Stationary Equipment
Pipe, Pipe Fitting, Storage Tank, Pipe Flange, Pressure Vessel, Valve, Gasket, Manufacturing, Filtration, Fastener, Furnace, Tubing, Pipeline Accessories, Stationary Equipment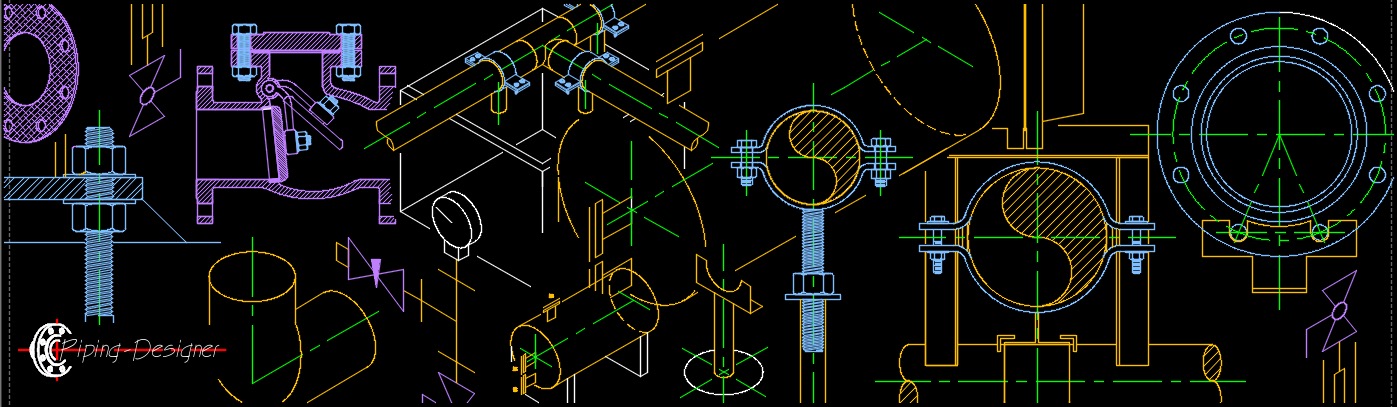 Stationary equipment is a general classification of mechanical equipment that does not move. Depending on the company it may be called "fixed equipment”, "static equipment” or "stationary equipment”.
Stationary equipment is a general classification of mechanical equipment that does not move. Depending on the company it may be called "fixed equipment”, "static equipment” or "stationary equipment”.
Stationary equipment refers to machinery or equipment that remains fixed in place during operation and is not designed to be moved from one location to another. This type of equipment is commonly used in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and energy.
| Engineering |
| Mechanical Engineering |
Stationary equipment may be powered by electricity, natural gas, oil, or other fuels. They may also require various types of maintenance, such as regular inspections, cleaning, and replacement of parts or components. It is important to follow manufacturer recommendations and safety guidelines when operating and maintaining stationary equipment to prevent accidents, equipment failure, or other safety hazards. Proper installation and setup of stationary equipment is also essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation. This may include tasks such as anchoring equipment to a stable foundation, providing appropriate ventilation or exhaust systems, and connecting equipment to appropriate power sources and control systems.

