|
|
|
\( B \;=\; \rho \cdot g \cdot V \) (Buoyancy)
\( \rho \;=\; \dfrac{ B }{ g \cdot V }\)
\( V \;=\; \dfrac{ B }{ \rho \cdot g } \)
|
| Symbol |
English |
Metric |
| \( B \) = Buoyancy |
\(lbf\) |
\(N\) |
| \( \rho \) (Greek symbol rho) = Fluid Density |
\(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) |
\(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( g \) = Gravitational Constant |
\(lbf-ft^2 \;/\; lbm^2\) |
\(N -m^2 \;/\; kg^2\) |
| \( V \) = Volume of Solid |
\(ft^3\) |
\(m^3\) |
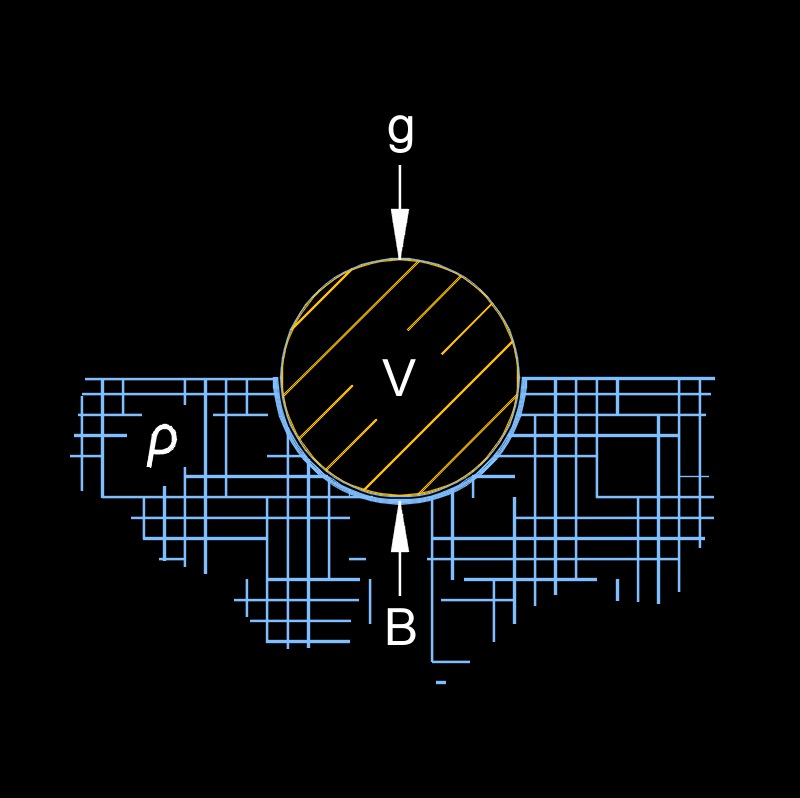 Buoyancy, abbreviated as B, is the upward force that is exerted on an object when it is immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) and displaces an amount of fluid with a weight equal to the weight of the object. It is a result of the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the object due to the weight of the fluid that is displaced. The magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid that is displaced by the object, and it acts in the opposite direction of gravity, which is why it causes objects to float.
Buoyancy, abbreviated as B, is the upward force that is exerted on an object when it is immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) and displaces an amount of fluid with a weight equal to the weight of the object. It is a result of the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the object due to the weight of the fluid that is displaced. The magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid that is displaced by the object, and it acts in the opposite direction of gravity, which is why it causes objects to float.
The principle behind buoyancy was described by Archimedes, who figured out that the buoyant force on an object equals the weight of the fluid it displaces. If an object displaces a volume of fluid heavier than itself, it floats; if its own weight is greater, it sinks. This is why a steel ship can float while a solid steel ball sinks, the ship’s shape displaces a lot of water, while the ball doesn’t displace enough to counter its weight.
What Affects Buoyancy
Density of the Fluid - The denser the fluid, the greater the buoyant force. For example, saltwater (denser than freshwater) provides more buoyancy, which is why it’s easier to float in the ocean than in a lake.
Volume of the Displaced Fluid - The more fluid an object displaces, the stronger the buoyant force. This depends on the object’s submerged volume, larger or hollow objects (like a ship) displace more fluid and get more lift.
Density of the Object - If the object’s density is less than the fluid’s, it floats; if greater, it sinks. A solid steel block sinks in water, but a steel ship with air inside has lower overall density and floats.
Gravity - The strength of gravity affects the weight of both the object and the displaced fluid. In lower gravity (like on the Moon), buoyant forces are weaker because weights are reduced, though the principle still applies.
Shape of the Object - Shape impacts how much fluid is displaced and how the pressure acts. A flat-bottomed boat displaces more water and stays stable, while a thin needle might sink despite low weight due to minimal displacement.
Depth of Submersion - Buoyancy only depends on the submerged portion of an object. If it’s only partly underwater, only that volume counts toward displacement. Fully submerged objects max out their buoyant force.
Fluid Pressure - Changes in atmospheric pressure or temperature can slightly alter fluid density and pressure, tweaking buoyancy. For instance, warmer water is less dense, reducing buoyancy compared to colder water.

 Buoyancy, abbreviated as B, is the upward force that is exerted on an object when it is immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) and displaces an amount of fluid with a weight equal to the weight of the object. It is a result of the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the object due to the weight of the fluid that is displaced. The magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid that is displaced by the object, and it acts in the opposite direction of gravity, which is why it causes objects to float.
Buoyancy, abbreviated as B, is the upward force that is exerted on an object when it is immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) and displaces an amount of fluid with a weight equal to the weight of the object. It is a result of the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the object due to the weight of the fluid that is displaced. The magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid that is displaced by the object, and it acts in the opposite direction of gravity, which is why it causes objects to float.
