Ball Valve Difference Between 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way
The difference between 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way ball valves lies in the number of ports (or openings) they have and how they direct fluid flow.
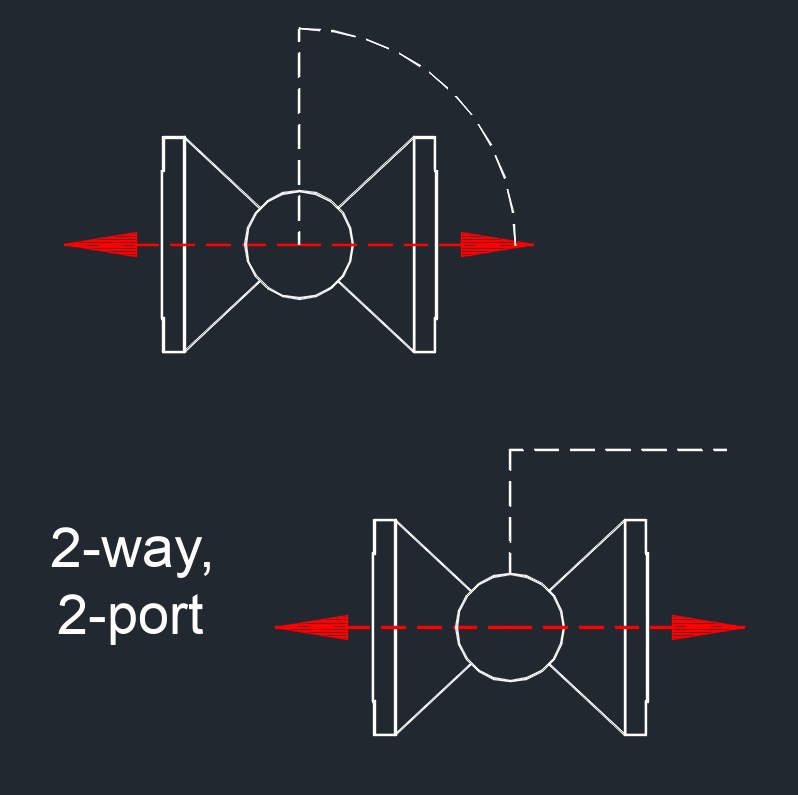 2-Way Ball Valve
2-Way Ball Valve
Ports - 2
Function - This valve has two ports, an inlet and an outlet. It’s the most common type of ball valve and is typically used to start, stop, or regulate flow in a straight line.
Operation - Turning the handle rotates the ball to either allow or block flow between the inlet and outlet.
Use Cases - Used in simple on/off applications, where fluid needs to go in one direction or be shut off.
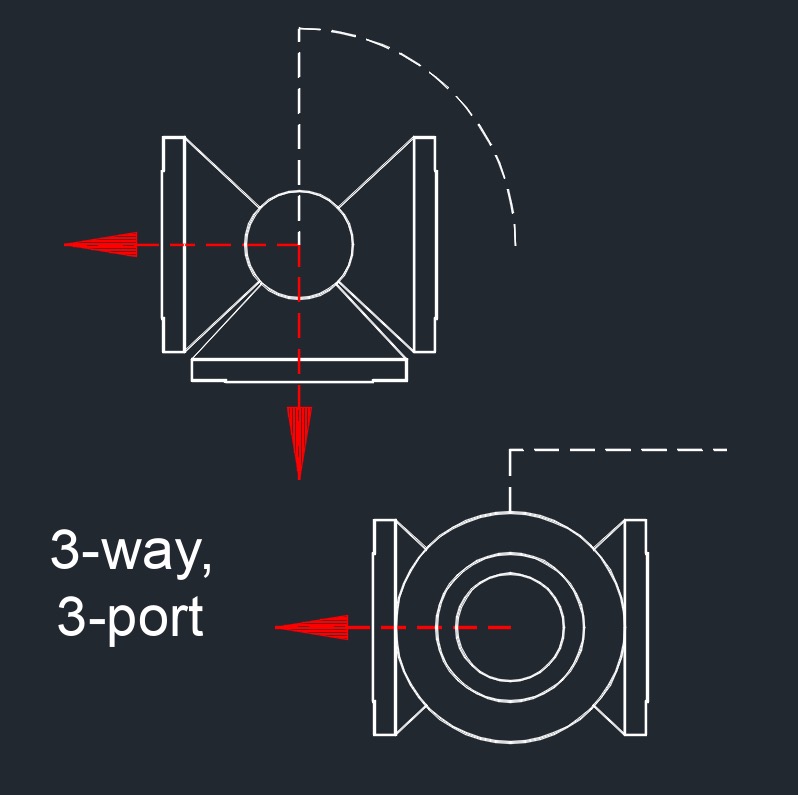 3-Way Ball Valve
3-Way Ball Valve
Ports - 3
Function - With three ports, this valve can direct flow between different paths, allowing for more complex flow control. The three ports are often arranged in an "L" or "T" configuration.
