Solid Unit Weight
Solid Unit Weight Formula |
||
|
\( \gamma_s \;=\; \dfrac{ W_s }{ V_s }\) (Solid Unit Weight) \( W_s \;=\; \gamma_s \cdot V_s \) \( V_s \;=\; \dfrac{ W_s }{ \gamma_s }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \gamma_s \) (Greek symbol gamma) = solid unit weight | \(lbm\;/\;ft^3\) | \(N\;/\;m^3\) |
| \( W_s \) = weight of soil | \(lbf\) | \(N\) |
| \( V_s\) = volume of solid soil | \(ft^3\) | \(m^3\) |
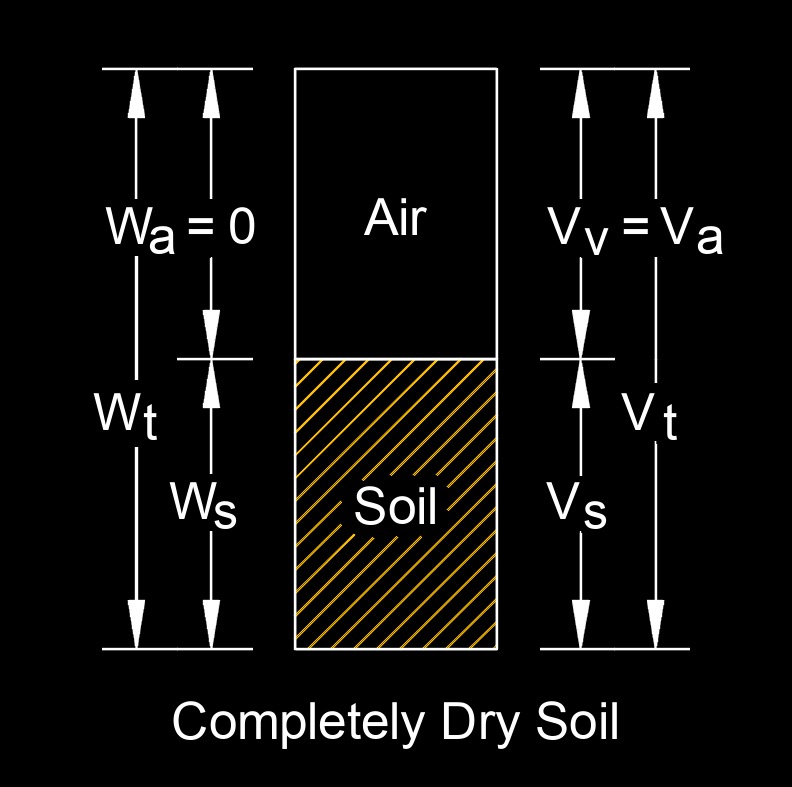 Solid unit weight, \( \gamma_s \) (Greek symbol gamma), also called bulk density or dry density, is the weight of a solid material per unit volume. It represents the density of a solid material without considering any voids or air spaces within it. The solid unit weight is calculated by dividing the total mass of the solid material by its total volume. The mass is typically determined by weighing the material, while the volume can be measured using various methods such as geometric measurements or displacement techniques. The solid unit weight can vary depending on the type of material being considered. Different materials have different densities due to variations in their composition, porosity, moisture content, and other factors.
Solid unit weight, \( \gamma_s \) (Greek symbol gamma), also called bulk density or dry density, is the weight of a solid material per unit volume. It represents the density of a solid material without considering any voids or air spaces within it. The solid unit weight is calculated by dividing the total mass of the solid material by its total volume. The mass is typically determined by weighing the material, while the volume can be measured using various methods such as geometric measurements or displacement techniques. The solid unit weight can vary depending on the type of material being considered. Different materials have different densities due to variations in their composition, porosity, moisture content, and other factors.
It's important to note that solid unit weight refers specifically to the weight of the solid material itself and does not take into account any voids or air spaces within the material. If the material contains voids or pores, such as in porous rocks or lightweight aggregates, the overall bulk density would be lower than the solid unit weight.

