Combined Gas Law
Combined Gas Law Formula |
||
|
\( \dfrac{ p_1\cdot V_1 }{ T_1 } \;=\; \dfrac{ p_2 \cdot V_2 }{ T_2 }\) (Combined Gas Law) \( p_1 \;=\; \dfrac{ T_1 \cdot p_2 \cdot V_2 }{ V_1 \cdot T_2 }\) \( V_1 \;=\; \dfrac{ T_1 \cdot p_2 \cdot V_2 }{ p_1 \cdot T_2 }\) \( T_1 \;=\; \dfrac{ p_1 \cdot V_1 \cdot T_2 }{ p_2\cdot V_2 }\) \( p_2 \;=\; \dfrac{ p_1 \cdot V_1 \cdot T_2 }{ T_1\cdot V_2 }\) \( V_2 \;=\; \dfrac{ p_1 \cdot V_1 \cdot T_2 }{ T_1\cdot p_2 }\) \( T_2 \;=\; \dfrac{ T_1 \cdot p_2 \cdot V_2 }{ p_1\cdot V_1 }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( p_1 \) = Pressure of the Gas Under Conditions | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( V_1 \) = Volume of the Gas Under Conditions | \(in^3\) | \(mm^3\) |
| \( T_1 \) = Temperature of the Gas Under Conditions | \(^\circ F\) | \(^\circ C\) |
| \( p_2 \) = Pressure of the Gas Under Conditions | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( V_2 \) = Volume of the Gas Under Conditions | \(in^3\) | \(mm^3\) |
| \( T_2 \) = Temperature of the Gas Under Conditions | \(^\circ F\) | \(^\circ C\) |
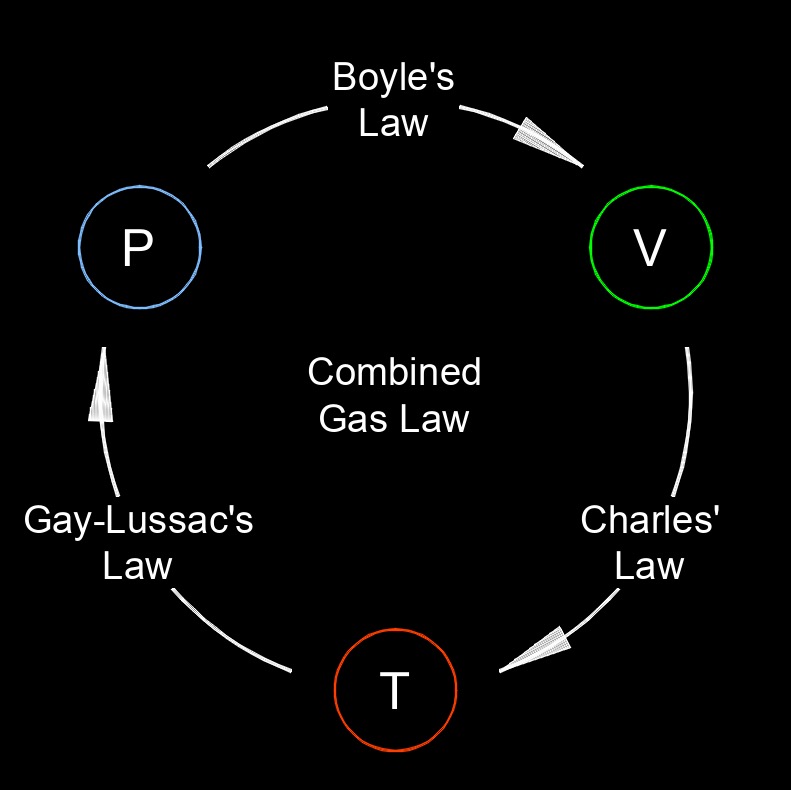 Combined gas law describes the proportional relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. It is derived by combining Boyle's law, Charles' law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The combined gas law is applicable to ideal gases, which are assumed to obey these laws under certain conditions. The law states that the product of the initial pressure and volume of a gas, divided by its initial temperature, is equal to the product of the final pressure and volume of the gas, divided by its final temperature. This equation allows for the calculation of changes in pressure, volume, or temperature of a gas when the other two variables are known.
Combined gas law describes the proportional relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. It is derived by combining Boyle's law, Charles' law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The combined gas law is applicable to ideal gases, which are assumed to obey these laws under certain conditions. The law states that the product of the initial pressure and volume of a gas, divided by its initial temperature, is equal to the product of the final pressure and volume of the gas, divided by its final temperature. This equation allows for the calculation of changes in pressure, volume, or temperature of a gas when the other two variables are known.
This law is particularly useful for analyzing and predicting the behavior of gases under changing conditions, such as when a gas is compressed or expands, or when the temperature is altered. It provides a valuable tool for understanding the relationship between these variables and allows for the prediction of the resulting changes in a gas system. However, it assumes ideal gas behavior and neglects factors such as intermolecular forces and molecular size, which can affect the behavior of real gases.

