Electric Current
Electric Current Formula |
||
|
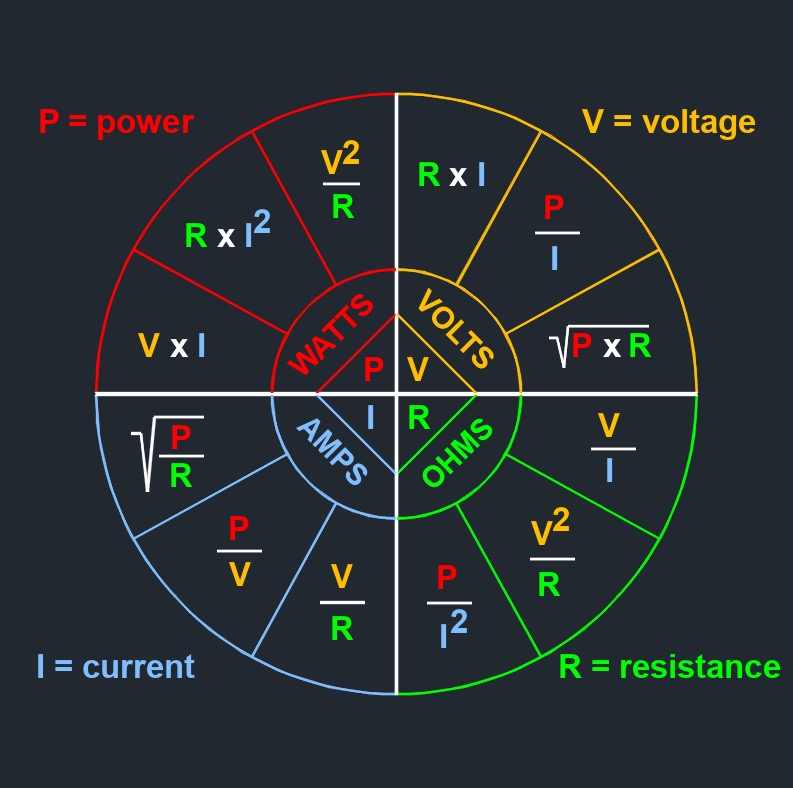
\( I \;=\; \dfrac{ V }{ R }\) (Electric Current) \( V \;=\; I \cdot R \) \( R \;=\; \dfrac{ V }{ I }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \(\ I \) = Current | \(A\) | \(A\) |
| \( V \) = Voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( R \) = Resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |
 Electric current, abbreviated as \(I\), is the flow of electric charge in a circuit or a conductor. The current flow is caused by the movement of electrons, which are negatively charged particles, through a conductor such as a wire. The rate of flow of electric charge (current) is typically determined by the voltage (potential difference) applied across the conductor and the resistance of the conductor. The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is described by Ohm's Law, which states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to its resistance.
Electric current, abbreviated as \(I\), is the flow of electric charge in a circuit or a conductor. The current flow is caused by the movement of electrons, which are negatively charged particles, through a conductor such as a wire. The rate of flow of electric charge (current) is typically determined by the voltage (potential difference) applied across the conductor and the resistance of the conductor. The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is described by Ohm's Law, which states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to its resistance.
Electric Current Formula |
||
|
\( I \;=\; \dfrac{ P }{ V }\) (Electric Current) \( P \;=\; I \cdot V \) \( V \;=\; \dfrac{ P }{ I }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = Current | \(A\) | \(A\) |
| \( P \) = Power | \(P\) | \(P\) |
| \( V \) = Voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |


Electric Current Formula |
||
|
\( I \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ P }{ R } }\) (Electric Current) \( P \;=\; I^2 \cdot R \) \( R \;=\; \dfrac{ P }{ I^2 }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = Current | \(A\) | \(A\) |
| \( P \) = Power | \(P\) | \(P\) |
| \( R \) = Resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |

Motor Current Formulas\(V\) = Voltage - \(I\) = Amps - \(PF\) = Power Factor - \(\eta\) = Efficiency - \(P\) = Power | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| To Find | Direct Current | Alternating Current | ||
| Single Phase | Two Phase Four Wire | Three Phase | ||
| Curremt | \(\large{\frac{ P }{ V \; \eta } }\) | \(\large{\frac{ P }{ V \; \eta \; PF } }\) | - | \(\large{\frac{ P }{ 1.732 \; V \; \eta \; PF } }\) |
Amps to Horsepower Formula |
||
|
\( HP \;=\; \dfrac{ I \cdot V \cdot \eta \cdot PF }{ 746 }\) (Amps to Horsepower) \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ HP \cdot 746 }{ V \cdot \eta \cdot PF }\) \( V \;=\; \dfrac{ HP \cdot 746 }{ I \cdot \eta \cdot PF } \) \( \eta \;=\; \dfrac{ HP \cdot 746 }{ I \cdot V \cdot PF }\) \( PF \;=\; \dfrac{ HP \cdot 746 }{ I \cdot V \cdot \eta }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( HP \) = Horsepower | \(lbf-ft\;/\;sec\) | \(C\;/\;s\) |
| \( I \) = Amps | \(A\) | \(A\) |
| \( V \) = Voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( \eta \) (Greek symbol eta) = Efficiency | \(dimensionless\) | \(dimensionless\) |
| \( PF \) = Power Factor | \(dimensionless\) | \(dimensionless\) |
Conversion Formulas
|
||
|
KVA to Amps Formulas \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ kVA }{ V} \cdot 1000 \) (Single Phase) \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ kVA \cdot 1000 }{ \sqrt{3} \cdot V }\) (Three Phase - Line to Line) \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ kVA \cdot 1000 }{ 3 \cdot V }\) (Three Phase - Line to Neutral) |
||
|
AMPS to KVA Formulas \( kVA \;=\; \dfrac{ V \cdot I }{ 1000 }\) (Single Phase) \( kVA \;=\; \sqrt{3} \cdot V \cdot I \) (Three Phase - Line to Line) \( kVA \;=\; 3 \cdot V \cdot I \) (Three Phase - Line to Neutral) |
||
|
Kilowatt-hours to Amp-hours Formula \( Ah \;=\; \dfrac{ kWh \cdot 1000 }{ V }\) |
