Rectangular Angle
- See Article - Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
Area of a Rectangular Angle Formula |
||
| \( A \;=\; t \cdot \left( w + d \right) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( d \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
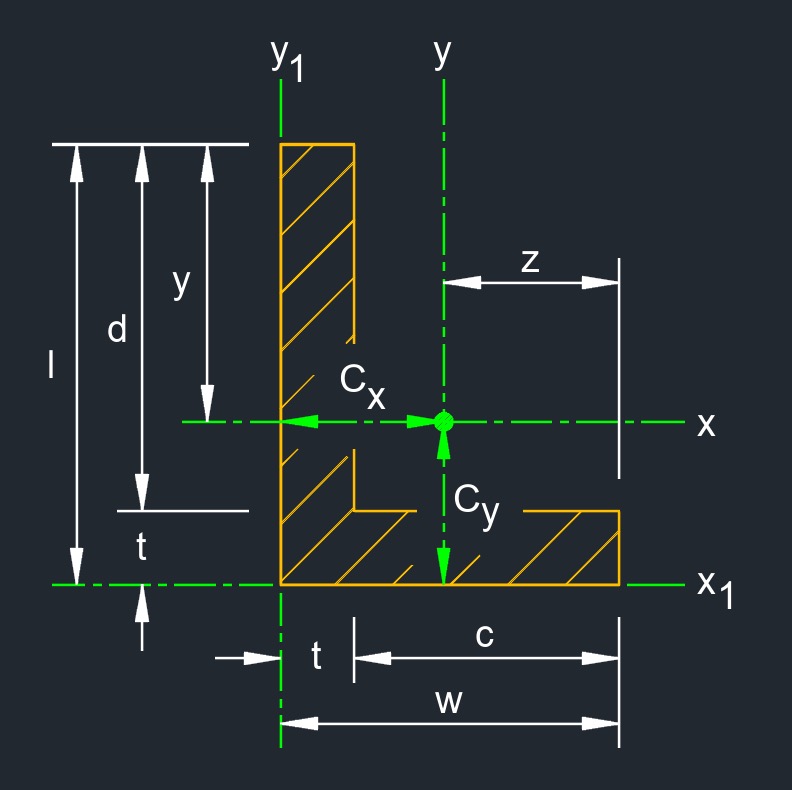 Rectangular angle, also called angle or angle iron, is a L-shaped structural member with rectangular legs. An angle iron has an L-shaped cross-section formed by bending a piece of steel at a 90-degree angle. This type of angle iron has unequal length sides forming a 90-degree corner. It's commonly used as a structural component in various construction and engineering applications due to its rigidity and load-bearing capacity.
Rectangular angle, also called angle or angle iron, is a L-shaped structural member with rectangular legs. An angle iron has an L-shaped cross-section formed by bending a piece of steel at a 90-degree angle. This type of angle iron has unequal length sides forming a 90-degree corner. It's commonly used as a structural component in various construction and engineering applications due to its rigidity and load-bearing capacity.
Distance from Centroid of a Rectangular Angle Formulas |
||
|
\( C_x \;=\; \dfrac{ t \cdot \left( 2\cdot c + l \right) + c^2 }{ 2 \cdot \left( c + l \right) } \) \( C_y \;=\; \dfrac{ t \cdot \left( 2\cdot d + w \right) + d^2 }{ 2 \cdot \left( d + w \right) } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( d \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( c \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Elastic Section Modulus of a Rectangular Angle Formulas |
||
|
\( S_x \;=\; \dfrac{ I_x }{ C_y } \) \( S_y \;=\; \dfrac{ I_y }{ C_x } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( S \) = elastic section modulus | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |

Perimeter of a Rectangular Angle Formula |
||
| \( P \;=\; 2 \cdot \left( w + l \right) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Polar Moment of Inertia of a Rectangular Angle Formulas |
||
|
\( J_z \;=\; I_x + I_y \) \( J_{z1} \;=\; I_{x1} + I_{y1} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \(\large{ J }\) = torsional constant | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \(\large{ I }\) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |

Radius of Gyration of a Rectangular Angle Formulas |
||
|
\( k_x \;=\; \dfrac{ t\cdot y^3 + w \cdot \left( l - y \right)^3 - \left( w - t \right) \cdot \left( l - y - t \right)^3 }{ 3\cdot t \cdot \left( w + l - t \right) } \) \( k_y \;=\; \dfrac{ t\cdot z^3 + l \cdot \left( w - z \right)^3 - \left( l - t \right) \cdot \left( w - z - t \right)^3 }{ 3\cdot t \cdot \left( w + l - t \right) } \) \( k_z \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x}{^2} + k_{y}{^2} } \) \( k_{x1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac { I_{x1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{y1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac { I_{y1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{z1} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x1}{^2} + k_{y1}{^2} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = radius of gyration | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( y \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( z \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Second Moment of Area of a Rectangular Angle Formulas |
||
|
\( I_x \;=\; \dfrac{ t\cdot y^3 + w \cdot \left( l - y \right)^3 - \left( w - t \right) \cdot \left( l - y - t \right)^3 }{3} \) \( I_y \;=\; \dfrac{ t\cdot z^3 + l \cdot \left( w - z \right)^3 - \left( l - t \right) \cdot \left( w - z - t \right)^3 }{3} \) \( I_{x1} \;=\; I_x + A\cdot C_{y}{^2} \) \( I_{y1} \;=\; I_y + A \cdot C_{x}{^2} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( y \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( z \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Tortional Constant of a Rectangular Angle Formula |
||
| \( J \;=\; \dfrac{ \left[ d - \left( \dfrac{t}{2} \right) \right] + \left[ w - \left( \dfrac{t}{2} \right) \right] \cdot t^3 }{ 3 } \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( J \) = torsional constant | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( d \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |


