Electric Resistance
Electric Resistance Formula |
||
|
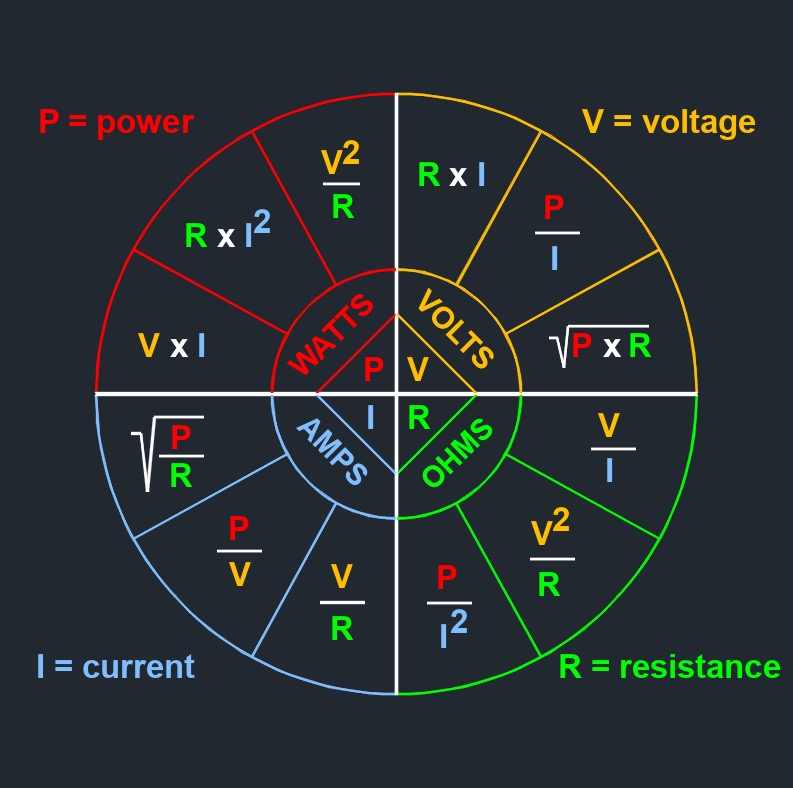
\( R \;=\; \dfrac{ V }{ I }\) (Electric Resistance) \( V \;=\; R \cdot I \) \( I \;=\;\dfrac{ V }{ R }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( R \) = Resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |
| \( V \) = Voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( I \) = Current | \(A\) | \(A\) |
 Electric resistance, abbreviated as \(R\), is a measure of how much an object or substance opposes the flow of electric current through it. In order to overcome the resistance and get the current to flow a higher voltage will be required. Resistance is measured in Ohms, represented by \(R\) and has a symbols \(\Omega\). The resistance of an object depends on its size, shape, material, and temperature.
Electric resistance, abbreviated as \(R\), is a measure of how much an object or substance opposes the flow of electric current through it. In order to overcome the resistance and get the current to flow a higher voltage will be required. Resistance is measured in Ohms, represented by \(R\) and has a symbols \(\Omega\). The resistance of an object depends on its size, shape, material, and temperature.
Electric Resistance Formula |
||
|
\( R \;=\; \dfrac{ V^2 }{ P }\) (Electric Resistance) \( V \;=\; \sqrt{ R \cdot P } \) \(\ P \;=\; \dfrac{ V^2 }{ R }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( R \) = Resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |
| \( V \) = Voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( P \) = Power | \(P\) | \(P\) |
 The resistance of a material can be calculated using Ohm's Law, which states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, and inversely proportional to its resistance.
The resistance of a material can be calculated using Ohm's Law, which states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, and inversely proportional to its resistance.
Electric Resistance Formula |
||
|
\( R \;=\; \dfrac{ P }{ I^2 }\) (Electric Resistance) \( P \;=\; I^2 \cdot R \) \( I \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ P }{ R } }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( R \) = Resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |
| \( P \) = Power | \(P\) | \(P\) |
| \( I \) = Current | \(A\) | \(A\) |


