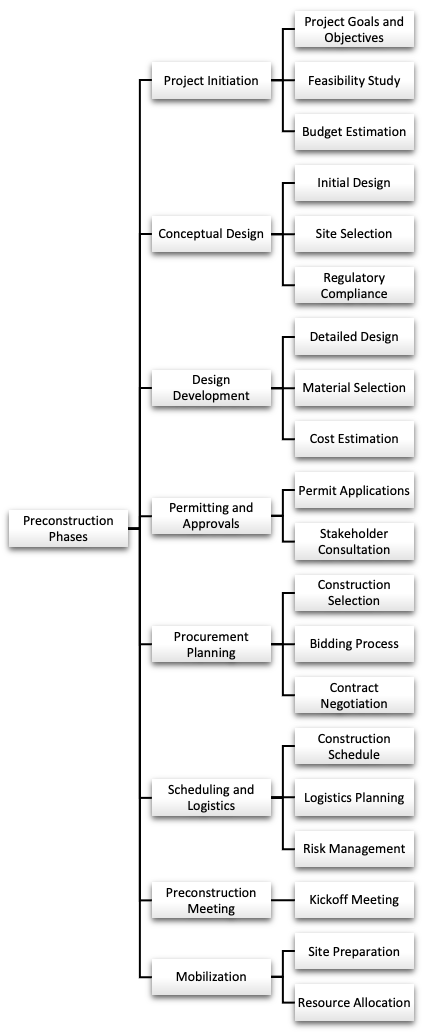
Preconstruction Phases
The preconstruction phase lays the groundwork for success or failure of the entire project. These phase are critical stage in the construction process where planning, coordination, and preparation take place before actual construction begins. The preconstruction phase lays the groundwork for success or failure of the entire project. The detail and accuracy of project information developed in this stage — specifications, budgets, estimates, bids, etc., can greatly simplify communication and streamline later work. During the planning process, close collaboration between the design team and the builders is essential to resolve potential issues before they impact the schedule and budget.
The main reason for preconstruction is to ensure that you’re doing the due diligence before you start building. Without preconstruction, you can lose money and people can get hurt. The construction phase also helps persuade your client about the feasibility of the project but it can also have the opposite effect if the project is too expensive or not viable for other reasons. This phase sets the foundation for a successful project and typically includes several key steps:
 Project Initiation and Feasibility Study
Project Initiation and Feasibility Study
- Project Goals and Objectives - Define the purpose, scope, and objectives of the project.
- Feasibility Study - Assess the technical, financial, and legal feasibility of the project. This may involve site analysis, environmental impact assessments, and risk evaluations.
- Budget Estimation - Develop a preliminary budget to determine the financial viability of the project.
Conceptual Design
- Initial Design - Create conceptual designs or sketches to visualize the project.
- Site Selection - Choose a suitable location for the project, considering factors like zoning, access, and environmental conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance - Ensure that the project complies with local building codes, zoning laws, and environmental regulations.
Design Development
- Detailed Design - Refine the conceptual design into more detailed plans, including architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems.
- Material Selection - Choose appropriate materials and construction methods.
- Cost Estimation - Prepare a more accurate cost estimate based on the detailed design.
Permitting and Approvals
- Permit Applications - Submit the necessary permit applications to local authorities for construction, environmental impact, zoning, and other regulatory approvals.
- Stakeholder Consultation - Engage with stakeholders, including community members, government agencies, and other interested parties, to address concerns and obtain approvals.
Procurement Planning
- Contractor Selection - Identify and prequalify contractors, subcontractors, and suppliers.
- Bidding Process - Prepare and issue bid documents, then evaluate and select the most qualified bidders.
- Contract Negotiation - Negotiate and finalize contracts with selected contractors and suppliers.
Scheduling and Logistics
- Construction Schedule - Develop a detailed project schedule outlining the timeline for each phase of construction.
- Logistics Planning - Plan for the delivery and storage of materials, equipment, and other resources on-site.
- Risk Management - Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
Preconstruction Meeting
- Kickoff Meeting - Hold a preconstruction meeting with all key stakeholders, including the project owner, design team, contractors, and suppliers, to review the project plan, schedule, and responsibilities.
Mobilization
- Site Preparation - Prepare the construction site, including clearing, grading, and setting up temporary facilities.
- Resource Allocation - Allocate resources, including labor, equipment, and materials, to ensure readiness for construction.
These phases are essential for minimizing risks, ensuring cost control, and setting clear expectations for all parties involved in the construction process.

