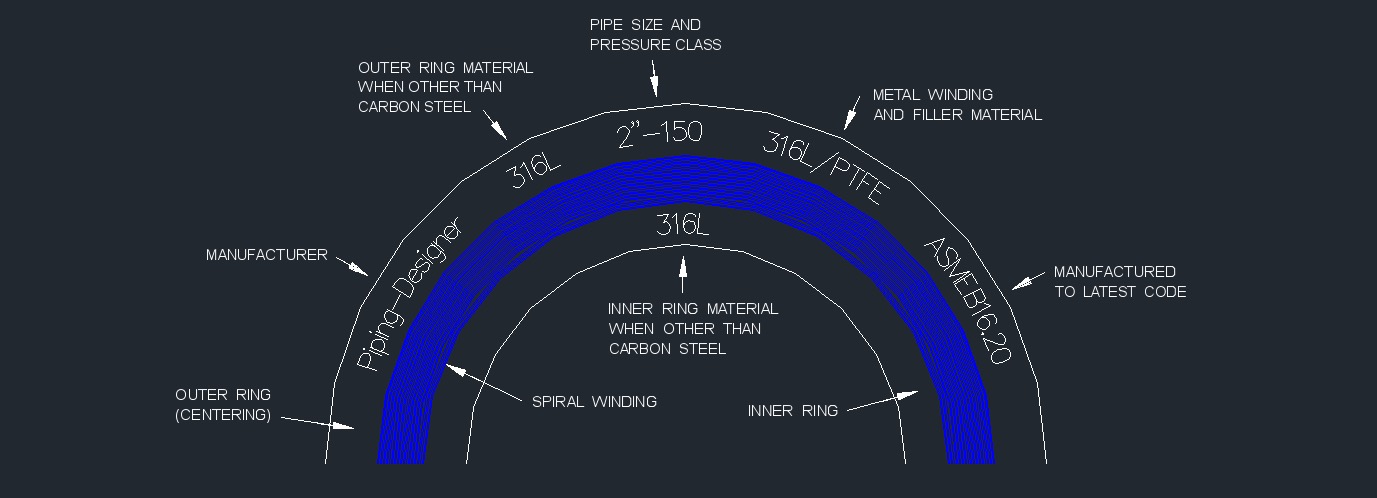
Spiral Wound Gasket
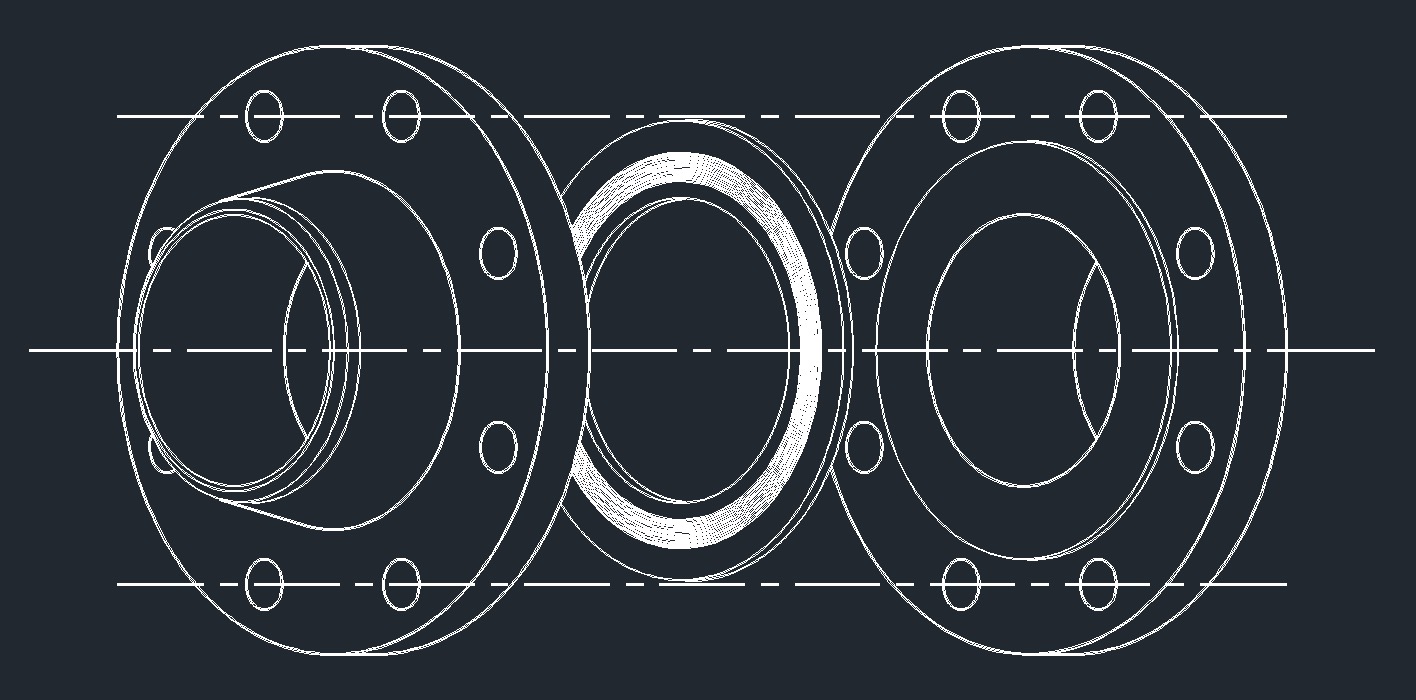 A spiral wound gasket is a type of mechanical seal used in piping and pressure vessel applications to prevent leaks and maintain a seal in environments with high temperature and pressure. It is a combination of metal and filler materials designed to provide resilience, strength, and sealing efficiency.
