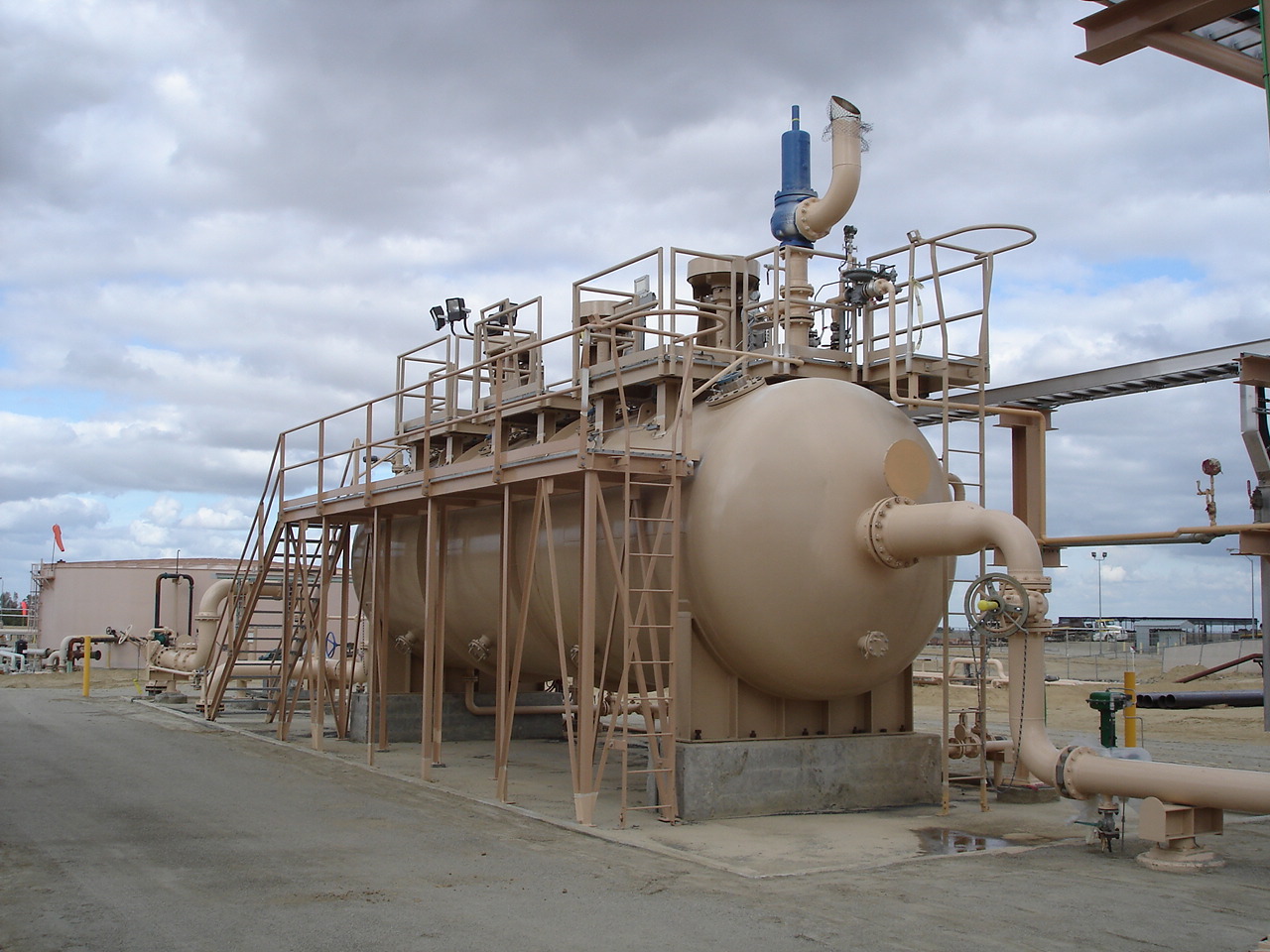
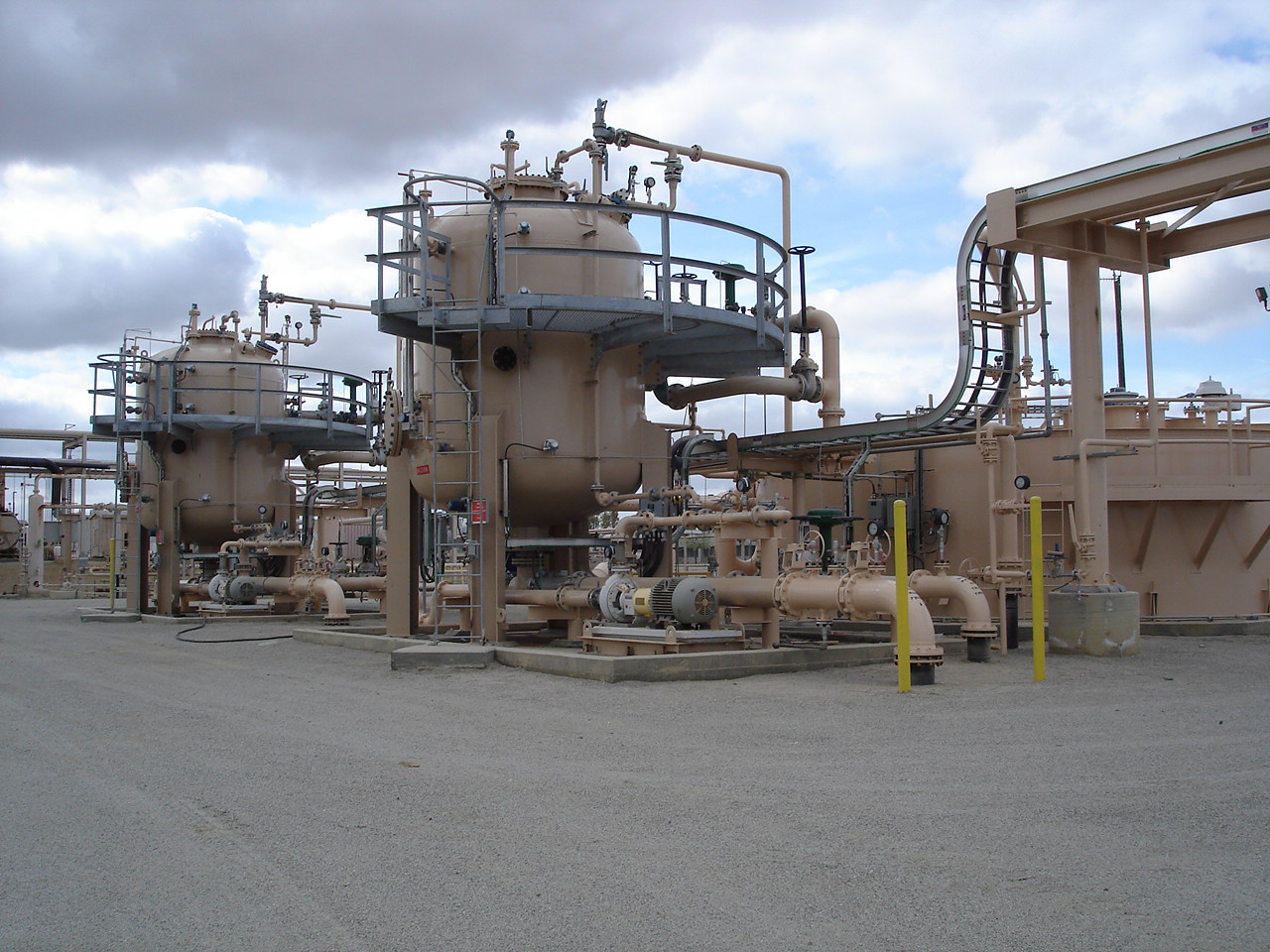
Pressure vessels are containers designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. They are used in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation. Each type of pressure vessel has its own specific design considerations depending on factors such as the material being contained, operating pressure, temperature, and safety regulations. There are several types of pressure vessels based on design, shape, and application. Below are the main types:
Based on Shape
Spherical Pressure Vessels - Used for storing high-pressure gases. The spherical shape distributes stress evenly, making it ideal for high-pressure applications.
Cylindrical Pressure Vessels: - Common in many industries. Can be oriented horizontally or vertically. Easier to manufacture than spherical vessels, but less efficient in terms of stress distribution.
Conical Pressure Vessels - Used in systems where materials need to be funneled or mixed, often at the bottom of a cylindrical vessel. The cone shape helps manage the flow of materials.
Based on Construction
Single-Wall Vessels - These are constructed with a single layer of material. Suitable for low to moderate pressures.
