Thermal Conductivity
Thermal Conductivity Formula |
||
|
\( k \;=\; \dfrac{ Q \cdot L }{ A \cdot \Delta T } \) (Thermal Conductivity) \( Q \;=\; \dfrac{ k \cdot A \cdot \Delta T }{ L } \) \( L \;=\; \dfrac{ k \cdot A \cdot \Delta T }{ Q } \) \( A \;=\; \dfrac{ Q \cdot L }{ k \cdot \Delta T } \) \( \Delta T \;=\; \dfrac{ Q \cdot L }{ k \cdot A } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = Thermal Conductivity | \(Btu\;/\;hr-ft-F\) | \(W\;/\;m-K\) |
| \( Q \) = Specific Heat Capacity | \(Btu\;/\;lbm-F\) | \(kJ\;/\;kg-K\) |
| \( L \) = Material Thickness or Length | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = Surface Area | \( in^2 \) | \(mm^2 \) |
| \( \Delta T \) = Change in Temperature | \(^\circ F \) | \(^\circ K \) |
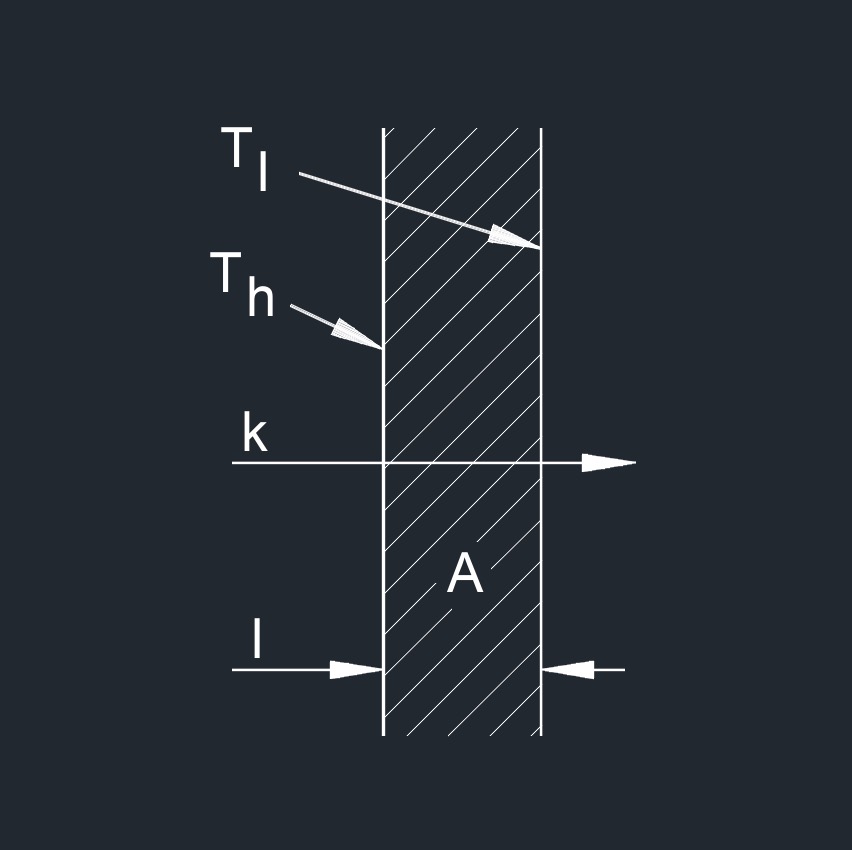 Thermal conductivity, abbreviated as \(k\), also called thermal conductance, or conductance, is a property that describes the ability of a material to conduct heat. It quantifies how easily heat can transfer through a substance when there is a temperature difference across it. Depending on the material, the transfer rate will vary. The lower the conductivity, the slower the transfer. The higher the conductivity, the faster the transfer.
Thermal conductivity, abbreviated as \(k\), also called thermal conductance, or conductance, is a property that describes the ability of a material to conduct heat. It quantifies how easily heat can transfer through a substance when there is a temperature difference across it. Depending on the material, the transfer rate will vary. The lower the conductivity, the slower the transfer. The higher the conductivity, the faster the transfer.
Materials with high thermal conductivity transfer heat more readily than those with low thermal conductivity. Metals, such as copper and aluminum, are examples of materials with high thermal conductivity. On the other hand, materials like air, foam, or certain insulating materials have low thermal conductivity and are considered good thermal insulators.
Thermal conductivity depends on various factors, including the nature and composition of the material, its density, temperature, and moisture content. In addition, thermal conductivity can vary with direction within an anisotropic material, meaning that it may have different values along different axes. Thermal conductivity is an important parameter in fields such as heat transfer, thermodynamics, and material science. It plays a crucial role in designing efficient heat exchangers, determining insulation requirements, optimizing thermal management in electronic devices, and analyzing thermal behavior in various engineering applications.

