Semi-major and Semi-minor Axis of an Ellipse
Semi-major and Semi-minor Axis of an Ellipse formula |
||
|
\( a \;=\; \dfrac{ l }{ 1 - \epsilon^2 }\) \( b \;=\; a \cdot \sqrt {1 - \epsilon^2} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( a \) = Length Semi-major Axis | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( b \) = Length Semi-minor Axis | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = Semi-latus Rectum | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \epsilon \) (Greek symbol epsilon) = Eccentricity | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
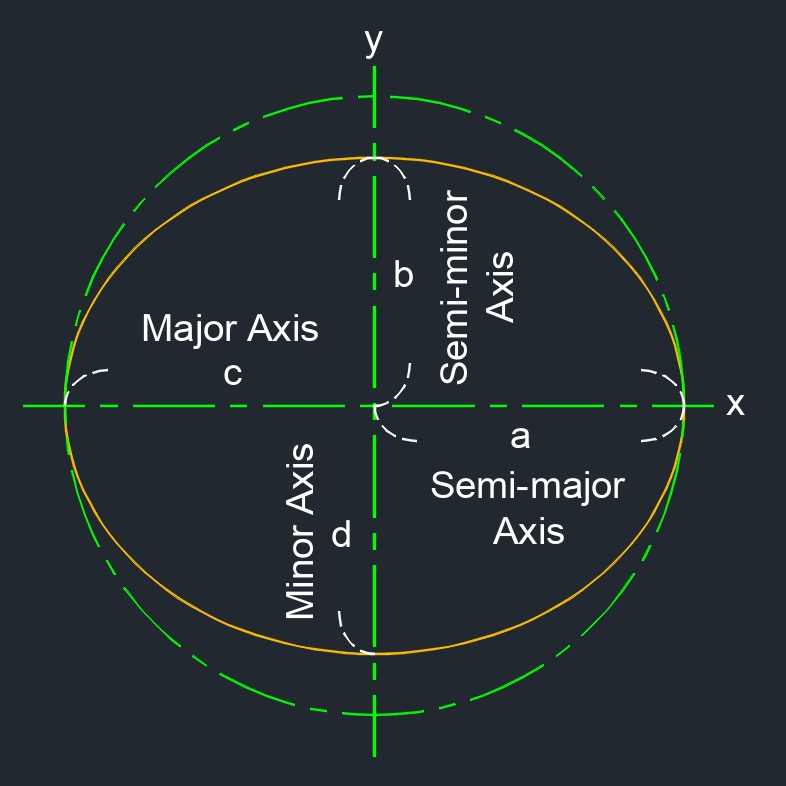 An ellipse is a type of conic section that is defined by two points, known as the foci. The semi-major axis and the semi-minor axis are two important parameters that characterize the size and shape of an ellipse.
An ellipse is a type of conic section that is defined by two points, known as the foci. The semi-major axis and the semi-minor axis are two important parameters that characterize the size and shape of an ellipse.
- Semi-Major Axis - The semi-major axis is the longest radius of an ellipse, extending from the center to one of the points on the ellipse along its major axis. It is half of the length of the major axis.
- Semi-Minor Axis - The semi-minor axis is the shortest radius of an ellipse, extending from the center to one of the points on the ellipse along its minor axis. It is half of the length of the minor axis.
The lengths of the semi-major and semi-minor axes determine the size and proportions of the ellipse. The relationship between the semi-major axis (a) and the semi-minor axis (b) is a fundamental aspect of the ellipse. In particular, the length of the semi-major axis is always greater than or equal to the length of the semi-minor axis.

