - |

