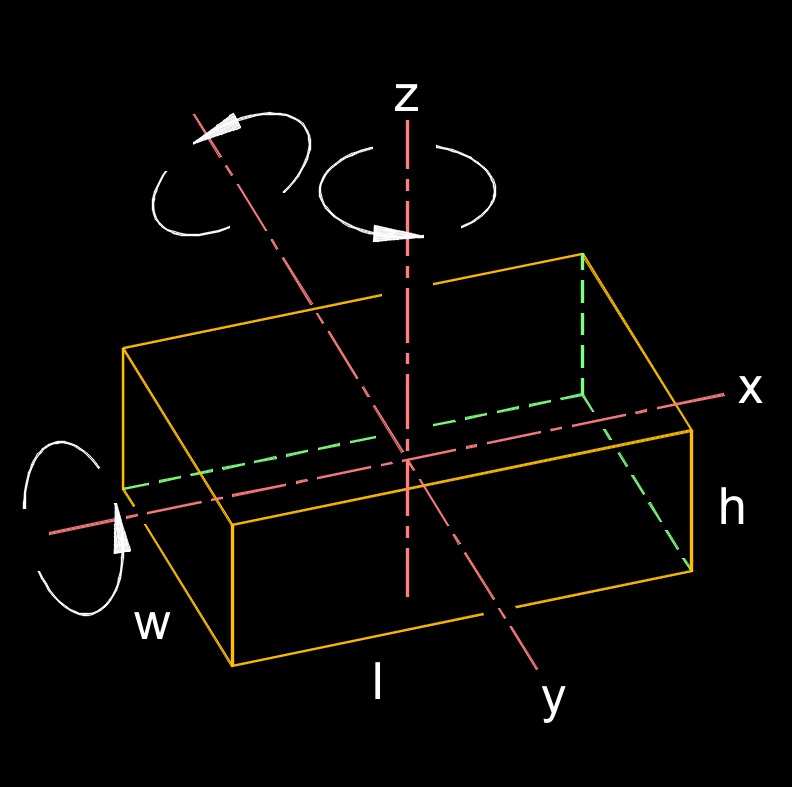
Moment of Inertia of a Cube
Moment of Inertia of a Cube Formulas |
||
|
\( I_h \;=\; \dfrac {1}{12} \cdot m \cdot ( l^2 + w^2 ) \) \( I_l \;=\; \dfrac {1}{12} \cdot m \cdot ( h^2 + w^2 ) \) \( I_w \;=\; \dfrac {1}{12} \cdot m \cdot ( l^2 + h^2 ) \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = Moment of Inertia | \(lbm \;/\; ft^2-sec\) | \(kg \;/\; m^2\) |
| \( h \) = Height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = Length | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( m \) = Mass | \( lbm \) | \( kg \) |
| \( w \) = Width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |