Valve
Pipe, Pipe Fitting, Pipe Sizing, Valve Sizing, Pipe Flange, Valve, Gasket, Valve Datasheets, Datasheets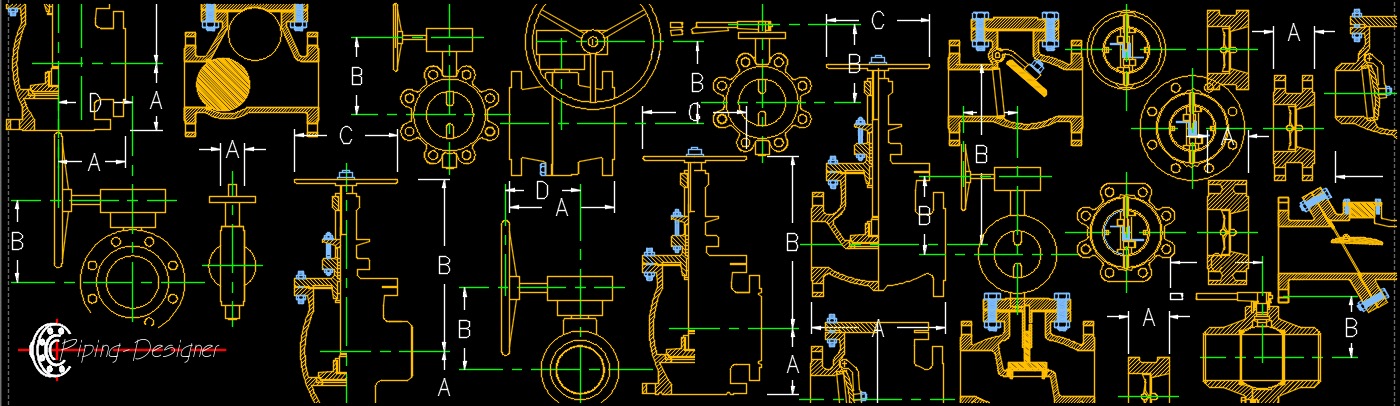 Valves, abbreviated as V, are mechanical devices used to control the flow of fluids (liquids or gases) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing a passage. Valves are used in a wide range of applications, from residential plumbing to industrial processes. Valves can be made of various materials, such as metal, plastic, or ceramic, depending on the application and the type of fluid being handled. They can also be operated manually or automatically, using mechanisms such as handwheels, levers, or electric motors.
Valves, abbreviated as V, are mechanical devices used to control the flow of fluids (liquids or gases) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing a passage. Valves are used in a wide range of applications, from residential plumbing to industrial processes. Valves can be made of various materials, such as metal, plastic, or ceramic, depending on the application and the type of fluid being handled. They can also be operated manually or automatically, using mechanisms such as handwheels, levers, or electric motors.
| Engineering |
| Mechanical Engineering |
- See Articles - List of Tags / List of Categories / List of Articles / List of Glossaries / Nomenclature and Symbols / (See Valve Glossary)
Valve Datasheets | |
|---|---|
| Valve Type | Datasheets |
| Valves | All Valves, ANSI (in) |
| Ball | Ball Valve, ANSI (in) |
| Butterfly | Butterfly Valve, ANSI (in) |
| Check | Check Valve, ANSI (in) |
| Gate | Gate Valve, ANSI (in) |
| Globe | Globe Valve, ANSI (in) |
| Plug | Plug Valve, ANSI (in) |
Valve Design Types
- Ball Valve - A ball valve, abbreviated as BV, is a quarter turn valve used for changing the direction of a process stream (divert or shut off). Ball valves can be automated to automatically shutdown or open depending on the orientation of the actuator.
- Butterfly Valve - A butterfly valve, abbreviated as BTFLV, is a quarter turn valve (90° or less) with a circular disk as its closing element. The standard design has the valve stem running through the disk, giving a symmetrical appearance.
