Cross
- See Article - Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
area of a Cross formula |
||
| \( A \;=\; l\cdot t + s \cdot \left( w - t \right) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \(A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
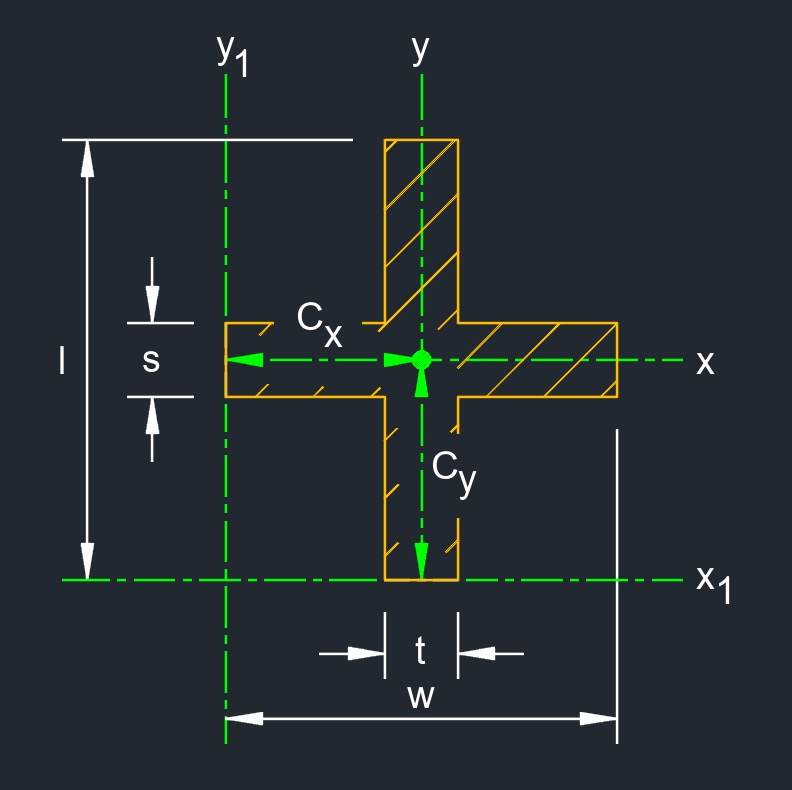 Cross is a type of structural beam with a cross shaped cross-sectional profile. The cross has a central vertical web and horizontal flanges at the center of the vertical web. The web and flange can have varying dimensions and thicknesses, depending on the specific load bearing requirements and design considerations of the structure.
Cross is a type of structural beam with a cross shaped cross-sectional profile. The cross has a central vertical web and horizontal flanges at the center of the vertical web. The web and flange can have varying dimensions and thicknesses, depending on the specific load bearing requirements and design considerations of the structure.

Distance from Centroid of a Cross formulas |
||
|
\( C_x \;=\; \dfrac{ w }{ 2 } \) \( C_y \;=\; \dfrac{ l }{ 2 } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Elastic Section Modulus of a Cross formulas |
||
|
\( S_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ I_{x} }{ C_{y} } \) \( S_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ I_{y} }{ C_{x} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( S \) = elastic section modulus | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |

Perimeter of a Cross formula |
||
| \( A \;=\; 2 \cdot \left( w + l \right) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Polar Moment of Inertia of a Cross formulas |
||
|
\( J_{z} \;=\; I_{x} + I_{y} \) \( J_{z1} \;=\; I_{x1} + I_{y1} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( J \) = torsional constant | \(\large{ in^4 }\) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \(\large{ in^4 }\) | \( mm^4 \) |

Radius of Gyration of a Cross formulas |
||
|
\( k_{x} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ t\cdot l^3 + s^3 \cdot \left( w - t \right) }{ 12 \cdot \left[ l\cdot t + s \cdot \left( w - t \right) \right] } } \) \( k_{y} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ s\cdot w^3 + t^3 \cdot \left( l - s \right) }{ 12 \cdot \left[ l\cdot t + s \cdot \left( w - t \right) \right] } } \) \( k_{z} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x}{^2} + k_{y}{^2} } \) \( k_{x1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac { I_{x1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{y1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac { I_{y1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{z1} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x1}{^2} + k_{y1}{^2} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \(\large{ k }\) = radius of gyration | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \(\large{ A }\) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \(\large{ l }\) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \(\large{ s }\) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \(\large{ t }\) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \(\large{ w }\) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Second Moment of Area of a Cross formulas |
||
|
\( I_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ t\cdot l^3 + s^3 \cdot \left( w - t \right) }{12} \) \( I_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ s\cdot w^3 + t^3 \cdot \left( l - s \right) }{12} \) \( I_{x1} \;=\; I_{x} + A\cdot C_{y}{^2} \) \( I_{y1} \;=\; I_{y} + A\cdot C_{x}{^2} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \(\large{ in }\) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \(\large{ in }\) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \(\large{ in }\) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \(\large{ in }\) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \(\large{ in }\) | \( mm \) |

