Gasket
Pipe Fitting, Pipe Flange, Valve, Gasket, Gasket Datasheets, Stationary Equipment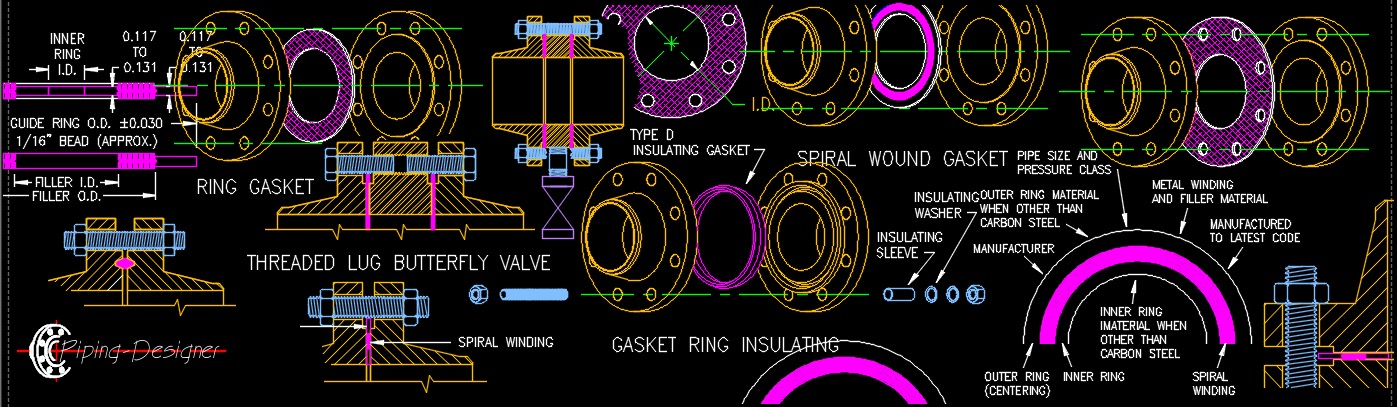 Gasket, abbreviated \(GSK\), is a material that is used to seal the face of flanges, valves and equipment. Gaskets can be made from materials that are soft or hard, but will compress to make a tight seal. When compressed between two flange faces it will deform to match the surface grooves and irregularities. A gasket must be installed properly to prevent leakage. The surface of the flange must be clear of all foreign bodies such as dust, dirt or grease that could prevent a proper seal. To ensure a seal through out the life of the gasket, sufficient pressure or stress should be maintained to prevent leakage. It is very important to select the right gasket material to be used.
Gasket, abbreviated \(GSK\), is a material that is used to seal the face of flanges, valves and equipment. Gaskets can be made from materials that are soft or hard, but will compress to make a tight seal. When compressed between two flange faces it will deform to match the surface grooves and irregularities. A gasket must be installed properly to prevent leakage. The surface of the flange must be clear of all foreign bodies such as dust, dirt or grease that could prevent a proper seal. To ensure a seal through out the life of the gasket, sufficient pressure or stress should be maintained to prevent leakage. It is very important to select the right gasket material to be used.
| Engineering |
| Mechanical Engineering |
- See Articles - List of Tags / List of Categories / List of Articles / List of Glossaries / Nomenclature and Symbols / (See Gasket Glossary)
Gasket Datasheets | |
|---|---|
| Gasket Type | Datasheets |
| Gasket | All Gaskets |
| Gasket | Full Face |
| Gasket | Ring Type |
| Gasket | Spiral Wound |
Gasket Types
Non-metallic Gasket
Also called "soft gaskets" are made from materials that are easily compressed under a low bolt load. They can be used with both flat and raised face flanges in low pressure applications. Materials used are different types of rubber, PTEF, ceramic fiber, glass fiber and more. ASME B16.21 - Nonmetallic Flat Gaskets for Pipe Flanges.