A spiral wound gasket is a type of mechanical seal used in piping and pressure vessel applications to prevent leaks and maintain a seal in environments with high temperature and pressure. It is a combination of metal and filler materials designed to provide resilience, strength, and sealing efficiency.
Primary Components of a Spiral Wound Gasket
Metal Winding Strip - Typically made of stainless steel, the metal winding strip is wound in a circular fashion, forming the central structural component of the gasket. The winding strip provides strength and resiliency to the gasket.
Filler Material - The filler material is usually a soft, compressible material such as graphite, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), or other materials with sealing properties. The filler material is placed between the layers of the metal winding strip and contributes to the gasket's ability to conform to irregularities in flange surfaces.
Outer Ring - An outer ring, often made of carbon steel or stainless steel, is added to the outer circumference of the gasket. It provides additional structural support and helps to center the gasket within the flange.
Inner Ring (Optional) - In some designs, an inner ring may be included to enhance stability and prevent the filler material from flowing into the pipeline. The inner ring is often made of the same material as the outer ring.
The winding strip and filler material combination allows the spiral wound gasket to effectively seal joints in flanged connections, preventing the leakage of fluids or gases. The design enables the gasket to maintain a seal under varying temperature and pressure conditions. The spiral wound configuration provides resilience, allowing the gasket to adapt to flange surface irregularities and variations.
Spiral wound gaskets are commonly used in industries such as petrochemical, chemical, oil and gas, power generation, and others where there is a need for reliable sealing in demanding conditions. Proper selection of materials and correct installation are crucial for the effective performance of spiral wound gaskets.
Spiral Wound Gasket per ASME B16.20
- ASME B16.20 - Metallic Gaskets for Pipe Flanges: Ring-Joint, Spiral-Wound, and Jacketed
- Inner rings are recommended for all graphite filled gaskets, required for all PTFE filled gaskets, and for NPS 24 and larger in Class 900, NPS 12 and larger in Class 1500, and NPS 4 and larger in Class 2500.
- The gasket outside diameter tolerance for NPS 1/2 through NPS 8 is ±0.03"; for NPS 10 through NPS 24, +0.06", –0.03".
- The gasket inside diameter tolerance for NPS 1/2 through NPS 8 is ±0.016"; for NPS 10 through NPS 24, ±0.03".
- The centering ring outside diameter tolerance is ±0.03".
- There are no Class 400 flanges in NPS 1/2 through NPS 3 (use Class 600), Class 900 flanges in NPS 1/2 through NPS 2-1/2 (use Class 1500), or Class 2500 flanges NPS 14 and larger.
Spiral Wound Gasket Styles
Style RW
- General purpose gasket suitable for flat face and raised face flanges up to Class 2500 (*)
- Centering ring accurately locates the gasket on the flange face, provides additional radial strength, and acts as a compression limiter.
- Spiral winding (sealing element) consists of preformed metal and soft filler material.
Style RWI
- Suitable for flat face and raised face flanges up to Class 2500 (*).
- Recommended for higher pressure applications, for use with PTFE fillers, and when mandated by ASME B16.20 as follows: NPS 24 and larger in Class 900, NPS 12 and larger in Class 1500, and NPS 4 and larger in Class 2500.
- Inner ring acts as compression limiter and protects sealing elements from process media attack.
Style SW
- Suitable for tongue and groove, male-female, or groove-to-flat face flanges (**).
- Spiral winding only, containing preformed metal and soft filler material.
- Also available with inner rings—Style SWI.
(*) Depending on gasket size, an inner ring is recommended for applications above Class 600, due to the high available bolt load.
(**) This design does not have a compression limiter.
Identification Markings Required by ASME B16.20

Tags: Gasket