Law of Conservation of Momentum
Law of Conservation of Momentum Formulas |
||
|
\( p_i \;=\; p_f \) \( p_i + p_f \;=\; p_i^{\prime} + p_f^{\prime} \) \( (m_i \cdot V_i) + (m_f \cdot V_f) \;=\; (m_i \cdot V_i^{\prime} )+ (m_f \cdot V_f^{\prime}) \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( p_i \) = Initial System's Momentum | \(lbm-ft\;/\;sec\) | \(kg-m\;/\;s\) |
| \( p_f \) = Final System's Momentum | \(lbm-ft\;/\;sec\) | \(kg-m\;/\;s\) |
| \( m_i \) = Initial Mass | \(lbm\) | \(kg\) |
| \( V_i \) = Initial Volume | \(ft^3\) | \(m^3\) |
| \( m_f \) = Final Mass | \(lbm\) | \(kg\) |
| \( V_f \) = Final Volume | \(ft^3\) | \(m^3\) |
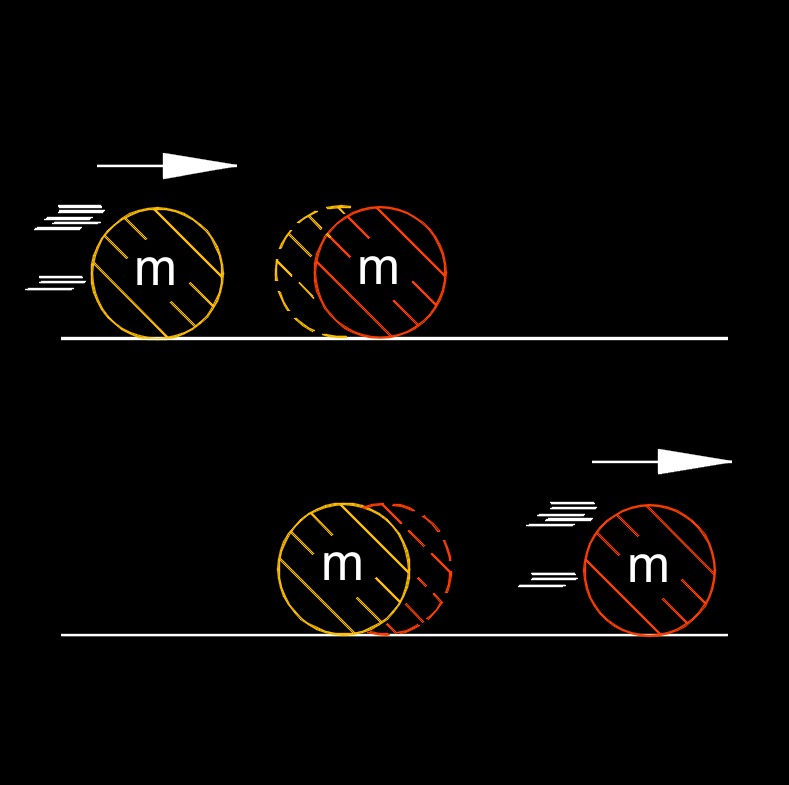
Law of conservation of momentum, abbreviated as \( p_i \), is a fundamental principle in physics that states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant if no external forces act upon it. In other words, the total momentum before an event or interaction is equal to the total momentum after the event or interaction. Momentum is a vector quantity that depends on an object's mass and velocity.
According to the law of conservation of momentum, if no external forces (such as friction or collisions with other objects) are acting on a system, the total momentum of that system will be conserved. This law finds broad applications in various areas of physics, such as mechanics, collisions, fluid dynamics, and particle physics. It helps in analyzing and predicting the motion and interactions of objects and particles in different physical scenarios.