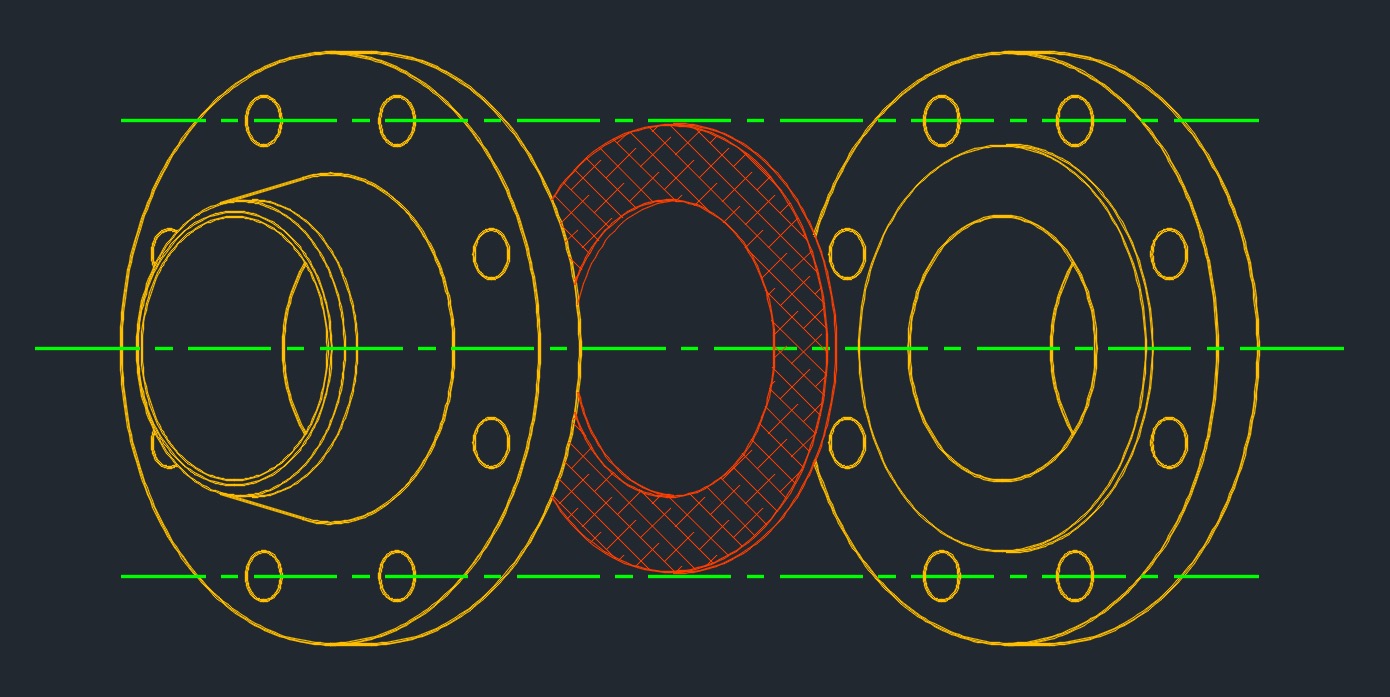 Ring Gasket
Ring Gasket
- Ring gaskets have no bolt holes.
- These gaskets are positioned inside the flange bolts and around the pipe bore.
- Ring gaskets are typically used on raised face flanges.
- When used on a raised face flange, the ring gasket is positioned on top of the raised surface of the flange.
- An advantage of ring gaskets is that they can be installed without having to fully disassemble the joint.
- The gasket ID and OD, thickness and the desired pressure tolerance of the gasket should be specified.
- Used for low pressure, low temperature and noncritical applications.
- Ring gaskets and spiral wound gaskets are used with raised face flanges.
