Instantaneous Angular Acceleration
Instantaneous Angular Acceleration Formula |
||
|
\( \alpha_i \;=\; \dfrac{ d\omega }{ dt }\) (Instantaneous Angular Acceleration) \( d\omega \;=\; \alpha_i \cdot dt \) \( \alpha_i \;=\; \dfrac{ d\omega }{ \alpha_i }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \alpha_i \) (Greek symbol alpha) = Instantaneous Angular Acceleration | \(deg \;/\; sec^2\) | \(rad \;/\; s^2\) |
| \( d\omega \) (Greek symbol omega) = Derivative in Angular Velocity | \(deg \;/\; sec\) | \(rad \;/\; s\) |
| \( dt \) = Derivative in Time | \(sec\) | \(s\) |
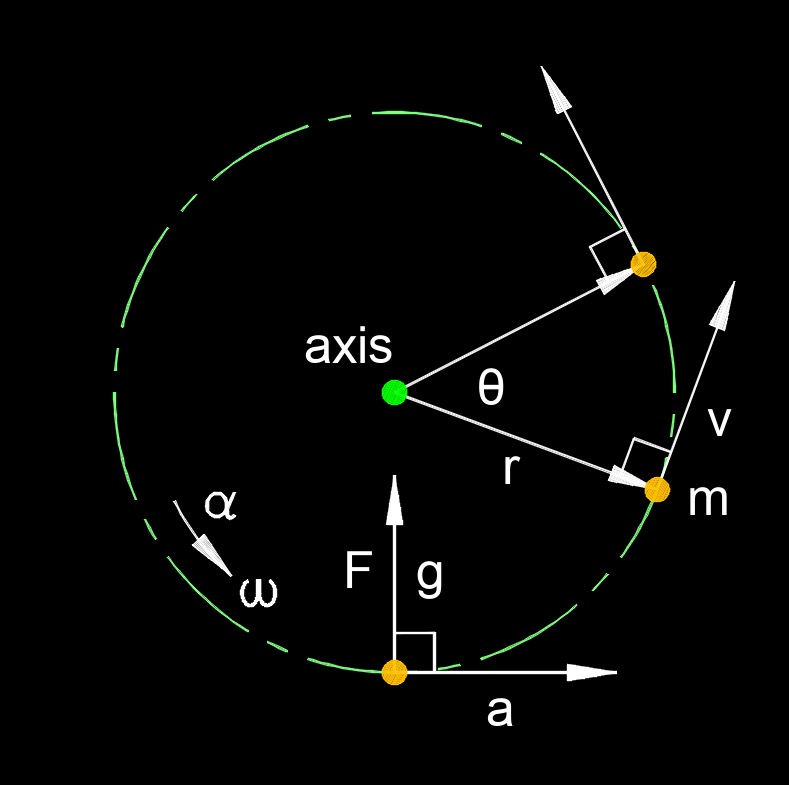 Instantaneous angular acceleration, abbreviated as \(\alpha_i\) (Greek symbol alpha), is the rate an object rotates in a circular path at a particular moment in time. Like instantaneous acceleration, the angular acceleration formula requires knowning the rate of change in the velocity. This can be measured by taking the derivative of the velocity as a function of time, or the second derivative of the position as a function of time.
Instantaneous angular acceleration, abbreviated as \(\alpha_i\) (Greek symbol alpha), is the rate an object rotates in a circular path at a particular moment in time. Like instantaneous acceleration, the angular acceleration formula requires knowning the rate of change in the velocity. This can be measured by taking the derivative of the velocity as a function of time, or the second derivative of the position as a function of time.

