Systems Engineering
Engineering, Management and Systems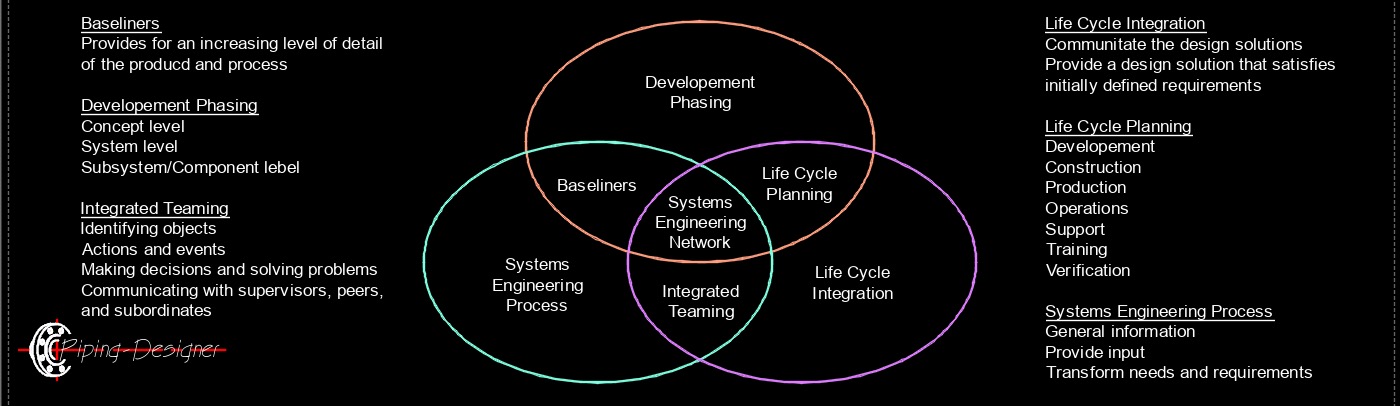 Systems engineering, abbreviated as SE, is an interdisciplinary approach and a systematic process used to design, develop, operate, and manage complex systems. It encompasses a broad range of activities that focus on achieving desired functionality, performance, and reliability while considering the interactions between various components and subsystems within a system. Systems engineering is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, defense, transportation, healthcare, telecommunications, and many others. Its primary focus is on achieving system-level objectives by considering the interactions and dependencies between subsystems, components, and stakeholders, thereby enabling the successful development and operation of complex systems.
Systems engineering, abbreviated as SE, is an interdisciplinary approach and a systematic process used to design, develop, operate, and manage complex systems. It encompasses a broad range of activities that focus on achieving desired functionality, performance, and reliability while considering the interactions between various components and subsystems within a system. Systems engineering is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, defense, transportation, healthcare, telecommunications, and many others. Its primary focus is on achieving system-level objectives by considering the interactions and dependencies between subsystems, components, and stakeholders, thereby enabling the successful development and operation of complex systems.
| Engineering |
| Management and Systems Engineering |
- See Article - Systems Glossary

