Storage Tank
Storage Tank, Storage Tank and Pressure Vessel, ASME Standards, API Standards, Stationary Equipment Storage tanks, abbreviated as TK, are containers used to store liquids, gases, or solids for various purposes, such as in industrial processes, commercial or residential use, or for transportation. They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials depending on the specific requirements of the application. Storage tanks can be made from a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and plastic. They can be designed to hold various types of liquids, such as water, oil, chemicals, and fuels, and can be equipped with a variety of features, such as vents, pumps, and level gauges, depending on the intended use.
Storage tanks, abbreviated as TK, are containers used to store liquids, gases, or solids for various purposes, such as in industrial processes, commercial or residential use, or for transportation. They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials depending on the specific requirements of the application. Storage tanks can be made from a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and plastic. They can be designed to hold various types of liquids, such as water, oil, chemicals, and fuels, and can be equipped with a variety of features, such as vents, pumps, and level gauges, depending on the intended use.
| Engineering |
| Mechanical Engineering |
- See Articles - List of Tags / List of Categories / List of Articles / List of Glossaries / Nomenclature and Symbols / (See Storage Tank Glossary)
Storage Tank Types
- Above-ground storage tanks (AST) - These are tanks that are located on the ground, typically in a vertical or horizontal configuration.
- Underground storage tanks (UST) - These are tanks that are buried underground, often used for storing petroleum products or hazardous chemicals.
- Portable storage tanks (PST) - These are tanks that can be moved from one location to another, often used for transportation of liquids or gases.
