Hollow Rectangle
- See Article - Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
Area of a Hollow Rectangle formula |
||
| \( A \;=\; b\cdot a - b_1\cdot a_1 \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( a, b, a_1, b_1 \) = edge | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
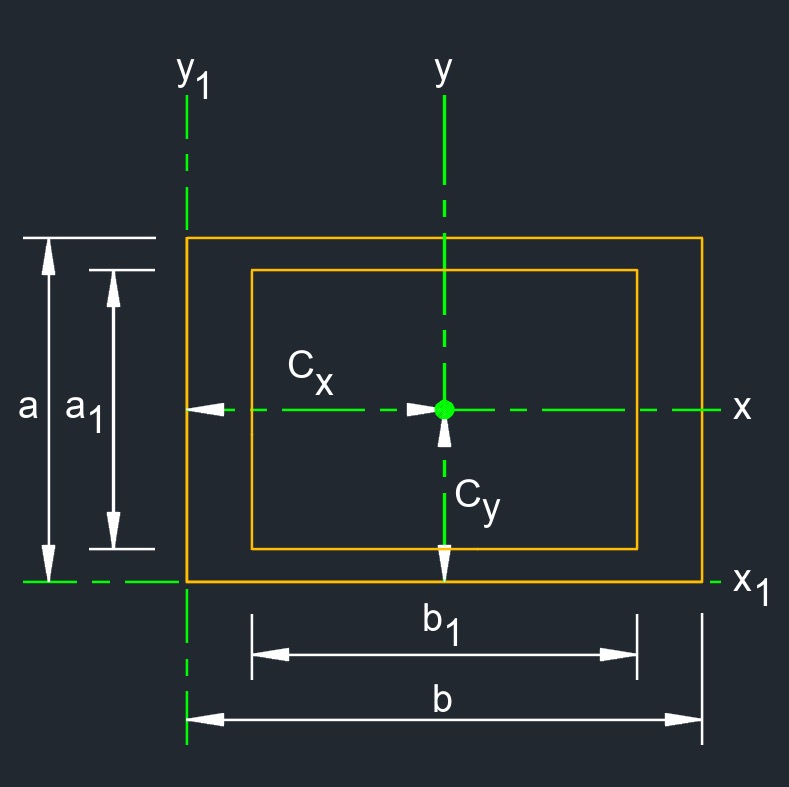 A two-dimensional figure that is a quadrilateral with two pair of parallel edges.
A two-dimensional figure that is a quadrilateral with two pair of parallel edges.- A hollow rectangle is a structural shape used in construction.
- Interior angles are 90°
- Exterior angles are 90°
Distance from Centroid of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( C_x \;=\; \dfrac{ b }{ 2 } \) \( C_y \;=\; \dfrac{ a }{ 2} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, a_1, b_1 \) = edge | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

Elastic Section Modulus of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( S_x \;=\; \dfrac{ I_x }{ C_y } \) \( S_y \;=\; \dfrac{ I_y }{ C_x } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( S \) = elastic section modulus | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( C \) = distance from centroid | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
Perimeter of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( P_o \;=\; 2\cdot \left( a + b \right) \) (Outside) \( P_i \;=\; 2\cdot \left( a_1 + b_2 \right) \) (Inside) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( a, b, a_1, b_1 \) = edge | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Polar Moment of Inertia of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( J_{z} \;=\; I_x + I_y \) \( J_{z1} \;=\; I_{x1} + I_{y1} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( J \) = torsional constant | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
Radius of Gyration of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( k_{x} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ b\cdot a^3 - b_1\cdot a_{1}{^3} }{ 12 \cdot \left( b\cdot a - b_1\cdot a_1 \right) } } \) \( k_{y} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ b^3 \cdot a - b_{1}{^3} \cdot a_1 }{ 12\cdot \left( b\cdot a - b_1\cdot a_1 \right) } } \) \( k_{z} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x}{^2} + k_{y}{^2} } \) \( k_{x1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ I_{x1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{y1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ I_{y1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{z1} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x1}{^2} + k_{y1}{^2} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = radius of gyration | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( a, b, a_1, b_1 \) = edge | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
Second Moment of Area of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( I_{x} \;=\; \dfrac{ b\cdot a^3 - b_1\cdot a_{1}{^3} }{12} \) \( I_{y} \;=\; \dfrac{ b^3 \cdot a - b_{1}{^3}\cdot a_1 }{12} \) \( I_{x1} \;=\; \dfrac{ b\cdot a^3 }{3} - \dfrac { b_1 \cdot a_1 \cdot \left( a_{1}{^2} + 3\cdot a^2 \right) }{12} \) \( I_{y1} \;=\; \dfrac{ b^3 \cdot a }{3} - \dfrac { b_1 \cdot a_1 \cdot \left( b_{1}{^2} + 3\cdot b^2 \right) }{12} \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( a, b, a_1, b_1 \) = edge | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Side of a Hollow Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( a \;=\; \dfrac{P}{2} - b \) \( b \;=\; \dfrac{P}{2} - a \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( a, b, a_1, b_1 \) = edge | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( P \) = perimeter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
