Environmental Resources
Environmental resources are the natural materials and components that are essential for life and are utilized by humans for various purposes. These resources are critical to the survival of ecosystems, human well-being, and economic development. Their sustainable management and conservation are crucial for ensuring that future generations can continue to benefit from them. Environmental resources can be broadly categorized into the following types:
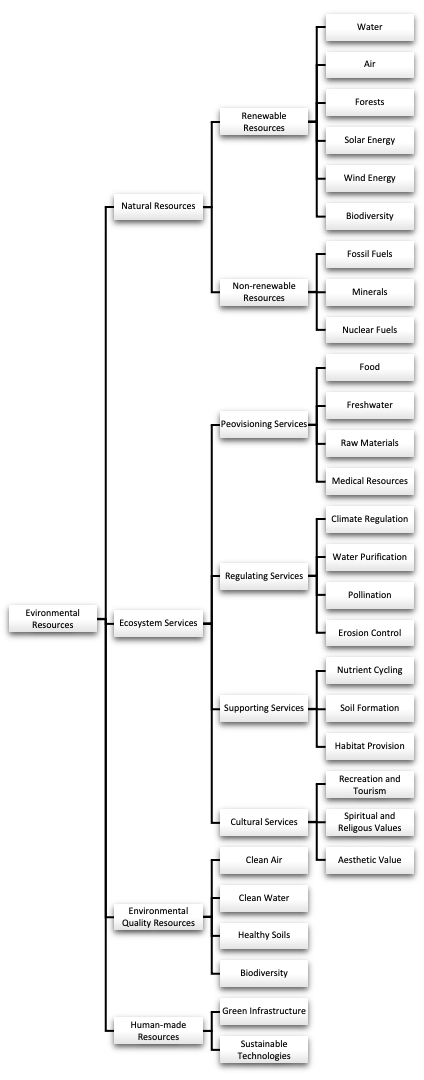 Natural Resources
Natural Resources
Renewable Resources - Resources that can be replenished naturally over time.
- Water - Rivers, lakes, groundwater, and oceans.
- Air - The atmosphere, which provides oxygen and other gases essential for life.
- Forests - Trees and plants that provide oxygen, timber, and habitat for wildlife.
- Solar Energy - Sunlight, used for energy production through solar panels.
- Wind Energy - Wind, harnessed for power generation.
- Biodiversity - The variety of plant and animal species, which provide food, medicine, and ecosystem services.
Non-Renewable Resources - Resources that exist in finite amounts and cannot be replaced once depleted.
- Fossil Fuels - Coal, oil, and natural gas used for energy production.
- Minerals - Metals (iron, copper, gold) and non-metals (limestone, salt) used in construction, manufacturing, and technology.
- Nuclear Fuels - Uranium and thorium used in nuclear power generation.
Ecosystem Services
Provisioning Services - Products obtained from ecosystems.
- Food - Crops, fish, livestock, and wild plants.
- Freshwater - Water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
- Raw Materials - Timber, fibers, and biofuels.
- Medicinal Resources - Plants and animals used in traditional and modern medicine.
Regulating Services - Benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes
- Climate Regulation - Forests and oceans that absorb carbon dioxide and regulate climate.
- Water Purification - Wetlands and soils that filter and clean water.
- Pollination - Bees, birds, and insects that pollinate crops and wild plants.
- Erosion Control - Vegetation that stabilizes soil and prevents erosion.
Supporting Services - Services that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services
- Nutrient Cycling - The movement and exchange of organic and inorganic matter, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, essential for plant growth.
- Soil Formation - The development of soil through weathering of rocks and decomposition of organic matter.
- Habitat Provision - Natural areas that provide living space for species, ensuring biodiversity.
Cultural Services - Non-material benefits obtained from ecosystems.
- Recreation and Tourism - Natural landscapes and wildlife that attract visitors.
- Spiritual and Religious Values - Sacred natural sites and landscapes with cultural significance.
- Aesthetic Value - The beauty of nature, which inspires art, culture, and human well-being.
Environmental Quality Resources
Clean Air - The availability of unpolluted air, essential for health and well-being.
Clean Water - The availability of unpolluted water for drinking, recreation, and agriculture.
Healthy Soils - Fertile soils that support agriculture and plant growth.
Biodiversity - The variety of life forms within an ecosystem, which ensures resilience and adaptability.
Human-Made Resources
Green Infrastructure - Human-designed systems that mimic natural processes, such as urban parks, green roofs, and constructed wetlands.
Sustainable Technologies - Innovations that reduce environmental impact, such as renewable energy technologies, efficient irrigation systems, and pollution control devices.

