Fastener
Pipe Fitting, Pipe Flange, Valve, Abbreviations, Fastener, Stationary Equipment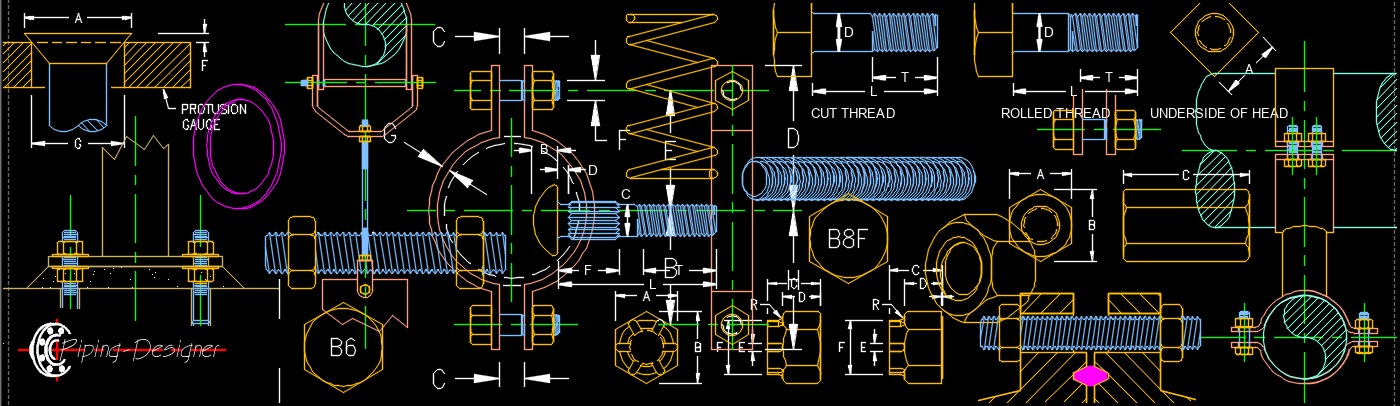 A fastener, abbreviated as FSTNR, is a type of hardware component used to mechanically join two or more objects together. Fasteners are typically used to create a non-permanent joint that can be easily disassembled or reassembled, such as in the case of screws, bolts, nuts, rivets, and clips. Fasteners come in many different shapes, sizes, and materials, and are designed to meet specific requirements of different applications. For example, some fasteners are designed to be resistant to corrosion or high temperatures, while others are designed to provide a secure and tamper-resistant connection. Fasteners are used in a wide variety of industries and applications, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. They play a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of structures and products, and are often subjected to rigorous testing and standards to ensure their performance and durability.
A fastener, abbreviated as FSTNR, is a type of hardware component used to mechanically join two or more objects together. Fasteners are typically used to create a non-permanent joint that can be easily disassembled or reassembled, such as in the case of screws, bolts, nuts, rivets, and clips. Fasteners come in many different shapes, sizes, and materials, and are designed to meet specific requirements of different applications. For example, some fasteners are designed to be resistant to corrosion or high temperatures, while others are designed to provide a secure and tamper-resistant connection. Fasteners are used in a wide variety of industries and applications, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. They play a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of structures and products, and are often subjected to rigorous testing and standards to ensure their performance and durability.
| Engineering |
| Mechanical Engineering |
- See Articles - List of Tags / List of Categories / List of Articles / List of Glossaries / Nomenclature and Symbols / (See Fastener Glossary)
Fastener Types
Permanent
These fasteners are single use, intended to join two materials and can’t be removed once installed.
- Nail
- Box Nail, Bright Nail, Casing Nail, Coated Nail, Common Nail, Duplex Nail, Drywall Nail, Finish Nail, Galvanized Nail, Electrogalvanized Nail, Hot-dip Galvanized Nail, Mechanical Galvanized Nail, Head Nail, Helix Nail, Length Nail, Phosphate-coated Nail, Point Nail, Ring Shank Nail, Shank Nail, Sinker Nail, Spike Nail
- Rivet
- Blind Rivet, Conical Head Rivet, Countersunk Rivet, Drive-pin Rivet, Flathead Rivet, Flush Rivet, Friction-lock Rivet, Mushroom Head Rivet, Pan Head with Tapered Neck Rivet, Self-piercing Rivet, Solid Rivet, Snap Head Rivet, Split Rivet,Tubular Rivet
- Weld
Removable
These fasteners are designed specifically to join two materials or objects, with the option to be removed and reused without damaging the objects they hold together.
- Bolt
- Carriage Bolt, Fin Neck, Carriage Bolt, Ribbed Neck, Carriage Bolt, Short Neck, Timber Bolt, Elevator Bolt, Wire Eye Bolt, Forged Eye Bolt, Forged Machinery Eye Bolt, Forged Eye Bolt with Shoulder, Forged Machinery Eye Bolt with Shoulder, Wire Eye Lag, Hanger Bolt, Hex Heavy Bolt, Hex Bolt Full thread tap bolt, Lag Bolt, Shoulder Bolt Socket drive, Square Bolt, J-Bolt Round bend, U-Bolt Round bend, U-Bolt Square bend
- Nut
- T-Nut, Two-way Reversible Lock Nut, Wing Nut, Square Nut, Square Heavy Nut, Square Machine Screw Nut, Hex Slotted Castle Nut, Hex Slotted Heavy Nut, Hex High Crown Cap Nut, Hex Low Crown Cap Nut, Hex Finished Jam Nut, Hex Heavy Jam Nut, Hex Jam Nylon Lock Nut, Hex Lock Nut Nylon Insert, Hex K-Lock Nut, Prevailing Torque Lock Nut, Hex Machine Screw Nut, Hex Heavy Coupling Nut, Hex Finished Coupling Nut, Hex Flange Nut, Hex Finished Nut, Hex Heavy Nut, Hex Acorn Nut, Hex Cap Nut
- Screw
- Decking Screw, Double Ended Screw, Drywall Screw, Eye Bolt Screw, Framing Screw, Fillister Head Screw, Hammer Drive Screw, Hex Cap Screw, Lag Screw, Machine Screw, Masonary Screw, Oval Head Screw, Pan Head Screw, Particle Board Screw, Pocket Hole Screw, Security Screw, Selt Tapping Screw, Set Screw, Sheet Metal Screw, Shoulder Screw, Socket Head Screw, Tamper Proof Screw, Thread Cutting Machine Screw, Washer Faced Screw, Weld Screw, Wood Screw
- Stud
- Bonding Stud, Clinch Stud, Double-end Stud Bolt, Double-end Stud Bolt with Reduced Shank, Dowel Screw, Full Threaded Stud Bolt, Flange Stud Bolt, Tap End Stud Bolt, Welding Stud
- Washer
- Dock Washer, Fender Washer, Finishing Washer, Flat Washer, SAE Flat Washer, USS Flat Washer, Lock Washer, Lock Washer External Tooth, Lock Washer Internal Tooth, High Collar Lock Washer, Ogee Washer, Square Dock Washer, Spring Washer, Tapper Washer, Tooth Washer