- Check Valve - Check valves, abbreviated as CV, are valves that are designed to allow the process fluid to flow in only one direction to prevent backflow. Check valves are also known as non-return valves, clack valves or one-way valves.
- Choke Valve - Used a severe service valves designed for oil and gas applications. They are used for controlling the flow rates or pressure on production, steam or water injection. Choke valves are subjected extreme conditions which can cause erosion, corrosion and other damage.
- Diverter Valve - A special equipment used to divert granular and powder material flow from one or more inlets to one or more outlets. This type of valve is gravity flow, meaning no or little pressure to higher pressure.
- Lift Chech Valve - A check valve that is very much like a piston check valve where the flow lifts a disk when the valve is open. The upstream side of the lift check is under the disk and the flow flows up through the disk. The disk is guided to keep the motion to be perpendicular to the line flow direction.
- Stop Check Valve - It is essentially, two valves built into one. It can act as a globe valve to isolate or control the flow rate. It also acts as a check valve by preventing reverse flow. This is critical to prevent boiler flooding by preventing steam and condensate from back flowing into the generator.
- Tilting Disk Check Valve - A check valve where the disc has a pivot point at the center of the disc. It is also known as a tilt check valve or a tilting-disk check valve. When flow is moving forward, the valve easily opens and when there is flow reversal, the valve immediately closes.
- Control Valve - A type of valve that is use to control the flow, pressure, level or even the direction of the fluid according to the need of the process.
- Back Pressure Valve
- Choke Valve
- Flow Control Valve
- Level Control Valve
- Pressure Control Valve
- Temperature Control Valve
- Diaphragm Valve - This is a shut-off valve and is bi-directional. A diaphragm is the opening and closing element in the valve which is made of a soft, flexible material which is elastic, non-corrosive, nonpermeable material such as rubber and plastic. This separates the fluid inside the valve body cavity from the cover cavity and the driving member which prevents contamination of the working medium and corrosion of operating parts.
- In-line Diaphragm Valve (Straight through Diaphragm Valve)
- Weir Diaphragm Valve
- Gate Valve - The gate valve, abbreviated as GV, is one of the most frequently used valve in piping systems and is classified as either "rising-stem" or "nonrising-stem" valves. The rising-stem gate valve has the stem attached to the gate, both gate and stem rise and lower together as the valve handwheel or actuator turns the stem. In the nonrising-stem gate valves the stem is threaded into the wedge, rising and lowering the wedge.
- Globe Valve - A globe valve, abbreviated as GLV, is a type of valve used for regulating fluid flow, both on/off and throttling, it is a control valve. The name globe valve comes from the globular shape of the valve body.
- Needle Valve - A valve with an adjustable tapered point which regulates the rate of flow.
- Pig Valve - A pigging valve is an alternative to conventional pig launchers. They are capable of launching and receiving foam, steel, and solid cast pigs in both cylindrical and spherical shapes. Original designs would only allow spherical shapes but machining innovations and technology have allowed for other shapes of pigs such as cups, disc, brushes and also foam pigs can be used.
- Pinch Valve - These valves are suited for the handling of slurries, liquids with large amounts of suspended solids, and systems that convey solids pneumatically. They consists of a sleeve molded of rubber or other synthetic material and a pinching mechanism. The sleve can be external or internal inside a body.
- Enclosed Pinch Valve
- Open Pinch Valve
- Plug Valve - A plug valve is a quarter turn valve that has a conical or cylindrical plug that is rotated within the valve body to stop flow when needed. Plug valves function similar to a ball valve where the plug has an opening in the plug that allows fluid to flow through the valve when it is open.
- Pressure Valve - Both the relief and safety valves work to release excess pressure, but each go about it is a little different.
- Pressure Relief Valve - Relief valves removes excessive pressure from a system by limiting its pressure level to a safe level. The valve opens gradually during normal operation to maintain an optimal pressure level inside the vessel.

