Geometry
Mathematics, Glossary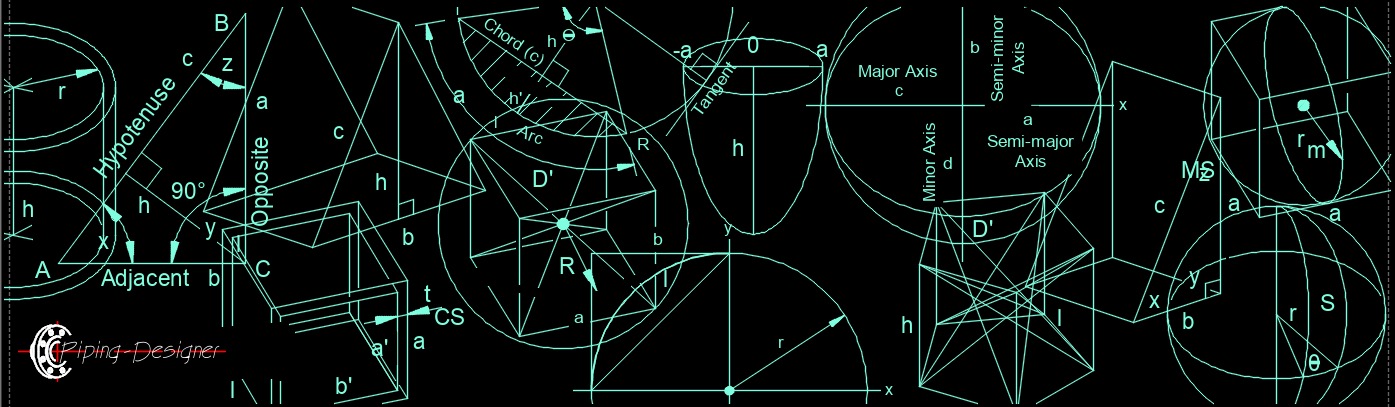 Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, positions, and the relationships between them. It is concerned with the study of points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids, and how they can be represented, measured, and manipulated. These relationships can be expressed in plane geometry, two-dimensional figures and solid geometry, three-dimensional figures. From the moment you get up in the morning geometry comes into play with everything in your environment, architecture, art, engineering, the floor you walk on, furnature, and so on.
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, positions, and the relationships between them. It is concerned with the study of points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids, and how they can be represented, measured, and manipulated. These relationships can be expressed in plane geometry, two-dimensional figures and solid geometry, three-dimensional figures. From the moment you get up in the morning geometry comes into play with everything in your environment, architecture, art, engineering, the floor you walk on, furnature, and so on.
Geometry has many practical applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, physics, and computer graphics. It is also used extensively in pure mathematics research, where it provides a foundation for other areas of mathematics. Geometry has many practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and computer graphics, where it is used to design and model physical structures and objects. It is also used in fields such as physics and astronomy, where it is used to model and analyze the behavior of physical systems.
Plane Geometry / Solid Geometry
Basic Geometrical Items
- Points, Line Segment, Line, Intersecting Lines, Parallel Lines, Ray, Angle, Curve, Circle, Ellipse, Polygon
Geometry Types
- Affine Geometry, Algebraic Geometry, Algebraic Topology, Analytic Geometry, Convex Geometry, Differential Geometry, Differential Topology, Discrete Geometry, Euclidean Geometry, General Topology, Geometric Topology, Non-Euclidean Geometry, Projective Geometry, Topology
- Euclidean Geometry - Plane Geometry, Solid Geometry
Geometry Glossary
A
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Abscissa - The distance along the x-coordinate axis to a point on the cordinate plane.
- Acute Angle - An angle that is more than 0° but less than 90°.
- Adjacent Angle - Two angles on a plane having the same vertex and a common line.
- Adjacent Side - Next to the angle in a general triangle or next to the angle of the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
- Algorithm - A procedure used to solve a problem or a desired result.
- Altitude - The shortest distance from the base to the apex.
- Analytic Geometry (Coordinate Geometry) - The study of coordinates in a two or three dimensional space.
- Angle - Two rays sharing a common point.
- Angle Bisector - A line that divides an angle into two equal angles.
- Angle of Depression - An angle measured below a particular reference point.
- Angle of Elevation - An angle measured above a particular reference point.
- Angle Types - In order of ascending: Acute angle, Right angle, Obtuce angle, Straight angle, Reflex angle
- Antipodal Point - Two points directly opposite each other on a sphere.
