Corrugated Steel Pipe
Corrugated steel pipe, abbreviated as CSP, is a type of pipe made from thin sheets of steel that are corrugated or shaped into a series of alternating ridges and valleys. This design gives the pipe added strength and flexibility, making it suitable for various applications, particularly in drainage, culvert systems, and underground infrastructure.
Key Points about Corrugated Steel Pipe
Strength - The corrugated design increases the pipe's strength and load-bearing capacity. It can withstand the weight of soil, vehicles, and other external pressures.
Flexibility - The corrugations allow the pipe to flex and adjust to ground movement or settlement without compromising its structural integrity.
Durability - Corrugated steel pipe is typically coated or lined to protect it from corrosion caused by exposure to water, chemicals, and environmental factors.
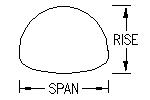
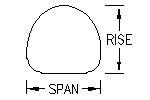
Variety of Shapes and Sizes - Corrugated steel pipes come in various shapes, including circular, elliptical, and arch shapes, to accommodate different flow and site requirements.
Installation - Corrugated steel pipes are relatively lightweight compared to other materials like concrete or solid metal pipes. This makes them easier to transport, handle, and install.
Cost Effective - Corrugated steel pipe can be a cost effective solution for drainage and culvert applications, especially in situations where a balance between cost, strength, and durability is required.
Corrugated steel pipes are commonly used for culverts, stormwater management systems, underpasses, pedestrian tunnels, and other underground applications. They are chosen for their ability to manage water flow efficiently, even under heavy loads and in varying soil conditions. Different coatings and linings are used to increase the durability of corrugated steel pipes, protecting them from the effects of corrosion over time. Examples include galvanized coatings, polymer coatings, and asphalt coatings.
Design Specifications |
|
| Agency | Specification |
| AASHTO | Standard Specifications for Highway Bridges-Division 1, Section 12 LRFD Bridge Design Specifications - Section 12 |
| ASTM | Standard Practice for Structural Design of Corrugated Steel Pipe, Pipe Arches, and Arches for Storm and Sanitary Sewers and Other Buried Applications - ASTM A796 |
| AREMA | Manual for Railway Engineering - Section 4.9 |
It's important to note that while corrugated steel pipes have numerous advantages, the specific choice of pipe material and design depends on factors such as the expected traffic load, environmental conditions, hydraulic performance, and local regulations. Proper design, installation, and maintenance are crucial to ensuring the long-term performance of corrugated steel pipe systems.

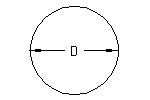
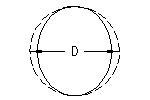
Diameter for Corrugated Steel Pipe
|
|
| Inside Diameter | Corrugation Pattern |
| 4" to 18" | 1 1/2" x 1/4" |
| 12" to 84" | 2 2/3" x 1/2" |
| 36" to 144" | 3" x 1" |
| 36" to 144" | 5" x 1" |
Installation Specifications |
|
| Agency | Specification |
| AASHTO | Standard Specifications for Highway Bridges-Division II, Section 26 LRFD Bridge Construction Specifications |
| ASTM | Standard Practice for Installing Factory Made Corrugated Steel Pipe for Sewers and Other Applications - ASTM A798 Standard Practice for Installing Corrugated Steel Structural Plate Pipe for Sewers and Other Applications - ASTM A807 |
| AREMA | Manual for Railway Engineering - Section 4.12 |
| U.S. Dept. of Agriculture - Natural Resources |
Conservation Service Construction Specification Section 51 Paragraph 6 Service |
| U.S. Dept. of Agriculture - Forest Service |
Specification for Construction of Roads and Bridges, Section 603.04 through 603.08. |
| Federal Lands Highway | FP92 Section 602.03, 602.05, 602.07, and 602.08 |
Material Description and Specifications |
||
| Material Group No. | Description | Specification |
| Zinc Coated sheets & coils |
Steel base metal* with 2 oz per ft2 zinc coating | AASHTO M218 - ASTM A929M |
| Polymer Coated Sheets and Coils | Polymer coatings applied to sheets* and coils* , 0,010 in. both sides | AASHTO M246 - ASTM A742M |
| Aluminum Coated coils - type 2 |
Steel base metal* coated with 1 ox. per ft2 of pure aluminum | AASHTO M274 - ASTM A929M |
| Sewer and Drainage Pipe |
Corrugated pipe fabricated from any of the above sheets of coils. Pipe is fabricated by corrugating continious coils into helical form with lock seam or welded seam, or by rolling annular corrugated mill sheets and riveting or spot welding seams: 1. Galvanized corrugated steel pipe 2. Polymeric pre-coated sewer and drainage pipe 3. Aluminized Type 2 corrugated steel pipe 4. Structual plate pipe |
|
| Ashalt Coated Steel Sewer Pipe | Corrugated steel pipe of any of the types shown above with a 0.050 in. asphalt coating | AASHTO M190 - ASTM A849 |
| Invert Paved Seel Sewer Pipe | Corrugated steel pipe of any one of the types shown above; 1. Ashalt coated pipe with 0.050 in. ashpalt coating and pavement poured in the invert to cover the currgation by 1.8 in. 2. With a field applied 3 in. (3250 psi) concrete invert or 1 1/2 in. high strength (9600 psi) concrete invert. 3. With polymer material applied 0.050 in. above the crest in the invert. |
AASHTO M190 - ASTM A849 ASTM A849 ASTM A849 |
| Fully Lined Steel Sewer Pipe |
Corrugated steel pipe of the types shown above: 1. With an internal asphalt lining centrifugally spun in place. 2. With an internal concrete lining in place. 3. Corrugated steel pipe with a smooth steel liner integrally formed with the corrugated shell or. 4. Corrugated steel pipe with a single thickness of smooth sheet fabricated with helical ribs porjected outward or. 5. With concrete pavement and linings installed in the field. |
AASHTO M190 - ASTM A849 AASHTO M36 - ASTM A849 AASHTO M36 - ASTM A760M AASHTO M36 - ASTM A760M |
| Cold Applied Bituminous Coatings | Mastic or coal tar base coating of various viscosities for field or sho coating of corrugated pipe or structural plate. | AASHTO M243 - ASTM A849 |
| Gaskets and Sealants |
1. Standard O-ring gaskets 2. Sponge neonprene sleeve gaskets 3. Gasketing strips, butyl or nioprene 4. Mastic sealant |
ASTM D1056
ASTM C361 |
Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) Abrasion Levels |
||
| Level | Type | Description |
| Level 1 | Non-Abrasion | No bed load regardless of velocity or storm sewer application. |
| Level 2 | Low Abrasion | Minor bed loads of sand and gravel and celocities of 5 ft/sec or less. |
| Level 3 | Moderate Abrasion | Bed loads of sand and small stone or gravel with velocities between 5 and 15 ft/sec. |
| Level 4 | Severe Abrasion | Heavy bed loads of gravel and rock with velocities exceeding 15 ft/sec. |