Unequal I Beam
- See Article - Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
Area of a Unequal I Beam Formula |
||
| \( A \;=\; b\cdot s + h\cdot t + w\cdot s \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
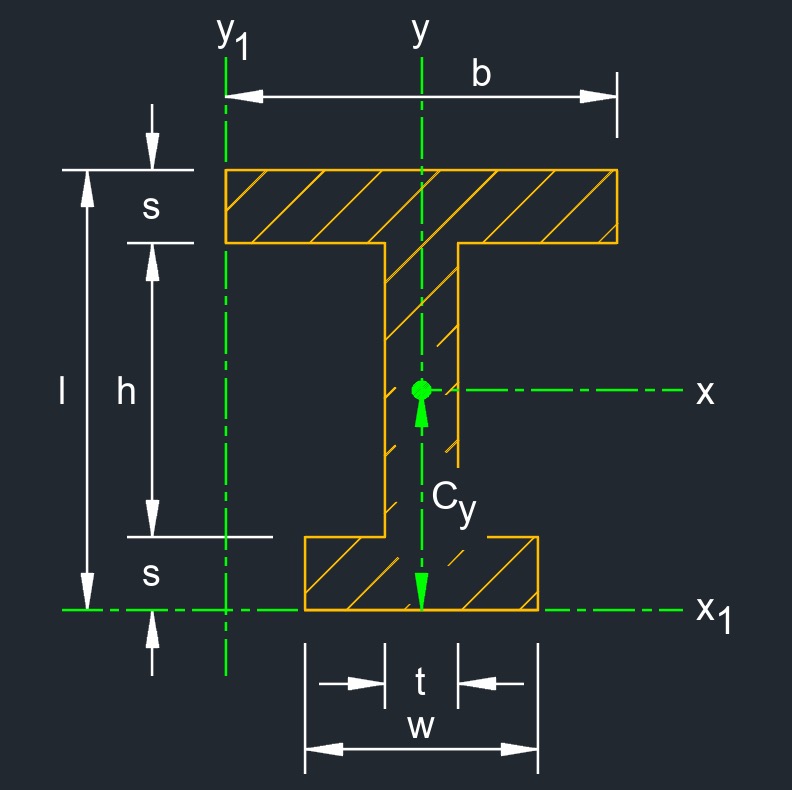 An unequal I-beam, also called unequal I-section or unequal beam, is a type of structural steel member with an I-shaped cross-sectional profile where the flanges (horizontal top and bottom parts) have different widths. This results in an asymmetrical shape where one flange is wider than the other. The unequal I-beam is designed to accommodate specific load and structural requirements where the loads are not symmetrically distributed. Unequal I-beams are commonly used in situations where the loads, spans, and other design considerations vary along the length of the beam. The wider flange typically corresponds to the side that experiences higher loads or needs to provide greater resistance to bending and shear forces.
An unequal I-beam, also called unequal I-section or unequal beam, is a type of structural steel member with an I-shaped cross-sectional profile where the flanges (horizontal top and bottom parts) have different widths. This results in an asymmetrical shape where one flange is wider than the other. The unequal I-beam is designed to accommodate specific load and structural requirements where the loads are not symmetrically distributed. Unequal I-beams are commonly used in situations where the loads, spans, and other design considerations vary along the length of the beam. The wider flange typically corresponds to the side that experiences higher loads or needs to provide greater resistance to bending and shear forces.
Distance from Centroid of a Unequal I Beam formulas |
||
|
\( C_x = 0 \) \( C_y \;=\; l - \dfrac{ 1 }{2\;A} \cdot \left[ t\cdot l^2 + s^2 \cdot \left( b - t \right) + s\cdot \left(w - t \right) \cdot \left(2\cdot l - s \right) \right] \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
 The design of an unequal I-beam involves calculating the dimensions of both flanges and the web (the vertical part connecting the flanges) to ensure that the beam can effectively handle the applied loads while maintaining structural stability. Engineering considerations such as bending moments, shear forces, and deflection are taken into account during the design process.
The design of an unequal I-beam involves calculating the dimensions of both flanges and the web (the vertical part connecting the flanges) to ensure that the beam can effectively handle the applied loads while maintaining structural stability. Engineering considerations such as bending moments, shear forces, and deflection are taken into account during the design process.

Elastic Section Modulus of a Unequal I Beam formulas |
||
|
\( S_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ I_x }{ C_y} \) \( S_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ I_y }{ C_x} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( S \) = elastic section modulus | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
Perimeter of a Unequal I Beam formula |
||
| \( P \;=\; 2 \cdot \left( w + b + l - t \right) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Radius of Gyration of a Unequal I Beam formulas |
||
|
\( k_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ \dfrac{1}{3} \cdot \left[ b \cdot \left(l - C_y \right)^3 + w \cdot C_{y}{^3} - \left(b - t \right) \cdot \left(l - C_y - s \right)^3 - \left(w - t \right) \cdot \left(C_y + s \right)^3 \right] }{ b\cdot s + h\cdot t + w\cdot s} \) \( k_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ \sqrt{ s \cdot \left(s^2 + 3 \right) \cdot \left(w - t \right)^3 + 2\cdot h\cdot t^3 } }{ 2\cdot \sqrt{6} \cdot \sqrt{w\cdot s + b\cdot s + h\cdot t } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = radius of gyration | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Second Moment of Area of a Unequal I Beam formulas |
||
|
\( I_x \;=\; \dfrac{1}{3} \cdot \left[ b \cdot \left(l - C_y \right)^3 + w \cdot C_{y}{^3} - \left(b - t \right) \left(l - C_y - s \right)^3 - \left(w - t \right) \left(C_y - s \right)^3 \right] \) \( I_y \;=\; 2 \cdot \left[ 2 \cdot \left( \dfrac{1}{96} \cdot s^3 \cdot \left(w - t \right)^3 + \dfrac{1}{32} \cdot s \cdot \left(w - t \right)^3 \right) + \dfrac{h\cdot t^3}{24} \right] \) \( I_z \;=\; l_x + I_y \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Torsional Constant of a Unequal I Beam formula |
||
| \( J \;=\; \dfrac{ w\cdot s^3 + b\cdot s^3 + \left( l - 5 \right) \cdot t^3 }{ 3 } \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( J \) = torsional constant | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
