Rhombus
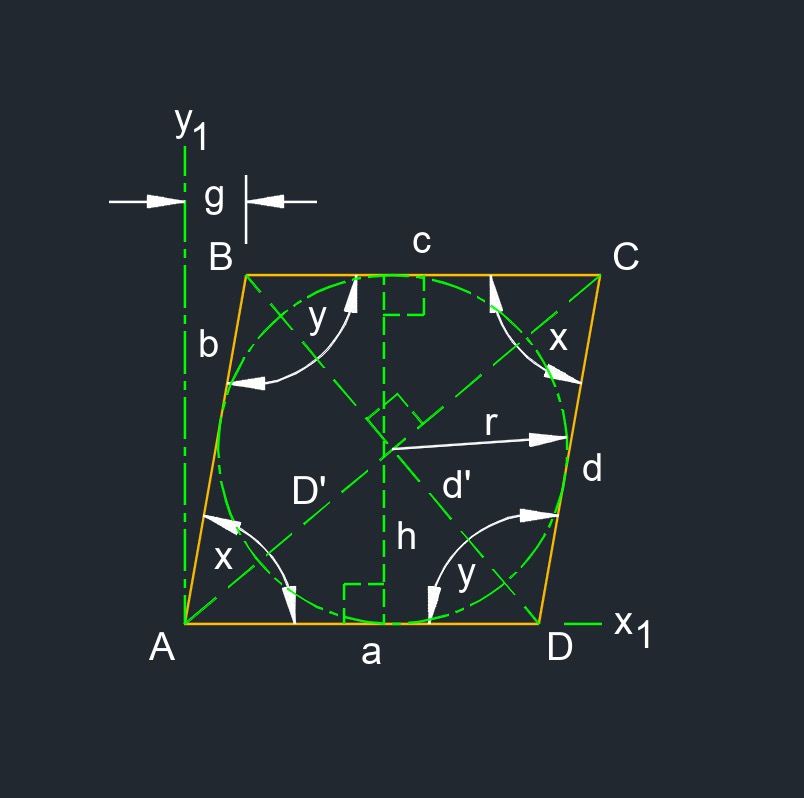 Rhombus (a two-dimensional figure) is a parallelogram with four congruent sides.
Rhombus (a two-dimensional figure) is a parallelogram with four congruent sides.- Acute angle measures less than 90°.
- Congruent is all sides having the same lengths and angles measure the same.
- Diagonal is a line from one vertices to another that is non adjacent.
- Inscribed circle is the largest circle possible that can fit on the inside of a two-dimensional figure.
- Obtuse angle measures more than 90°.
- Parallelogram (a two-dimensional figure) is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel opposite sides.
- a ∥ c
- b ∥ d
- a = b = c = d
- ∠A & ∠C < 90°
- ∠B & ∠D > 90°
- ∠A + ∠B = 180°
- ∠C + ∠D = 180°
- 4 angle
- 2 diagonals
- 4 edges
- 4 vertexs
Angle of a Rhombus formula |
||
| \( y \;=\; 180° - x \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( x \) = acute angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
| \( y \) = obtuce angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
Area of a Rhombus formulas |
||
|
\( A_{area} \;=\; \dfrac{ D' \cdot d' }{ 2 } \) \( A_{area} \;=\; h \cdot a \) \( A_{area} \;=\; a^2 \cdot sin( x) \) \( A_{area} \;=\; 2\cdot a\cdot r \) \( A_{area} \;=\; \dfrac{ 4\cdot r^2 }{ sin( x) } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \(in^2\) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( x \) = acute angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
| \( d', D' \) = diagonal | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, c, d \) = edge | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( r \) = inside radius | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( y \) = obtuce angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
Angle of a Rhombus formulas |
||
|
\( sin( x) \;=\; \dfrac{2\cdot D\cdot d '}{ D'^2 + d'^2} \) \( sin( y) \;=\; \dfrac{2\cdot D' \cdot d'}{D'^2 + d'^2} \) \( cos( x) \;=\; 1 - \dfrac{d'^2}{2\cdot a^2} \) \( cos( x) \;=\; \dfrac{D'^2}{2\cdot a^2} - 1 \) \( cos( y) \;=\; 1 - \dfrac{D'^2}{2\cdot a^2} \) \( cos( y) \;=\; \dfrac{d'^2}{2\cdot a^2} - 1 \) \( sin( x) \;=\; \dfrac{A}{a^2 } \) \( sin( y) \;=\; \dfrac{A}{a^2 } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( x \) = acute angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \(in^2\) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( d', D' \) = diagonal | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, c, d \) = edge | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( y \) = obtuce angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
Diagonal of a Rhombus formulas |
||
|
