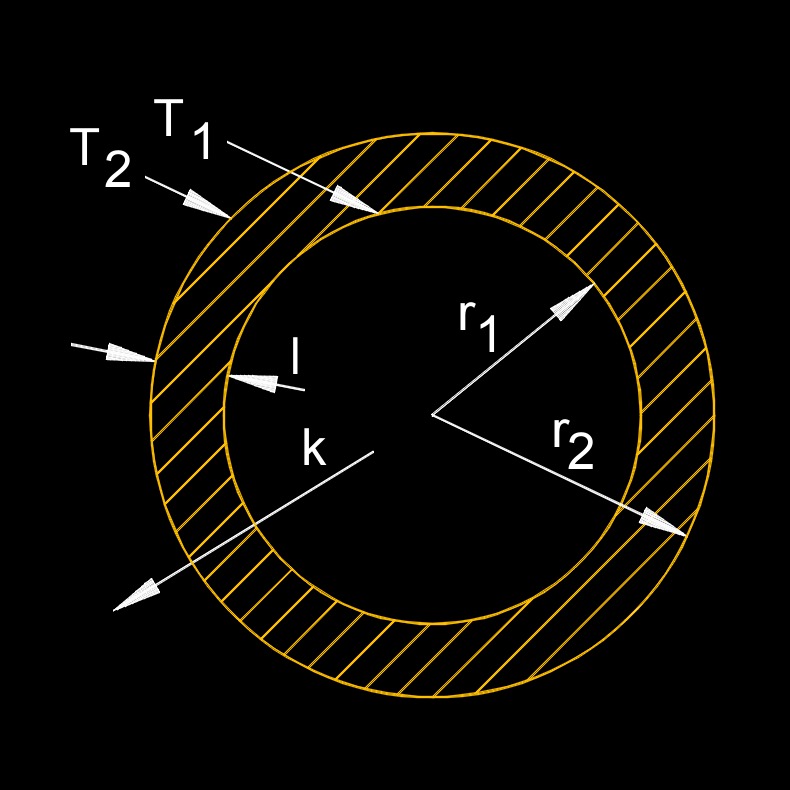
Heat Transfer by Conduction through a Cylindrical Wall
Heat Transfer by Conduction Through a Cylindrical Wall Formula |
||
|
\( Q_c \;=\; \dfrac { 2 \cdot \pi \cdot k \cdot l \cdot \left( T_1 - T_2 \right) }{ ln \left( \dfrac {r_2 }{ r_1 } \right) } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( Q_c \) = heat transfer by conduction | \(Btu\;/\;hr\) | \(W\) |
| \( l \) = material length | \(ft\) | \(m\) |
| \( r_1 \) = radius inside diameter (ID) | \(in\) | \(mm\) |
| \( r_2 \) = radius outside diameter (OD) | \(in\) | \(mm\) |
| \( T_1 \) = temperature of one surface of the wall | \(^\circ F\) | \(^\circ K\) |
| \( T_2 \) = temperature of the other surface of the wall | \(^\circ F\) | \(^\circ K\) |
| \( k \) = thermal conductivity | \(Btu\;/\;hr-ft-F\) | \(W\;/\;m-K\) |