- L-Port - Directs flow between two of the three ports at a time, allowing for directional control (choosing between two output paths).
- T-Port - Can mix flow from multiple sources or divert flow to multiple destinations, allowing for even more flexibility.
Operation - By turning the handle, the ball can be positioned to allow flow through different combinations of the three ports.
Use Cases - Commonly used for diverting, mixing, or splitting flow, such as in heating systems or liquid transfer.
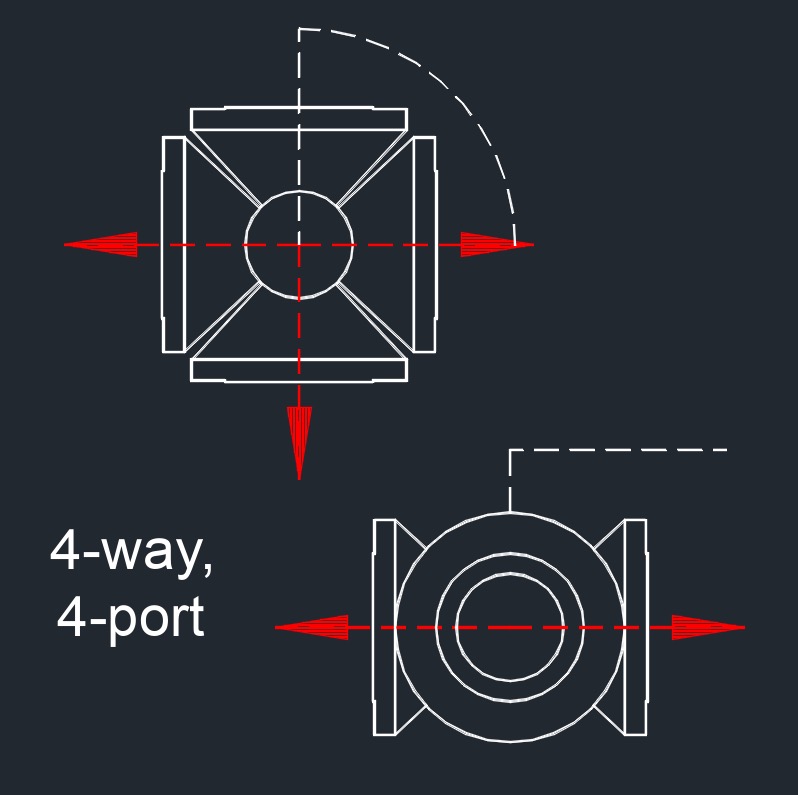 4-Way Ball Valve
4-Way Ball Valve
Ports - 4
Function - This valve has four ports, typically used to handle more complex flow requirements, such as reversing the direction of flow or distributing flow among multiple paths.
Operation - A 4-way valve generally uses an "X" pattern, allowing the operator to switch the direction or route of the flow.
Use Cases - Often used in systems requiring flow reversal or complex flow arrangements, like in hydraulic systems, heat exchangers, or certain process control systems.
Ball Valve Port Types
|
|||
| Type | Ports | Configuration | Typical Use |
| 2-way | 2 | Inlet and Outlet | Simple On/Off Flow Control |
| 3-way | 3 | L and T Ports | Flow direction Control, Mixing, and Diverting |
| 4-way | 4 | X Ports | Flow reversal or Complex Routing |