- Apex - The vertex at the tip of a cone or pyramid.
- Apothem - A line segment from the center of a regular polygon to the mid point of a side.
- Arc Length - The distance along the arc or the circumference of a circle or any curve.
- Area - The inside space of a figure.
- Area Differential - The difference between an expanded or reduced area of an object.
- Arm of an Angle - Either of the two arms making up an angle.
- Ascending Order - Arranged from smallest to largest.
- Asymmetric (Asymmetrical) - Not symmetric.
- Asymptote - A line that constantly approcches a curved line but never reaches it at any distance.
- Axes - A horizontal and vertical number lines that intersect at a zero point location.
- Axiom - A statement accepted as true without proof.
- Axis - A referencr line.
- Axis of Symmetry - A line through a shape so that each side is a mirror image.
- Azimith - The direction of a line related to north.
B
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Base - The bottom of a figure in either plane or solid geometry. If the bottom and top are parallel then either can be called base.
- Base Area - The base surface area of a solid figure.
- Bearing - An angle in degrees measured clockwise from north.
- Bisect - Divide into two congruent (equal) parts.
C
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Cardinality - The number of objects in a set. It can either be finite set or infinite set.
- Center of a Circle - A point at a fixed equal distance from all points of the circumference of a circle.
- Center of Rotation - A point that does not move in a rotation.
- Central Angle - An angle in a circle with the vertex at the circle's center.
- Centroid - The center of a plane or mass.
- Cevian - A line or line segment that extends from a vertex of a triangle to the opposite side.
- Chord - A line segment on the interior of a circle.
- Circle - All points are at a fixed equal distance from a center point.
- Circumcenter - The point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the sides.
- Circumscribed Circle (Circumcircle, Outradius) - A circle that passes through all the vertices of a two-dimensional figure.
- Circumscribed (Outside) - A circle that touches every vertex.
- Circumscribed Geometry - The study of algorithms in terms of geometry.
- Circumscribed Sphere - A polyhedron is a sphere that contains the polyhedron and touches each of the ployhedron's vertices.
- Circumference - The outside of a circle or a complete circular arc.
- Collinear - When three or more points lie on a straight line.
- Collinear Points - Points that lie on the same line.
- Complememt of an Angle - Acute angle A (25°) + B = 90°. Complement of 25° is 65°.
- Complememtary Angle - Angles that add up to 90°.
- Composite Figure - One figure made up from two or more geometric figures.
- Compute - To figure out or evaluate.
- Concave - An internal angle is greater than 180°.
- Concentric - Like geometric figures that share a common center.
- Conclusion - The then... part of a conditional statement to be proved.
- Concurrent - Lines or curves that all intersect at a single point.
- Conditional Statement - An if... then... statement.
- Cone - A three-dimensional figure having one circular base tapering to an apex.
- Congruent - All sides having the same lengths and angles measure the same.
- Congruent Lines - Line segments having the same length but not necessarily the same angle.
- Conjecture - A statement that might be true, but is not proven.
- Conjugate Angle - Angles that add up to 360°.
- Conic Section - A section on any plane through a circle, ellipse, hyperbola, and parabola.
- Converse - A conditional statement (if... then...) made be switched with parts of another statement.
- Convex - No internal angle is greater than 180°.
- Coordinate - Any point on a plane.
- Coordinate Plane - A plane having a horizontal and vertical axis number line intersecting at the origin.
- Coplanar - Lines and points lying on the same plane.
- Coplanar Points - Points that lying on the same plane.
- Corollary - A theroem that follows on from another theroem.
- Cross Section - A three-dimensional solid figure that is intersected by a plane creating a two-dimensional figure.
- Cylinder - A three-dimensional figure having two circular parallel congruent bases.
D
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Degree - When an angle goes all the way around a circle it is divided equal to 360 degrees.
- Descending Order - Arranged from largest to smallest.
- Differential - Deals with smooth curvy objects and their properties.
- Diagonal - A line from one vertices to another that is non adjacent.
- Diameter - The distance across the center of a circle.
- Directrix - The path followed by a point or line when moving.
- Distance Between Two Points - Using two given coordinate points.
E
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Edge - A line where two or more vertices come together.
- Elastic Section Modulus (S) - A single parameter that measures a cross-section's strength in bending.
- Ellipse - A two-dimensional figure with a conic section or a stretched circle.
- Ellipsoid - A three-dimensional figure sphere like surface for which all cross sections are ellipses.
