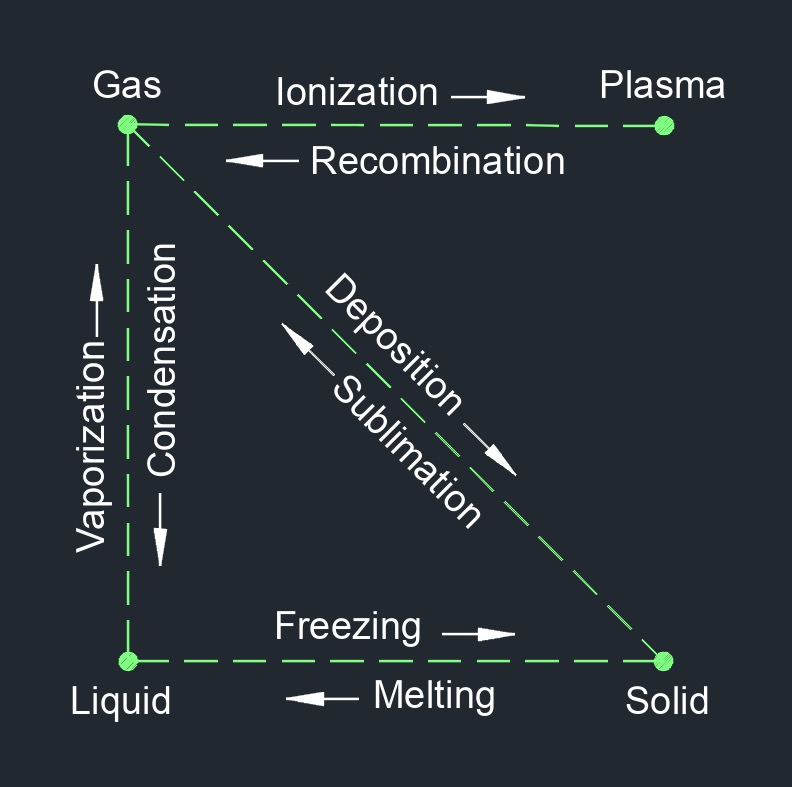
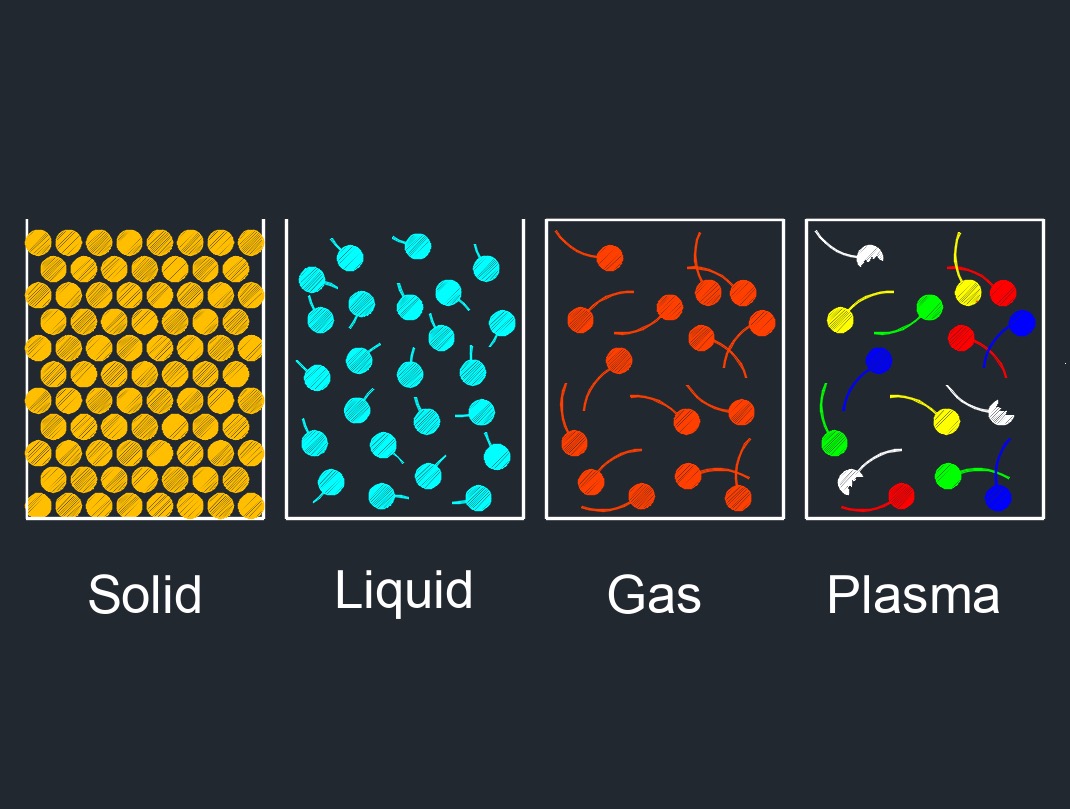
 Ionization is the process by which an atom or molecule gains or loses one or more electrons, resulting in the formation of charged particles called ions. This process can occur through various means such as exposure to radiation, collisions with other particles, or through chemical reactions.
Ionization is the process by which an atom or molecule gains or loses one or more electrons, resulting in the formation of charged particles called ions. This process can occur through various means such as exposure to radiation, collisions with other particles, or through chemical reactions.
When an atom or molecule loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. When it gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. The number of electrons lost or gained determines the charge of the resulting ion.
Ionization is an important process in various fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology. It is used in analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry, where ionization is used to create charged particles from neutral molecules, allowing them to be separated and detected based on their mass-to-charge ratio.
In atmospheric physics, ionization is responsible for the formation of the ionosphere, a layer of charged particles in the Earth's upper atmosphere that plays a role in the propagation of radio waves and the phenomenon of auroras. Ionization is also an important process in biological systems, as it can cause damage to DNA and other biomolecules through the formation of free radicals. It is also used in medical applications such as radiation therapy, where ionizing radiation is used to kill cancer cells.



 Ionization is the process by which an atom or molecule gains or loses one or more electrons, resulting in the formation of charged particles called ions. This process can occur through various means such as exposure to radiation, collisions with other particles, or through chemical reactions.
Ionization is the process by which an atom or molecule gains or loses one or more electrons, resulting in the formation of charged particles called ions. This process can occur through various means such as exposure to radiation, collisions with other particles, or through chemical reactions. 