Isosceles Triangle
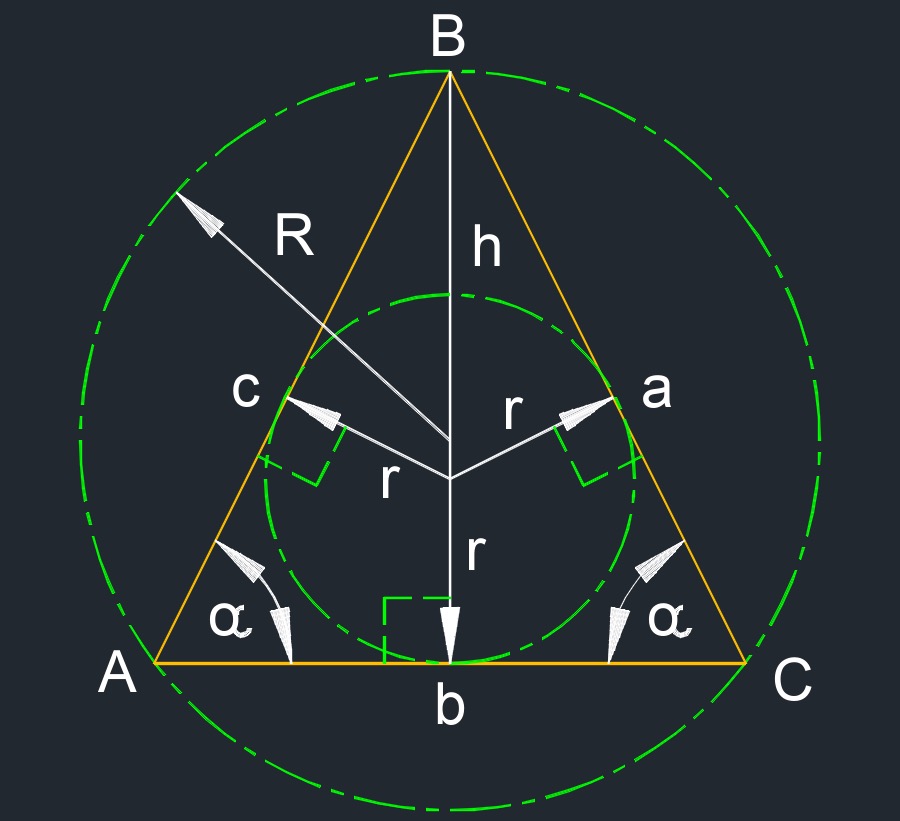
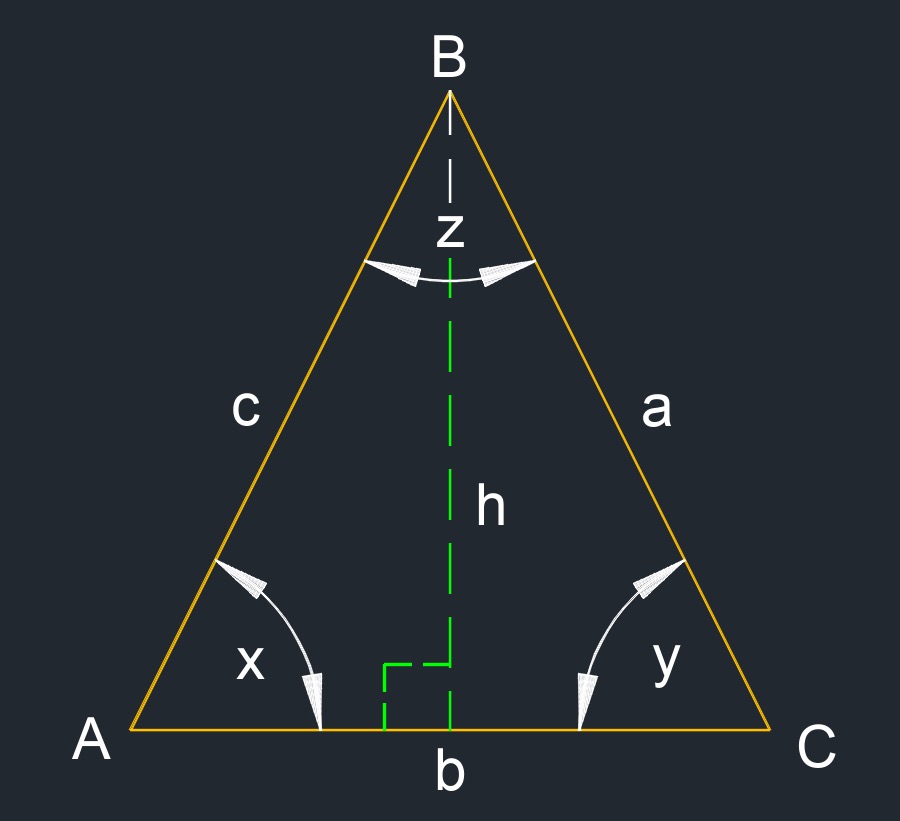 Isosceles triangle (a two-dimensional figure) has two sides that are the same length or at least two congruent sides.
