Electric Flux Density
Electric flux density formula |
||
|
\( D \;=\; \dfrac{ \phi_E }{ A }\) (Electric Flux Density) \( \phi_E \;=\; D \cdot A \) \( A \;=\; \dfrac{ \phi_E }{ D }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( D \) = Electric Flux Density | \(C\;/\;ft^2\) | \(C\;/\;m^2\) |
| \( \phi_E \) (Greek symbol phi) = Electric Flux | \(lbf\;/\;C\) | \(N-m^2\;/\;C\) |
| \( A \) = Surface Area Cross-section | \(ft^2\) | \(m^2\) |
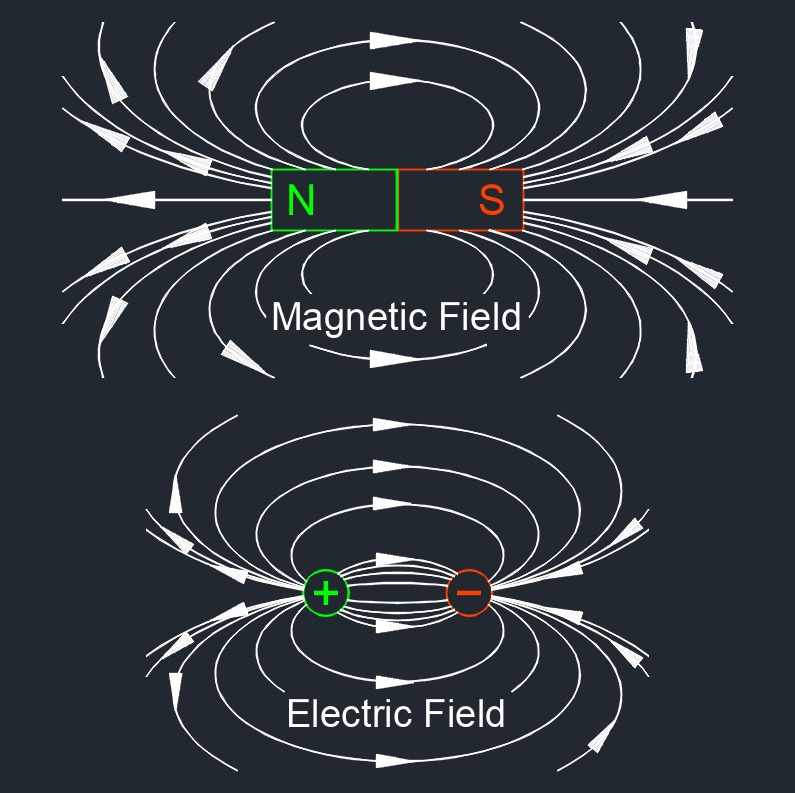 Electric flux density, abbreviated as D, is the amount of electric flux passing through a given area per unit area. In a vacuum, where there is no material influence, the electric flux density and the electric field are directly proportional and have the same direction. However, in materials (such as dielectrics), the electric displacement field accounts for the polarization of the material and differs from the electric field. Electric flux density is important in understanding the behavior of electric fields in different materials, including insulators, conductors, and dielectrics.
Electric flux density, abbreviated as D, is the amount of electric flux passing through a given area per unit area. In a vacuum, where there is no material influence, the electric flux density and the electric field are directly proportional and have the same direction. However, in materials (such as dielectrics), the electric displacement field accounts for the polarization of the material and differs from the electric field. Electric flux density is important in understanding the behavior of electric fields in different materials, including insulators, conductors, and dielectrics.
