Zed
- See Article - Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
area of a Zed formula |
||
| \( A \;=\; t \cdot \left[ l + 2 \cdot \left( w - t \right) \right] \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
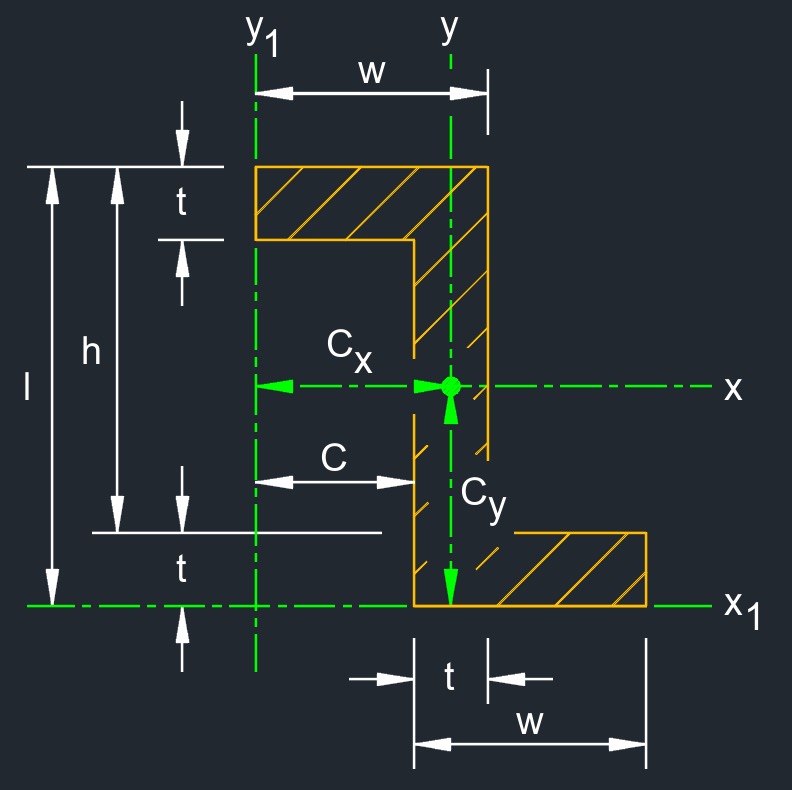 Zed beam, also called known as a "Z-shaped" or "Z-section" beam, is a variation of the letter "Z," which reflects the shape of the cross-sectional profile of the beam. A Zed beam, or Z-section beam, has a cross-sectional shape resembling the letter "Z," with flanges (horizontal top and bottom parts) that are parallel and connected by a vertical web. The flanges are usually smaller in width than those of an I-beam, and they extend outward from the web at the top and bottom. The web connects the two flanges and provides vertical rigidity to the beam.
Zed beam, also called known as a "Z-shaped" or "Z-section" beam, is a variation of the letter "Z," which reflects the shape of the cross-sectional profile of the beam. A Zed beam, or Z-section beam, has a cross-sectional shape resembling the letter "Z," with flanges (horizontal top and bottom parts) that are parallel and connected by a vertical web. The flanges are usually smaller in width than those of an I-beam, and they extend outward from the web at the top and bottom. The web connects the two flanges and provides vertical rigidity to the beam.
Distance from Centroid of a Zed formulas |
||
|
\( C_x \;=\; \dfrac{ 2\cdot w - t }{ 2 } \) \( C_y \;=\; \dfrac{ l }{ 2 } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Elastic Section Modulus of a Zed formulas |
||
|
\( S_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ I_{x} }{ C_{y} } \) \( S_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ I_{y} }{ C_{x} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( S \) = elastic section modulus | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
Perimeter of a Zed formula |
||
| \( P \;=\; 2 \cdot \left( w + l \right) - t \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Polar Moment of Inertia of a Zed formulas |
||
|
\( J_{z} \;=\; I_{x} + I_{y} \) \( J_{z1} \;=\; I_{x1} + I_{y1} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( J \) = torsional constant | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
Radius of Gyration of a Zed formulas |
||
|
\( k_{x} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ w\cdot l^3 - c \cdot \left( l - 2\cdot t \right)^3 }{ 12\cdot t \cdot \left[ l + 2 \cdot \left( w - t \right) \right] } } \) \( k_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{l \cdot \left( w + c \right)^3 - 2c^3 \cdot h - 6\cdot w^2\cdot c\cdot h }{ 12\cdot t \cdot \left[ l + 2 \cdot \left( w - t \right) \right] } \) \( k_{z} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x}{^2} + k_{y}{^2} } \) \( k_{x1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ I_{x1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{y1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ I_{y1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{z1} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x1}{^2} + k_{y1}{^2} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = radius of gyration | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( c \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Second Moment of Area of a Zed formulas |
||
|
\( I_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ w\cdot l^3 - c \cdot \left( l - 2\cdot t \right)^3 }{12} \) \( I_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ l \cdot \left( w + c \right)^3 - 2\cdot c^3\cdot h - 6\cdot w^2 \cdot c\cdot h }{12} \) \( I_{x1} \;= \; I_{x} + A\cdot C_{y}{^2} \) \( I_{y1} \;=\; I_{y} + A\cdot C_{x}{^2} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( c \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