Storage tanks play a critical role in many industries and applications, such as in the energy, chemical, and food processing industries. They must be designed, installed, and maintained properly to ensure safety and environmental protection.
Storage Tank Design Classification
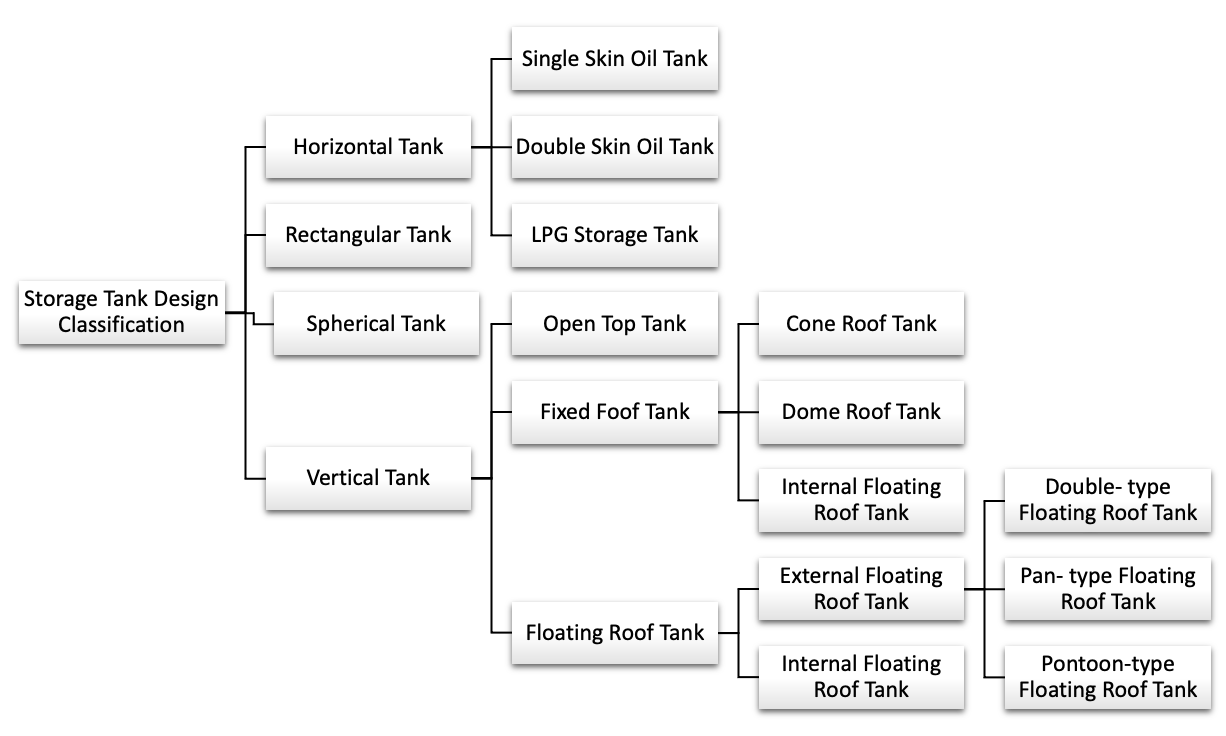
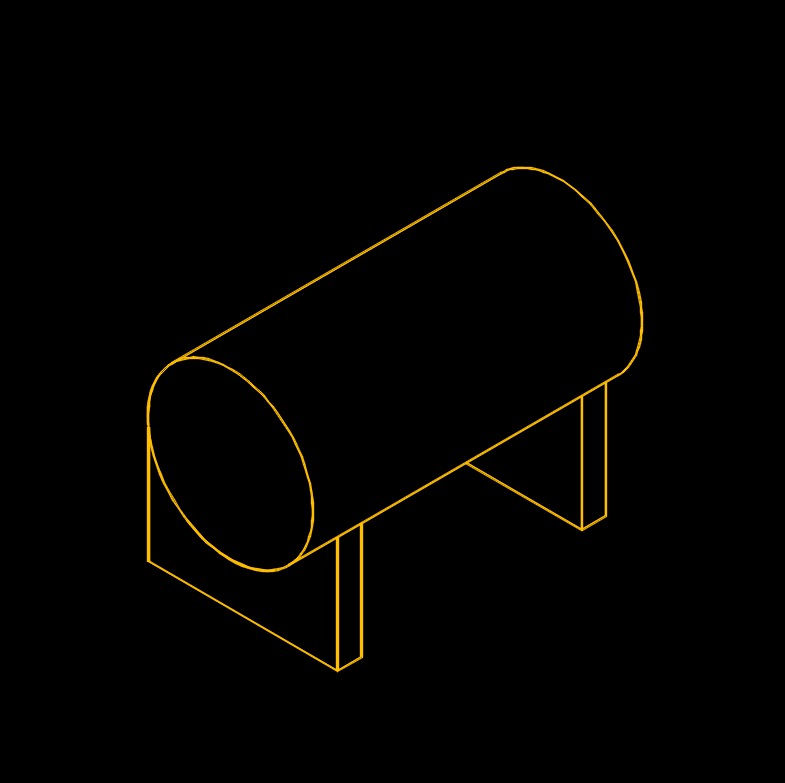 Horizontal Tank (double wall and single wall) - A cylindrical steel tank with flat or dished end operating at atmospheric conditions or at pressure and provided with suitable support saddles intended for aboveground storage of non-corrosive, stable, flammable and combustible liquids
Horizontal Tank (double wall and single wall) - A cylindrical steel tank with flat or dished end operating at atmospheric conditions or at pressure and provided with suitable support saddles intended for aboveground storage of non-corrosive, stable, flammable and combustible liquids
- Single Skin Oil Tank - The body of the horizontal tank consists of cylindrical and end wall parts. The cylindrical part is called a wall and the ends called bottoms. These tanks are used to store non-aggressive and environmentally frendly liquids.
- Double Skin Oil Tank - A special vessel with two shells and a free space between them. The interspace, the area between two shells, is filled with antifreeze or gaseous nitrogen. The thickness of this tank ensures oil, oil products, and hazardoud chemical products will not leak into the environment.
- LPG Storage Tank (Bullet Tank) - A specialized type of storage tank used for the storage of Liquefied Natural Gas. LNG Storage tanks have the ability to store LNG at the very low temperature of -162°C. LNG storage tanks have double containers, where the inner contains LNG and the outer container contains insulation materials.
Rectangular Tank - This tank can be used to store dry or liquid materials. The main advantage of rectangular tanks is that they can be stacked on top of each other to save space.