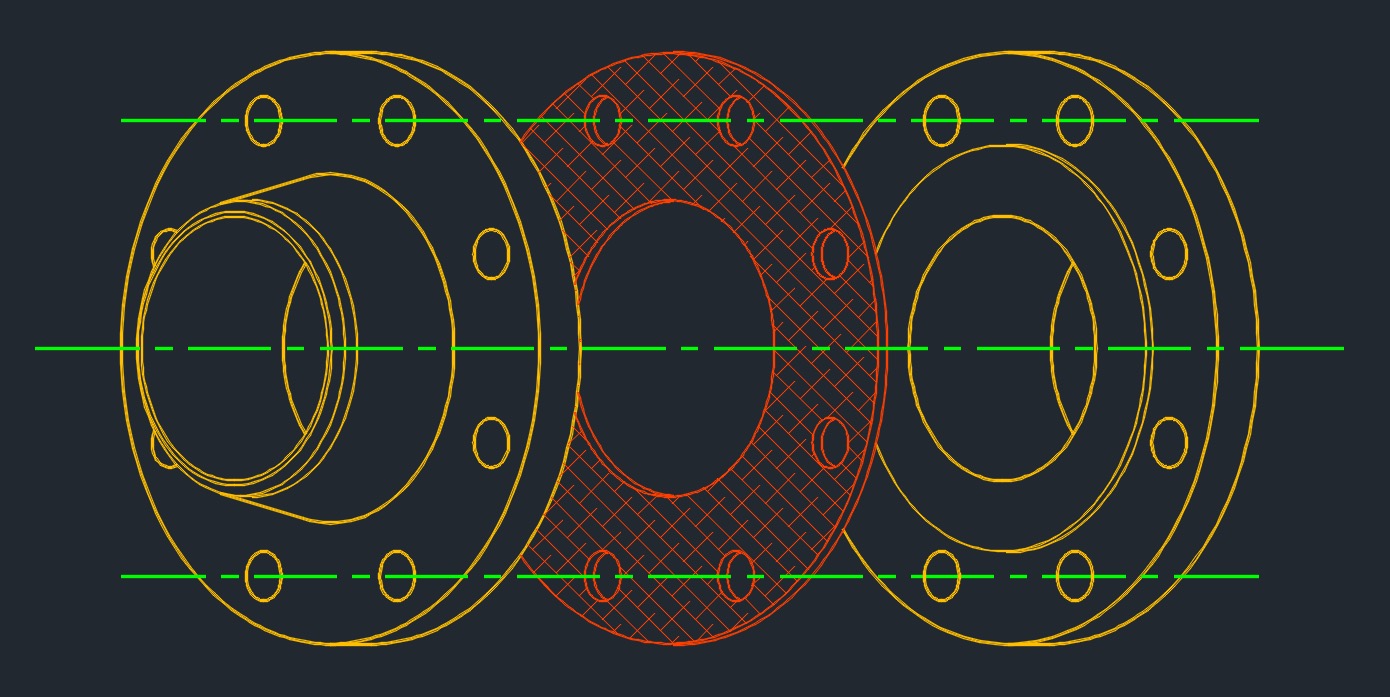 Full Face Gasket
Full Face Gasket
- These gasket covers the entire face of the flange.
- Full-face gaskets are typically used on flat face flanges.
- Full-face gaskets are cut with bolt holes which allow the insertion of the flange bolts through the gasket.
- Used for low pressure, low temperature and noncritical applications.
- Full face gaskets are used with flat face flanges.
- The ID and OD must be specified together with the bolt circle diameter and the number and spacing of the bolt holes.
- Gasket thickness and the desired pressure tolerance of the gasket should also be specified.
Semi-metallic Gasket
Made from both non-metallic and metallic materials and can operate at both high temperature and pressure applications. They can be used with raised face, male and female, and tongue and groove flanges, and many sizes and styles. ASME B16.20 - Metallic Gaskets for Pipe Flanges: Ring-Joint, Spiral-Wound, and Jacketed.
Metallic Gasket
Made from a combination of materials. These gaskets are used for special applications where a tight fit is needed. Ring joint flanges (RJF) often use these gaskets. ASME B16.20 - Metallic Gaskets for Pipe Flanges: Ring-Joint, Spiral-Wound, and Jacketed.