- Empty set - A set with no objects.
- Equilateral - All the sides of a polygon are the same length.
- Euclidean Geometry - The study of plane and solid figures.
- Euclid's Postulates - Euclid's five postulates are basic rules that govern geometric figures.
- Euler line - The centroid, circumcenter, and orthocenter of any triangle always lies on a straight line.
- Euler's Constant - Also called Euler Number, is a mathematical constant.
- Expression - Any combination of numbers and variables used to create a mathematical expression or formula.
- Exterior Angle - An angle on the exterior of two rays of a plane figure.
F
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Face - Any flat surface of a solid figure.
- Foci - Two fixed points on the interior of an ellipse used to define the curve.
- Focus - The points that construct a conic section.
- Full Angle - An angle that measures 360°.
G
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Geodesic - The shortest distance between two points of a line segment on a sphere or other curved surface.
- Geometric Figure - Any set of points on a plane or in space (arc, circle, line, plane figure, point, solid figure, etc.).
- Geometric Properties - Characteristics of geometric figures supported by these statements: definations, postulates, theorems, and corollaries.
- Generatrix - A point or line when moved along a certain path creates a new shape.
- Geometry Postulate - A postulate is a statement that is assumed true without proof.
- Geometry Theorem - A theorem is a true statement that can be proven.
- Golden Angle - The smaller of two angles created by sectioning the circumference of a circle according to the golder ratio.
- Golden Ratio (Divine Porportion, Golden Mean, Golden Section) - A mathematical ratio commonly found in nature and design. \(\large{ \varphi=1 : 1.6180339887... }\)
- Golden Rectangle - A rectangle that can be divided into a square and a rectangle that is similar to the original rectangle.
- Great Circle - The intersection of a sphere and a plane that contains the center of the sphere.
H
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Heron's Formula -
- Hexahedron - Any polyhedron with six faces.
- Horizontal - Parallel to a flat or level surface of the earth.
- Horizontal Line - A line extending left or right but not up or down.
- Hyporenuse - The side of right triangle opposite the right angle, which is the longest side.
- Hypothesis - A tentative statement that might be true. Identify the problem, research the problem, then make a proposed solution to the problem.
- Pythagorean Theorem - The hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the other two sides in a right triangle.
I
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Incenter - The point where the angle bisectors meet for a regular polygon or triangle.
- Incircle - A circle that touches all lines of a figure.
- Initial Side of an Angle - The inside of a ray of an x-axis of an angle.
- Inradius - The radius of a inscribed circle.
- Inscribed (Inside) - A sphere that touches the center of every faces.
- Inscribed Angle - An angle inside a circle with its vertex in the circle.
- Inscribed Circle - The largest circle possible that can fit on the inside of a two-dimensional figure.
- Inscribed Sphere (Insphere) - A convex polyhedron is a sphere that is contained within the polyhedron and tangent to each of the polyhedron's faces.
- Inside Angle - An angle on the interior of two rays of a plane figure.
- Interior Angle - An angle on the interior of two rays of a plane figure.
- Intersecting Lines - Lines that have only point in common.
- Interval - The region or space between two defined values.
- Inverse Statement - Disaliow both the hypohesis and conclusion of the origional statement.
- Isometric - A representation of a three-dimensional figure where all three sides can be seen.
J
K
L
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Lateral Surface Area (Lateral Surface) - The surface area of a solid figure excluding the area bases of the solid figure, just the sides.
- Line - A straight path connecting two points.
- Line Segment (Segment) - All points bertween two points.
- Line Segment Bisector - A line or line segment that cuts another line segment into two equal parts.
- Linear Pair - An interior angle combined with an exterior angle sharing the same side.
- Locus - A set of points that form a geometric figure or graph.
- Long Diagonal - Always crosses the center point of the figure.
M
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Major Arc - The longest of two arcs of a circle or ellipse.
- Major Axis - The longest axis of a circle or ellipse.
- Mean - Another word for average.
- Median - The middle number in a data set.
- Median of a Trapezoid - A line segment from the midpoint of the legs of a trapezoid.
- Median of a Triangle - A line segment from a vertex (corner point) to the midpoint of the opposite side.
- Menelaus's Theorem - The way two cevians of a triangle divide each other and two of the triangle's sides.
- Midpoint - A point on a line segment that divides the segment into two congruent segments.
- Midsphere - A polyhedron is a sphere that is tangent to every edge of the polyhedron.