Electric flux density formula |
||
|
\( D \;=\; \epsilon \cdot E \) (Electric Flux Density) \( D \;=\; \dfrac{ D }{ E }\) \( D \;=\; \dfrac{ D }{ \epsilon }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( D \) = Electric Flux Density | \(C\;/\;ft^2\) | \(C\;/\;m^2\) |
| \(\epsilon\) (Greek symbol epsilon) = Permittivity (Material Through Which the Electric Field Passes) | \(CGS\) | \(F\;/\;m\) |
| \( E \) = Electric Field | \(N\;/\;C\) | \(V\;/\;m\) |
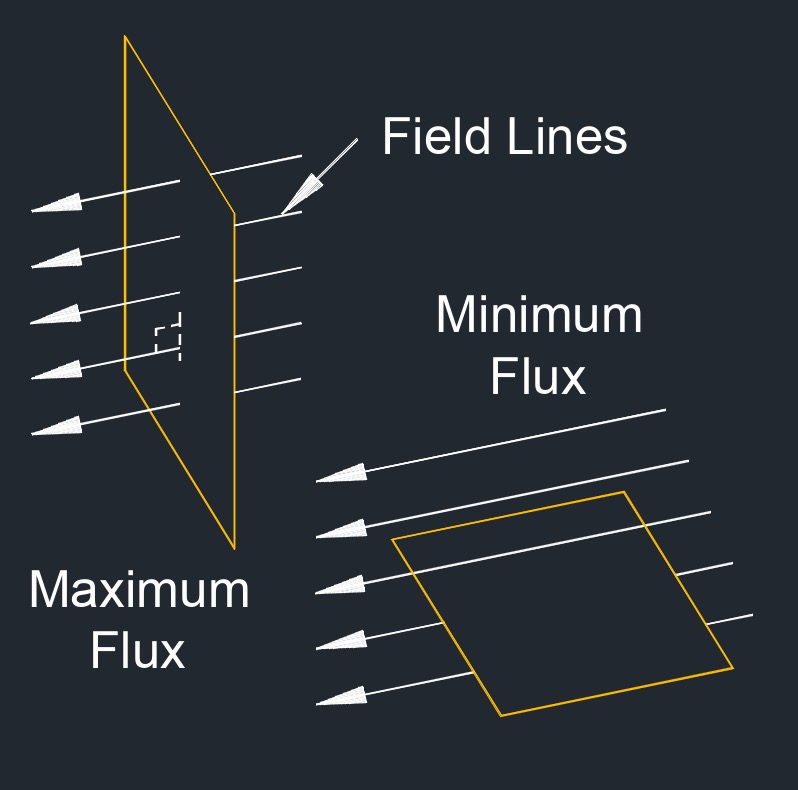
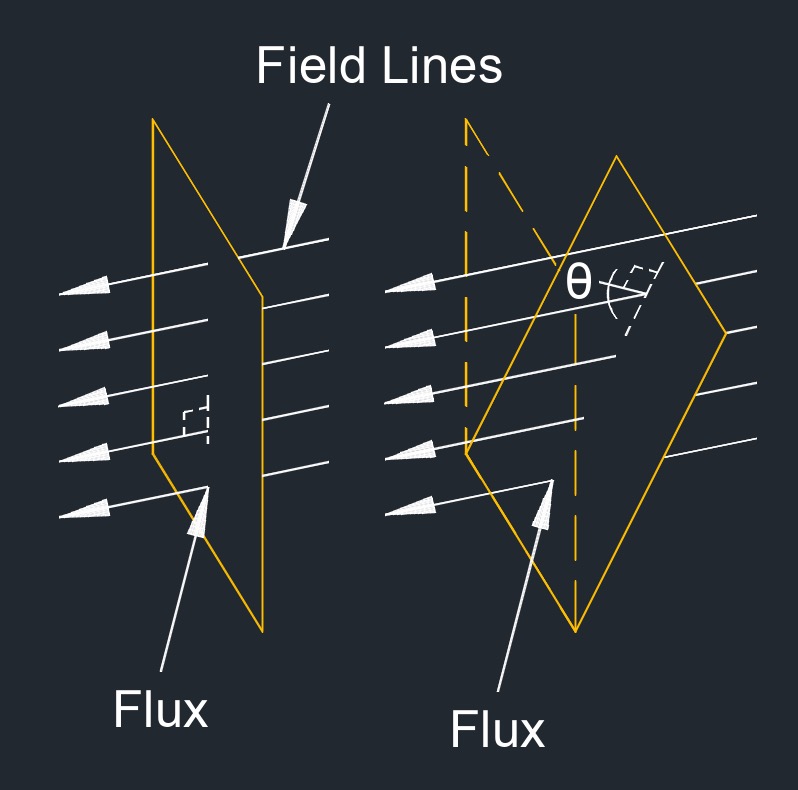

Electric flux density Formula |
||
|
\( D \;=\; \dfrac{ q }{ 4 \cdot \pi \cdot R^2 }\) (Electric Flux Density) \( q \;=\; 4 \cdot \pi \cdot R^2 \cdot D \) \( R \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ q }{ 4 \cdot \pi \cdot D } }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( D \) = Electric Flux Density | \(C\;/\;ft^2\) | \(C\;/\;m^2\) |
| \( q \) = Electric Charge Inside of Surface A (Single Point Charge) | \(C\) | \(C\) |
| \(\large{ \pi }\) = Pi | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) |
| \( R \) = q at Distance R | \(ft^2\) | \(m^2\) |
