Reservoir Fluid Permeability
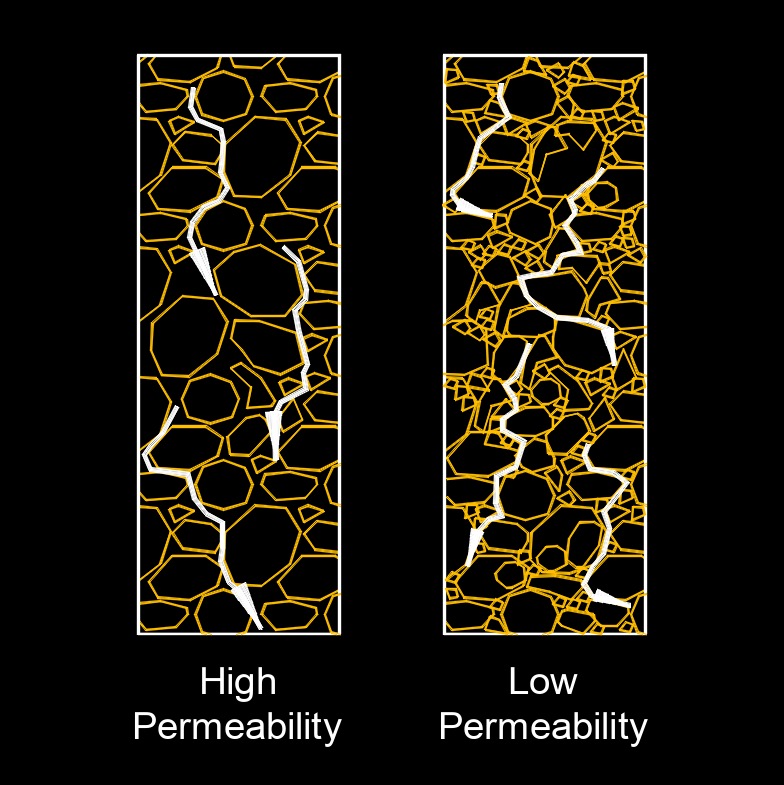 Reservoir fluid permeability is a measure of the ability of a porous material (such as rock in a reservoir) to allow fluids (such as oil, gas, or water) to pass through it. It is used in petroleum engineering and hydrogeology for understanding and predicting fluid flow in reservoirs. The higher the permeability, the more easily fluids can flow through the rock. Permeability is usually determined through laboratory measurements on core samples or inferred from well tests and log data. Understanding permeability is essential for efficient reservoir management and for optimizing the extraction of hydrocarbons.
Reservoir fluid permeability is a measure of the ability of a porous material (such as rock in a reservoir) to allow fluids (such as oil, gas, or water) to pass through it. It is used in petroleum engineering and hydrogeology for understanding and predicting fluid flow in reservoirs. The higher the permeability, the more easily fluids can flow through the rock. Permeability is usually determined through laboratory measurements on core samples or inferred from well tests and log data. Understanding permeability is essential for efficient reservoir management and for optimizing the extraction of hydrocarbons.
Factors that Affect Permeability
Pore Size and Distribution - Larger and more well connected pores typically result in higher permeability.
Rock Type - Different rock types (sandstone, limestone) have different inherent permeability properties.
Presence of Fractures - Natural or artificial fractures can significantly increase permeability.
Fluid Properties - The viscosity and density of the fluid can also influence the effective permeability.
Reservoir Fluid Permeability FORMULA |
||
|
\( k \;=\; \dfrac{ \eta \cdot V \cdot P_l }{ A_p \cdot p_g \cdot t }\) (Reservoir Fluid Permeability) \( \eta \;=\; \dfrac{ k \cdot A_p \cdot p_g \cdot t }{ V \cdot P_l }\) \( V \;=\; \dfrac{ k \cdot A_p \cdot p_g \cdot t }{ \eta \cdot P_l }\) \( P_l \;=\; \dfrac{ k \cdot A_p \cdot p_g \cdot t }{ \eta \cdot V }\) \( A_p \;=\; \dfrac{ \eta \cdot V \cdot P_l }{ k \cdot p_g \cdot t }\) \( p_g \;=\; \dfrac{ \eta \cdot V \cdot P_l }{ k \cdot A_p \cdot t }\) \( t \;=\; \dfrac{ \eta \cdot V \cdot P_l }{ k \cdot A_p \cdot p_g }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) (Greek symbol mu) = Medium Permeability | \(ft^2\) | \(m^2\) |
| \( \eta \) (Greek symbol eta) = Viscosity of Liquid Phase | \(lbf - sec \;/\; ft^2\) | \( Pa - s \) |
| \( V \) = Liquid Volume that Flows in Time - Burette Volume | \(in^3\) | \(cm^3\) |
| \( P_l \) = Plug Length | \(in\) | \(cm\) |
| \( A_p \) = Plug Open Flow Area | \(in^2\) | \(cm^2\) |
| \( p_g \) = Pressure Value from Pressure Gauge (psi) | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( t \) = Flow Time | \(sec\) | \(s\) |