- Minor Arc - The shorter of two arcs of a circle or ellipse.
- Minor Axis - Always the shortest axis of a circle or ellipse.
- Mixed Number - A number written as a whole number and a fraction.
N
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Non-collinear - Points that do not all lie on the same line.
- Non-collinear Points - Points that do not all lie on the same line.
- Non-coplanar Points - Points that do not all lie on the same plane.
- Non-polyhedron - Has a solid with curved edges or sides.
- Normal - In math it means to be at right angles.
O
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Oblique - Tilted at an angle, not horizontal or vertical.
- Oblique Cone - A three-dimensional figure with the apex not alligned above the center at 90° to the base.
- Oblique Cylinder - A three-dimensional figure with both bases not alligned above each other and the center not at 90° to the other base center.
- Oblique Line - A line not horizontal or vertical.
- Oblique Prism - A three-dimensional figure with both bases not alligned above each other and the center not at 90° to the other base center.
- Oblique Pyramid - A three-dimensional figure with the apex not alligned above the center at 90° to the base.
- Obtuse Angle - An angle that is more than 90° but less than 180°.
- Opposite Angle (Vertical Angle) - The opposite angles when two lines intersect.
- Opposite Leg - The leg of a right triangles opposite from the reference angle.
- Ordinate - The distance along the y-coordinate axis to a point on the cordinate plane.
- Origin - The intersection point (0, 0) of horizontal and vertical number lines.
- Outlier - A data point in a data set that is far outside of an established pattern.
P
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Parallel Lines - Two lines that do not intersect.
- Parallel Planes - Two planes that do not intersect.
- Perimeter - The sum of the lengths of all sides of a plane figure.
- Perpendicular - An angle that measures 90°.
- Perpendicular Bisector - A line perpendicular to a segment passing through the segment's midpoint.
- Pi - \(\large{ \pi=3.1415926535 ... }\)
- Plane - An infinate expanse of points in two directions.
- Plane Geometry - A two dimensional figure, also called planar geometry, with edges. The edges are line segments or edges and curve segments or arcs, all lying on a flat plane.
- Plastic Section Modulus (Z) - Used to determine the capacity of a member to resist bending when the material has yielded and is behaving plastically. It is related to the plastic moment capacity of a section and is typically used in conjunction with the yield strength of the material to determine the full plastic moment.
- Platonic Solid - A three-dimensional figure where each face is a regular polygon. There are five, cube, dodecahedron, icosahedron, octahedron, and tetrahedron.
- Point - A single location or the intersection of two lines.
- Polygon - A closed plane figure for which all edges are line segments and not necessarly congruent.
- Polyhedron - A three-dimensional figure that is a solid with no curved edges or sides.
- Proportional - Having a constant ratio.
- Precision - The level of detail in a number or estimate.
- Prism - A three-dimensional figure with two parallel ends that are exactly the same.
- Pyramid - A three-dimensional figure that is a polyhedron with a polygonal base and lateral faces that taper to an apex.
- Pythagorean Theorem - The hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the other two sides in a right triangle.
Q
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Quadrilateral - A polygon with four sides.
- Quadrants - Four sections divided by the x and y axis on the x-y plane. Quadrant I is the upper right, Quadrant II is the upper left, Quadrant III is the lower left, and Quadrant IV is the lower right,
- Quotient - The answer after dividing one number or expression by another.
R
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Radian - There are 360 degrees in a circle and 2 \(\pi\) radians in a circle.
- Radical - A square root.
- Radius - A line segment between the center point and a point on a circle or sphere.
-
Radius of Gyration - Used in physics and engineering to describe how the mass of an object is distributed around its axis of rotation. It essentially represents the distance from the axis where the entire mass of the object can be assumed to be concentrated, while maintaining the same moment of inertia. In simpler terms, it indicates how "spread out" or "compact" an object is in relation to rotation.
- Range - The difference between the largest and smallest nunbers in a data set.
- Ray - A line starting at a point and extending infinitely in one direction.
- Rectangular Angle - Two rectangles with different lengths that intersect at a 90° angle at one end each.
- Reference Angle - The smallest angle that the terminal side of a given angle makes with the x-axes.
- Reflection of a Line Section - Every point on a line segment appears an equal distance on the other side of a line.
- Reflex Angle - An angle that is more than 180° but less than 360°.
- Right Angle - An angle that is 90°.
S
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Sagitta - The perpendicular from the midpoint of the arc's chord to the arc itself.