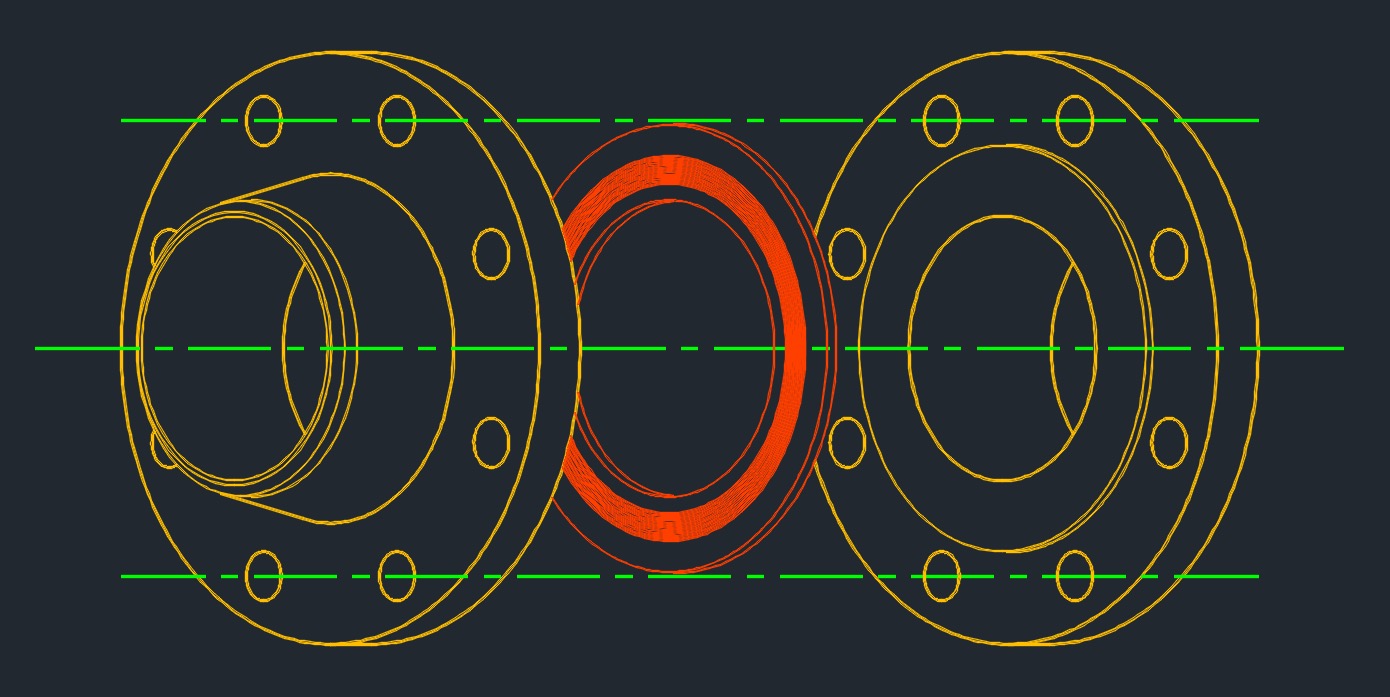 Spiral Wound Gasket - Spiral wound gaskets are formed by winding a metallic and nonmetallic material together in a spiral, which enhances flexibility and durability. These gaskets can also tolerate a greater range of operating conditions, recover quickly, and accommodate flange surface irregularities. Because they can withstand vibration, shock, and pressure and temperature fluctuations, spiral wound gaskets are ideal for pipes and pump systems.
Spiral Wound Gasket - Spiral wound gaskets are formed by winding a metallic and nonmetallic material together in a spiral, which enhances flexibility and durability. These gaskets can also tolerate a greater range of operating conditions, recover quickly, and accommodate flange surface irregularities. Because they can withstand vibration, shock, and pressure and temperature fluctuations, spiral wound gaskets are ideal for pipes and pump systems.-
- Spiral wound gaskets with no Inner Ring (RW) is engineered for ASME flanges with metal windings, filler material, and a centering ring. This style offers excellent general purpose performance for raised face flanges.
- Spiral wound gaskets with Inner Ring (RWI) features an inner ring, spiral winding, filler material, and a centering ring for use in higher pressure applications.
- A forged ring that fits into the machined groove of an ring type joint flanges.
- A metallic sealing ring.
- Produced to specific tolerances, using using high quality materials and machining processes.
- Used for heavy duty, high pressure, high temperature and critical applications.
- Used with high temperatures and/or alternating pressures.
- Selecting based upon chemical compactibility with the media and hardness of the flange.
- The flange groove should match the ring gasket style.
- The groove and ring gasket should be properly aligned in order to create the proper seal.
- Gasket and flange groove must be free of imperfections and debris.
- Ring type joint gaskets are used with ring type joint flanges.
- Gasket Styles:
- R - R type rings are used for the flange rating from Class 150 to 2500.
- Oval - The original design of the R type gasket is Oval.
- Octagonal - The octagonal RTJ is a modification to the oval design and provides better sealing.
- BX - These gaskets are used for the Class rating of 2000 to 20,000 psi. The BX type gasket has a pressure passage hole for pressure equalization on each sealing face sides.
- RX - The flange face-to-face separation will be higher when compared with the R type gasket. RX type gaskets are normally specified up to Class 5000 flanges.