\( d' \;=\; \dfrac{2\cdot A_{area}}{D'} \) \( D' \;=\; \dfrac {2\cdot A_{area}}{d'} \) \( d' \;=\; \sqrt{ 4\cdot a^2 - D'^2 } \) \( D' \;=\; \sqrt{ 4\cdot a^2 - d'^2 } \) \( d' \;=\; a \cdot \sqrt{ 2 - 2 \cdot cos( x) } \) \( d' \;=\; a \cdot \sqrt{ 2+ 2 \cdot cos( y) } \) \( D' \;=\; a \cdot \sqrt{ 2 - 2 \cdot cos( y) } \) \( D' \;=\; a \cdot \sqrt{ 2 + 2 \cdot cos( x) } \) \( d' \;=\; 2\cdot a \cdot cos \left( \dfrac{y}{ 2} \right) \) \( d' \;=\; 2\cdot a \cdot sin \left( \dfrac{x}{ 2} \right) \) \( D' \;=\; 2\cdot a \cdot cos \left( \dfrac{x}{ 2} \right) \) \( D' \;=\; 2\cdot a \cdot sin \left( \dfrac{y}{ 2} \right) \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( d', D' \) = diagonal | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( x \) = acute angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \( in^2\) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( a, b, c, d \) = edge | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( y \) = obtuce angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
Edge of a Rhombus formulas |
||
|
\( a \;=\; \dfrac{P}{4} \) \( a \;=\; \dfrac{ \sqrt{ D'^2 + D'^2 } }{ 2 } \) \( a \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ A }{ sin( x) } } \) \( a \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ A }{ sin( y) } } \) \( a \;=\; \dfrac{ d' }{ \sqrt{ 2 - 2 \cdot cos( x) } } \) \( a \;=\; \dfrac{ d' }{ \sqrt{ 2 + 2 \cdot cos( y) } } \) \( a \;=\; \dfrac{ D' }{ \sqrt{ 2 - 2 \cdot cos( y) } } \) \( a \;=\; \dfrac{ D' }{ \sqrt{ 2 + 2 \cdot cos( x) } } \) \( a \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ D' \cdot d' }{ 2 \cdot sin( x) } } \) \( a \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ D' \cdot d' }{ 2 \cdot sin( y) } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( a, b, c, d \) = edge | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( x \) = acute angles | \( deg\) | \(\large{ rad}\) |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \(in^2\) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( d',\; D' \) = diagonal | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( y \) = obtuce angles | \( deg\) | \( rad\) |
Inscribed Circle Radius of a Rhombus formulas |
||
|
\( r \;=\; \dfrac{h}{2} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{A_{area}}{2 a} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{D' \cdot d'}{4 \cdot a} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ \sqrt{A_{area}\cdot sin( x) } }{2} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{a\cdot sin( x) }{2} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{a\cdot sin( y) }{2} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ D'\cdot sin \left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right) }{2} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ d'\cdot sin \left(\frac{y}{2}\right) }{2} \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ D'\cdot d' }{ 2\cdot \sqrt{ D'^2 + d'^2 } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( r \) = inside radius | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( A_{area} \) = area | \(in^2\) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( d',\; D' \) = diagonal | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, c, d \) = edge | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = hight | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
Perimeter of a Rhombus formulas |
||
| \( P \;=\; 4\cdot a \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in\) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, c, d \) = edge | \( in\) | \( mm \) |