Multi-Wall Vessels - Constructed with multiple layers to handle very high pressures. Common in nuclear reactors and high-pressure industrial applications.
Based On Function
Storage Tanks - Used for storing liquids or gases at a given pressure. Can be either low- or high-pressure vessels.
Process Vessels - Used in chemical, petrochemical, and refinery industries to carry out reactions under pressure. Include reactors, heat exchangers, and separators.
Boilers - Specifically designed for heating water or producing steam under pressure. Common in power plants, industrial processes, and residential heating systems.
Based on Pressure
Low-Pressure Vessels - Typically operate below 15 psi (pounds per square inch). Used for storage and processing applications that do not require high pressure.
High-Pressure Vessels - Operate at pressures above 15 psi. Often used in industrial chemical reactions, gas storage, or power generation.
Based on Orientation
Horizontal Pressure Vessels - More common for storage purposes, especially for gases like LPG. Easy to install and maintain.
Vertical Pressure Vessels - Often used in industrial processes for reactors, towers, and columns. Takes up less floor space but may be more complex to maintain.
Specialized Pressure Vessel
Heat Exchangers -
Transfer heat between two or more fluids under pressure. Essential in processes involving cooling or heating.
Autoclaves - Used to carry out industrial processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure. Commonly used in sterilization or curing composite materials.
Reactors - Designed for chemical reactions under pressure. The internal environment is carefully controlled to manage temperature, pressure, and reaction rates.
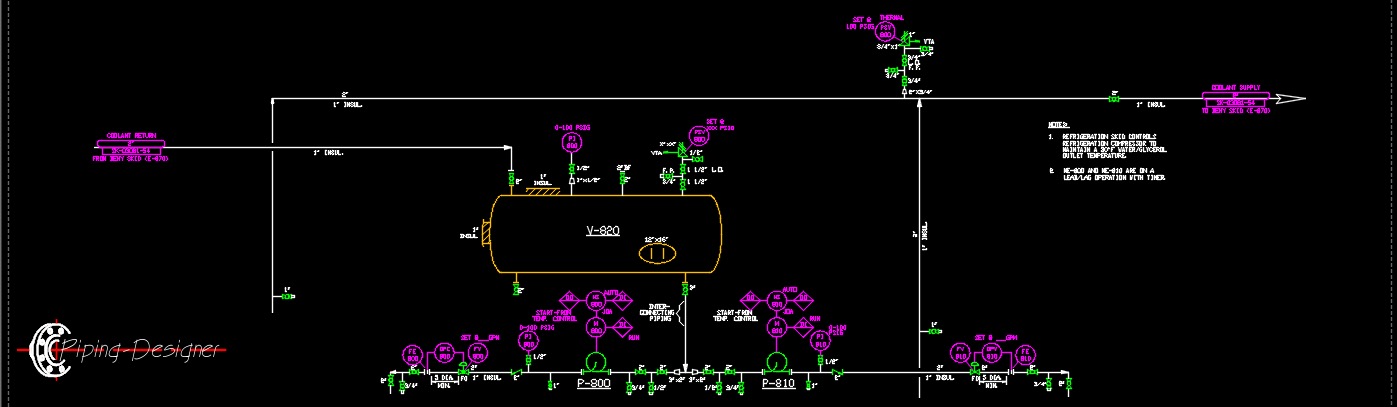 Pressure vessels, abbreviated as PV, are designed to hold or contain process fluids, liquids or gas, at a pressure significantly higher or lower than the ambient pressure, either internally or externially. Each pressure vessel must be operated within it's design temperature and pressure, which is the vessel's safety limits. These vessels serve many functions. They can used for storage of high pressure gas, gas scrubbers, two and three phase separators and other functions. They can have various internals depending on the process. Two phase separators may have a wave breaker, vortex breaker, mist eliminator and splash plate. Three phase separators will typically contain a the same components with the addition of a weir to help ensure separation.
Pressure vessels, abbreviated as PV, are designed to hold or contain process fluids, liquids or gas, at a pressure significantly higher or lower than the ambient pressure, either internally or externially. Each pressure vessel must be operated within it's design temperature and pressure, which is the vessel's safety limits. These vessels serve many functions. They can used for storage of high pressure gas, gas scrubbers, two and three phase separators and other functions. They can have various internals depending on the process. Two phase separators may have a wave breaker, vortex breaker, mist eliminator and splash plate. Three phase separators will typically contain a the same components with the addition of a weir to help ensure separation.