- R - R type rings are used for the flange rating from Class 150 to 2500.
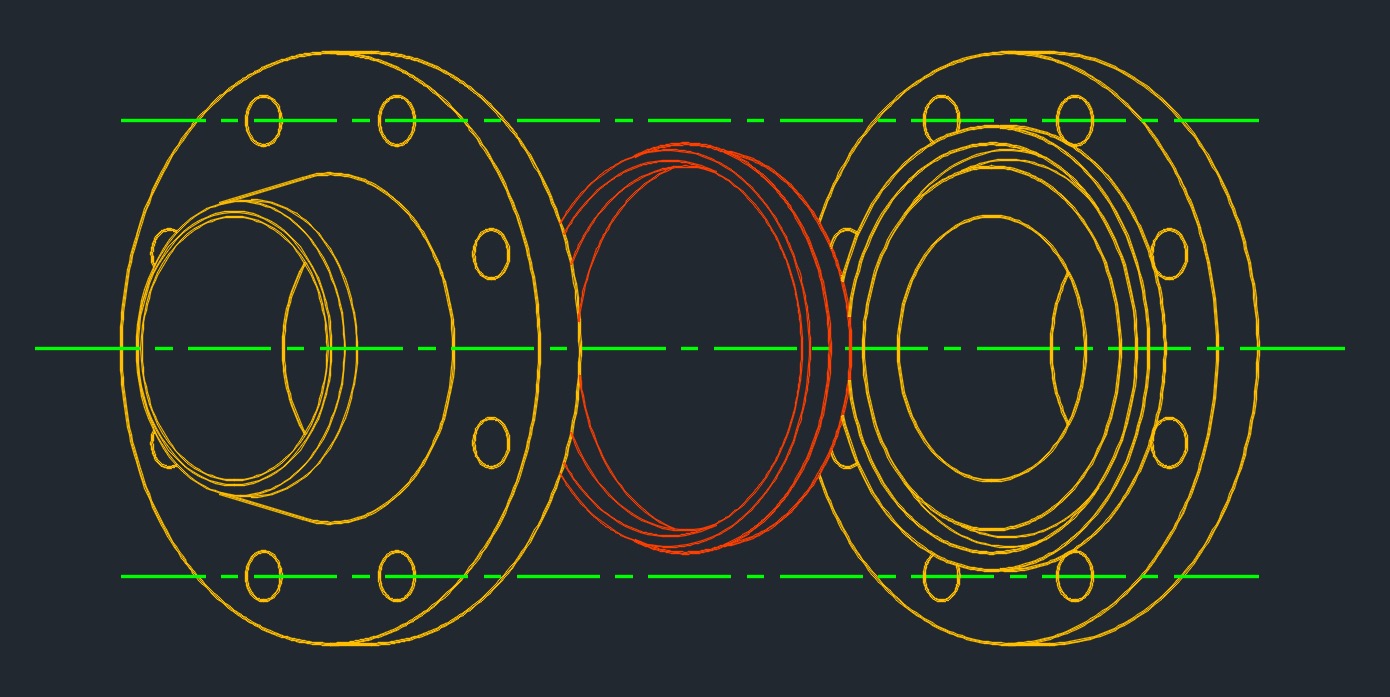 Ring-type-joint Gasket - These gaskets provide a high integrity, high temperature seal and are widely used in the petrochemical, oil and gas industries. RTJ gaskets have a smooth surface finish to provide an optimal metal-to-metal seal.
Ring-type-joint Gasket - These gaskets provide a high integrity, high temperature seal and are widely used in the petrochemical, oil and gas industries. RTJ gaskets have a smooth surface finish to provide an optimal metal-to-metal seal.- Kammprofile Gasket - Kammprofile gaskets consist of a metal core with a nonmetallic outer layer. The metal provides reinforcement, while the nonmetallic material allows the gasket to form a tight seal.
- Tanged Graphite Gasket Sheet - This gasker is made with high purity flexible graphite reinforced with metallic or non-metallic inserts. Graphite gasketing provides a reliable seal as it seals easily under moderate bolt load. It offers superior torque retention, retains dimensional stability in high temperatures and seals tightly, even during pressure fluctuations.
- Metal Jacketed Gasket - A gasket comprised of a soft pliable core inside a metallic jacket. Almost any metal or alloy can be found in sheet form can be used as a jacket.