Isosceles triangle (a two-dimensional figure) has two sides that are the same length or at least two congruent sides.- Isosceles triangle (a two-dimensional figure) has two sides that are the same length or at least two congruent sides.
- Angle bisector of a right isosceles triangle is a line that splits an angle into two equal angles.
- Circumcircle is a circle that passes through all the vertices of a two-dimensional figure.
- Congruent is all sides having the same lengths and angles measure the same.
- Inscribed circle is the largest circle possible that can fit on the inside of a two-dimensional figure.
- Semiperimeter is one half of the perimeter.
- a = c
- x = y
- x + y + z = 180°
- Height: \(h_a\), \(h_b\), \(h_c\)
- Median: \(m_a\), \(m_b\), \(m_c\) - A line segment from a vertex (corner point) to the midpoint of the opposite side
- Angle bisectors: \(t_a\), \(t_b\), \(t_c\) - A line that splits an angle into two equal angles
- 3 edges
- 3 vertexs
Area of an Isosceles Triangle formula |
||
| \( A_{area} \;=\; \dfrac{ h \cdot b }{ 2 } \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Circumcircle of an Isosceles Triangle formula |
||
| \( R \;=\; \dfrac{ a^2 }{ \sqrt{ 4 \cdot a^2 - b^2 } } \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( R \) = outcircle | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Height of an Isosceles Triangle formula |
||
|
\( h \;=\; 2 \cdot \dfrac {A_{area} }{ b } \) \( h \;=\; \sqrt{ a^2 - \dfrac{ b^2 }{ 4 } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Inscribed Circle of an Isosceles Triangle formulas
|
||
|
\( r \;=\; \dfrac{ b }{ 2 } \cdot \sqrt{ \dfrac{ 2 \cdot a - b }{ 2 \cdot a + b } } \) \( r \;=\; a \cdot \dfrac{ sine( \alpha) \cdot cos( \alpha) }{ 1 + cos( \alpha) } \;=\; \alpha \cdot cos( \alpha) \cdot tan\left( \dfrac{ \alpha }{ 2 } \right) \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ b}{2} \cdot \dfrac{ sine( \alpha) }{ 1 + cos( \alpha) } \;=\; \dfrac {b}{2} \cdot tan\left( \dfrac{ \alpha }{ 2 } \right) \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ b \cdot h }{ b + \sqrt{ 4 \cdot h^2 + b^2 } } \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ h \cdot \sqrt{ a^2 - h^2 } }{ a + \sqrt{ a^2 - h^2 } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( r \) = incircle | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \alpha \) (Greek symbol alpha) = angle | \( deg \) | \( rad \) |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle formula |
||
| \( P \;=\; 2 \cdot a + b \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Semiperimeter of an Isosceles Triangle formula |
||
| \( s \;=\; \dfrac{ a + b + c }{ 2 } \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( s \) = semiperimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Side of an Isosceles Triangle formulas |
||
|
\( a \;=\; \dfrac{P}{2} - \dfrac{b}{2} \) \( b \;=\; P - 2 \cdot a \) \( b \;=\; 2 \cdot \dfrac{A_{area} }{ h } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( a, b, c \) = side | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Trig Functions |
||
Find A
|
||
Find B
|
||
Find a
|
||
Find b
|
||
Find c
|
||
Find Area
|