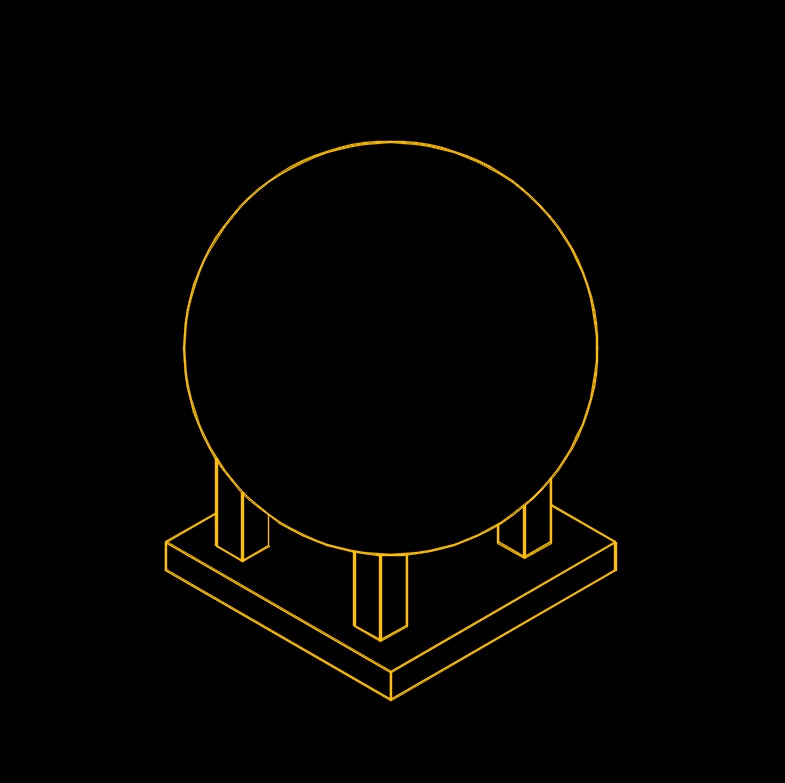 Spherical Tank - These tanks are a closed container designed to hold gas or liquid at a significantly different pressure with the external environment.
Spherical Tank - These tanks are a closed container designed to hold gas or liquid at a significantly different pressure with the external environment.
 Vertical Tank (bolted and welded) (double wall and single wall) - Vertical storage tanks are most frequently used for bulk storage of water, fertilizer, agricultural and industrial chemicals.
Vertical Tank (bolted and welded) (double wall and single wall) - Vertical storage tanks are most frequently used for bulk storage of water, fertilizer, agricultural and industrial chemicals.
- Open Top Tank (atmospheric) - Normally for petroleum products but can contain cooling water and fire water.
- Fixed Roof Tank (atmospheric, low pressure, high pressure) - Can either be self supported or rafter/trusses supported depending on the size of this non moving roof. They have a solid top that is attached directly to the shell. Depending on age and design, these tanks may or may not be vapor and liquid tight. These tanks meet the minimum requirements for storing most liquids and are the cheapest to construct.
- Cone Roof Tank (supported and self supported)
- Dome Roof Tank (supported and self supported)
- Internal Floating Roof Tank (supported and self supported)
- Floating Roof Tank - Roof sits directly on top of product. These tanks are designed to reduce vapor emissions and volume inside of the tank. This is achieved with the roof floating on the surface of the liquid inside the vessel. The roof raises and lowers with the liquid level, preventing a buildup of vapor inside.
- External Floating Roof Tank - The roof floats directly on top of the product or on pontoons at the liquid level. The tank is open to the atmosphere.
- Double-type Floating Roof Tank
- Pan-type Floating Roof Tank
- Pontoon-type Floating Roof Tank
- Internal Floating Roof Tank - This tank has two roofs. The floating roof is the internal component, floating on the liquid. Above it, there is a fixed roof at the top of the storage vessel.
- External Floating Roof Tank - The roof floats directly on top of the product or on pontoons at the liquid level. The tank is open to the atmosphere.

