Melting
 Melting is a process by which a solid substance changes its state from a solid to a liquid as a result of absorbing heat. This occurs when a solid is heated to its melting point, which is the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium. When a solid is heated, the molecules or atoms within it begin to vibrate more rapidly due to the added energy. As the temperature rises, the kinetic energy of the molecules or atoms increases and they gain enough energy to break the intermolecular forces that hold them in a rigid structure. This results in the formation of a liquid, which has a higher degree of molecular disorder than a solid.
Melting is a process by which a solid substance changes its state from a solid to a liquid as a result of absorbing heat. This occurs when a solid is heated to its melting point, which is the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium. When a solid is heated, the molecules or atoms within it begin to vibrate more rapidly due to the added energy. As the temperature rises, the kinetic energy of the molecules or atoms increases and they gain enough energy to break the intermolecular forces that hold them in a rigid structure. This results in the formation of a liquid, which has a higher degree of molecular disorder than a solid.
The melting point of a substance is a physical property that is specific to each substance and is dependent on factors such as pressure and purity. The melting point can be used as a tool to identify and purify substances.
Melting is an important process in many industrial and scientific applications. It is used in metalworking to shape and join metals, and in materials science to prepare samples for analysis. It is also an important process in the Earth's geology, where the melting of rocks and minerals in the Earth's mantle plays a role in the formation of magma and volcanic activity
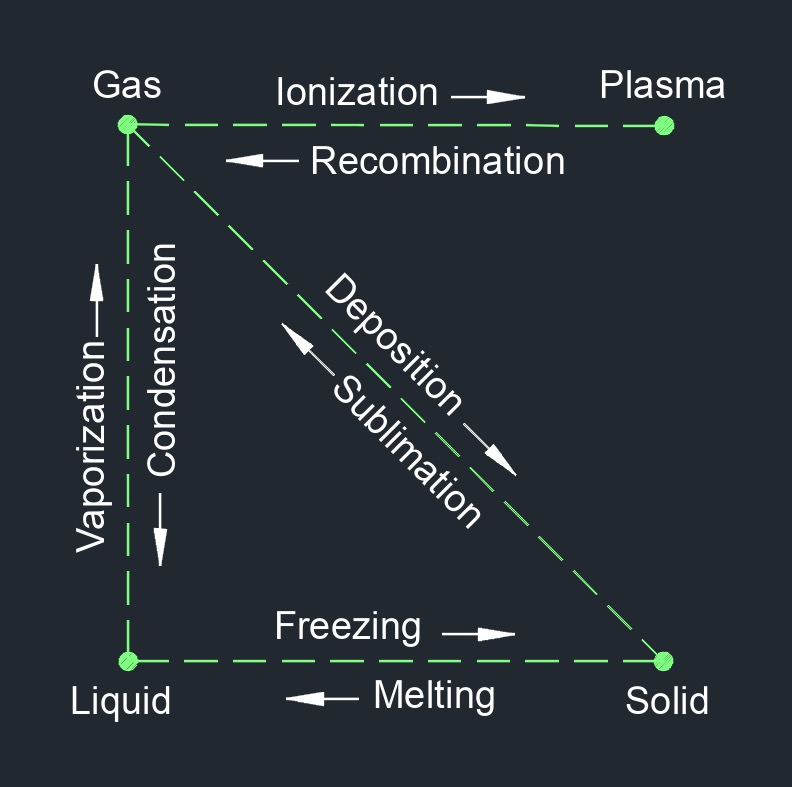
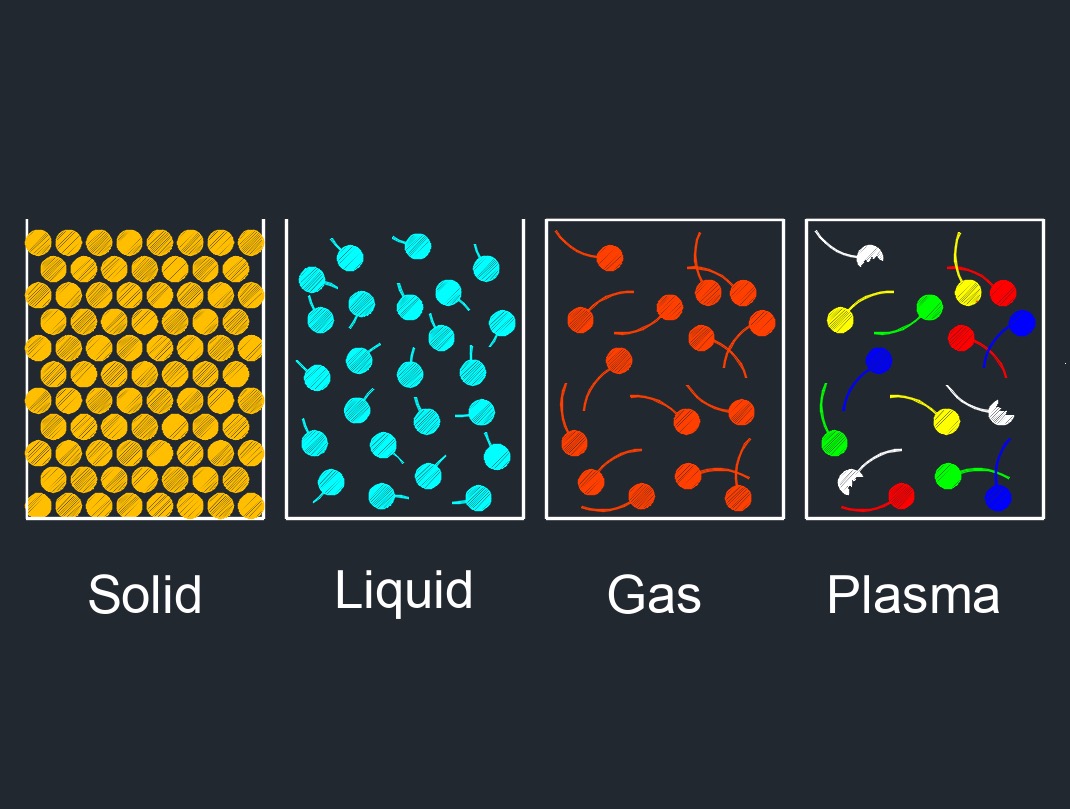
There are four phases of matter: gas, liquid, plasma, and solid.

