Instrumentation & Controls Engineering
Pump, Electrical, Motor, Instrumentation and Controls, Engineering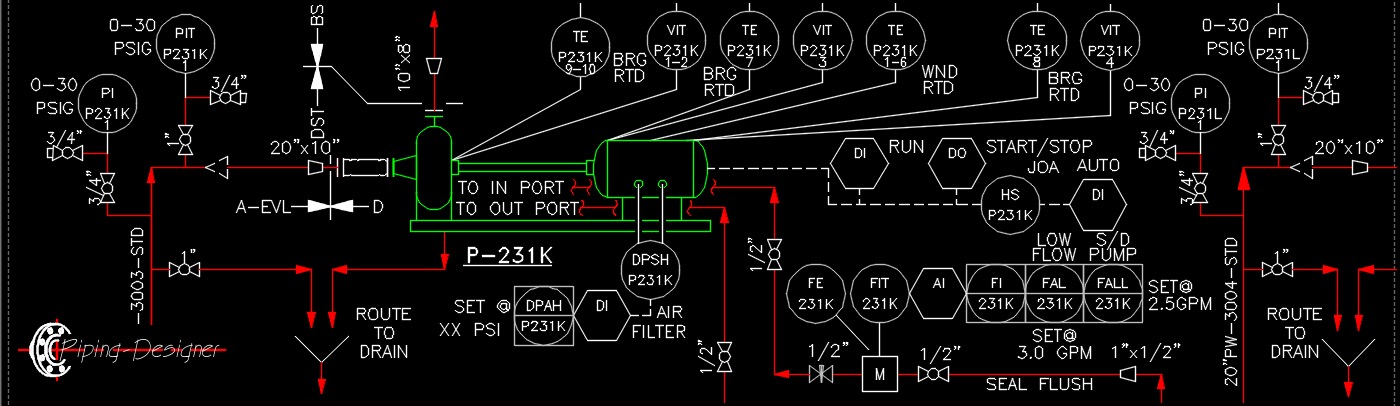 Instrumentation and controls engineering (I&C) is a branch of engineering that focuses on the measurement, control, and automation of industrial processes. I&C engineers use a variety of tools and techniques to design, install, and maintain control systems that monitor and adjust the operation of industrial equipment, such as pumps, valves, and turbines. The work of an I&C engineer typically involves selecting and integrating sensors, actuators, and controllers to create a system that can monitor and control a process. They may use various technologies, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCS), or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, to manage and optimize industrial processes.
Instrumentation and controls engineering (I&C) is a branch of engineering that focuses on the measurement, control, and automation of industrial processes. I&C engineers use a variety of tools and techniques to design, install, and maintain control systems that monitor and adjust the operation of industrial equipment, such as pumps, valves, and turbines. The work of an I&C engineer typically involves selecting and integrating sensors, actuators, and controllers to create a system that can monitor and control a process. They may use various technologies, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCS), or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, to manage and optimize industrial processes.
| Engineering |
| Electrical Engineering |
- See Articles - Instrumentation and Controls Glossary / Electrical Glossary / Instrument Naming / ISA 5.1 Table 2 - Typical Letter Combinations / Instrumentation Matrix / Instrumentation Abbreviations
I&C engineers work in a variety of industries, including oil and gas, power generation, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment. They are responsible for ensuring that industrial processes operate safely, efficiently, and reliably, while also minimizing environmental impact and complying with regulatory requirements.
In addition to designing and installing control systems, I&C engineers also perform testing, troubleshooting, and maintenance to ensure that systems continue to operate properly over time. They may also work on projects related to process optimization, plant modernization, or system upgrades. I&C is a critical field that plays a key role in many industries. By designing and maintaining control systems that monitor and adjust industrial processes, I&C engineers help to ensure that our modern infrastructure operates safely and efficiently, while also minimizing environmental impact.

