Law of Conservation of Matter
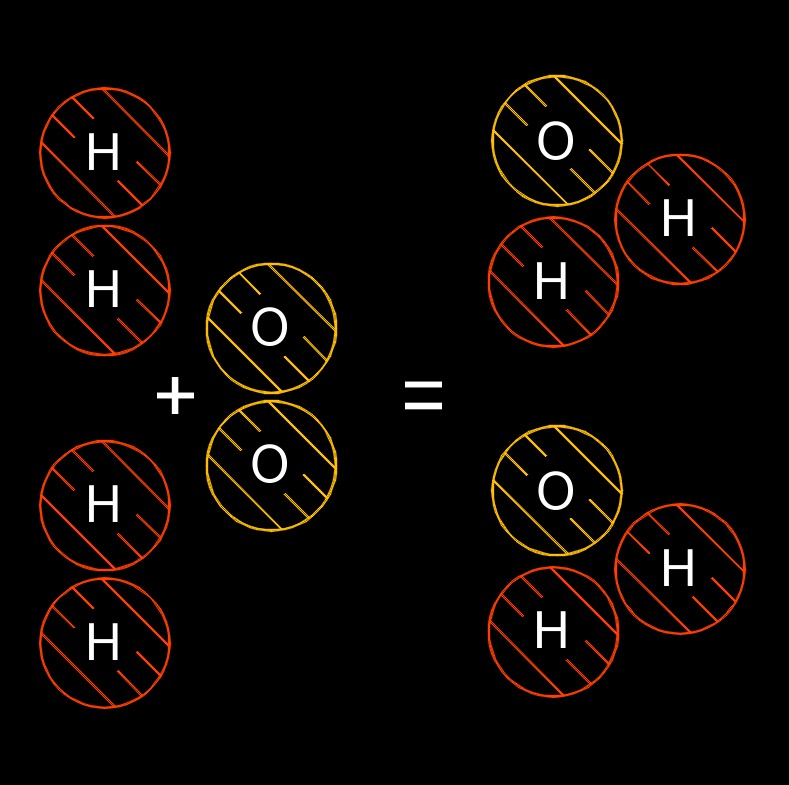 Law of Conservation of Matter is a fundamental principle in chemistry and physics that states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction or a physical change. This means that the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction must be equal to the total mass of the products that are formed.
Law of Conservation of Matter is a fundamental principle in chemistry and physics that states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction or a physical change. This means that the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction must be equal to the total mass of the products that are formed.
In other words, the Law of Conservation of Matter asserts that matter is conserved, or remains constant, during a chemical reaction or a physical change. The atoms or molecules that make up the reactants are rearranged to form new products, but the total number of atoms and molecules remains the same. The Law of Conservation of Matter is a fundamental principle that is used to understand and predict the outcomes of chemical reactions and physical changes. It is an essential concept in the study of chemistry, and is also important in physics, environmental science, and other fields.