- Scale Factor - The ratio of any two corresponding lengths in two similar geometric figures.
- Scalene - If no two sides have the same length.
- Secant Line - A line that passes through at least two points on a curve.
- Section Modulus - Geometric properties for a given cross-section used in design of beams or flexable members.
- Sector of a Circle - A sector is a fraction of the area of a circle with a radius on each side and an arc.
- Segment (Line Segment) - All points bertween two points.
- Segment of a Circle - An interior part of a circle bound by a chord and an arc.
- Semi-major Axis - Half of the longest axis of a circle or ellipse.
- Semi-minor Axis - Half of the shortest axis of a circle or ellipse.
- Semicircle - Half of a circle.
- Semiperimeter - One half of the perimeter.
- Set - A defined group of objects.
- Side - Any line segment of an figure.
- Similar - Identical in shape, but not necessarily the same size.
- Skew Lines - Lines that are not in the same plane and do not intersect.
- Skewed Data - Not symmetric around the mean and the data (graph) has a long tail on one or the other.
- Short Diagonal - Does not cross the center point of the figure.
- Solid - A three dimensional figure with height, width, and depth.
- Solid Geometry - A three-dimensional figure with connecting edges on multiple planes. The surface of each two-dimensional plane is called a face.
- Straight Angle - An angle that is 180° or pi radians.
- Standard Position of an Angle - An angle where its vertex is located at the origin and one ray is on the positive x-axis. One side of the angle is always fixed along the positive x-axis.
- Subtend - To be opposite to and extend from one side to the other of a hypotenuse.
- Supplement of an Angle - Any angle A between 0° and 180°. A is 180° - A
- Supplementary Angles - Two angles that sum to 180°.
- Surface - A three-dimensional figure excluding internal points.
- Surface Area - The total area of all the surfaces of a three dimensional figure, bottom, top, and sides.
- Symmetric (Aymmetrical) - When two or more parts are congruent or identical to each other.
- Symmetry - When one shape becomes exactly like another if you flip or turn it.
T
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Tangent - A line that touches a curve at just one point such that it is perpendicular to a radius line of the curve.
- Terminal Side of an Angle - The inside of a ray of an angle oposite the x-axis initial side.
- Tessellation - A pattern made of identical shapes.
- Tetrahedron - Known as triangular pyramid.
- Three-dimensional - A figure with height, width, and depth.
- Three-dimensional Coordinates - A system for locating points in three dimension (height, width, and depth) using x, y, z coordinates.
- Torsional Constant (K, J) - A property of a structural member that quantifies its resistance to twisting (torsion). It relates the applied torque to the resulting angle of twist in the member. A higher torsional constant indicates greater resistance to twisting
- Triangulation - By observing the direction and or distance to an object from two or more observation points, the position of an object can be located.
- Translation - Moving a shape to a new location with no other changes.
- Transversal - A line that intersects at least two or more lines.
- Triangle Exterior Angle Theorm - An exteroir angle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles.
- Triangle Inequality Theorem - Any side of a triangle is always shorter than the sum of the other two sides.
- Triangle Inequality Theorem Converse - A triangle cannot be constructed from three line segments if any of them is longer than the sum of the other two.
- Two-dimensional - A flat figure on a single plane represented by 0, 0.
U
V
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- Variable - A symbol used to represent a number that we do not know yet.
- Vector - A quantity with both magnitude and direction.
- Vertex - A point where two or more curves, edges, or lines meet.
- Vertical - Perpendicular to horizontal or straight up or down.
- Vertical Angle (Opposite Angle) - The opposite angles when two lines intersect.
- Vertical Line - A line at a right angle to the horizon.
- Vertices - Plural of vertex.
- Volume - The amount of space in an solid figure.
W
X
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- x-axis - A horizontal number line on a grid on a two-dimensional plane.
- x-coordinate - The first element \(\large{ x }\) in an ordered set \(\large{ \left( x, y \right) }\) on a two-dimensional plane.
Y
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- y-axis - A vertical number line on a grid on a two-dimensional plane.
- y-coordinate - The second element \(\large{ y }\) in an ordered set \(\large{ \left( x, y \right) }\) on a two-dimensional plane.
Z
- A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
- z-axis - You could say depth number line on a grid on a three-dimensional plane.
- z-coordinate - The third element \(\large{ z }\) in an ordered set \(\large{ \left( x, y, z \right) }\) on a three-dimensional plane.

