Kinetic Energy
 Kinetic energy, abbreviated as KE, is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its motion. It is a scalar quantity and is dependent on the mass and speed of the object. If it moves, it has kinetic energy. The energy an object possesses due to its motion. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude and no direction. It is a type of mechanical energy, which is the sum of kinetic and potential energy in a system.
Kinetic energy, abbreviated as KE, is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its motion. It is a scalar quantity and is dependent on the mass and speed of the object. If it moves, it has kinetic energy. The energy an object possesses due to its motion. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude and no direction. It is a type of mechanical energy, which is the sum of kinetic and potential energy in a system.
Kinetic Energy Types
Electric Energy - Energy stored in an electric field or transported by an electric current.
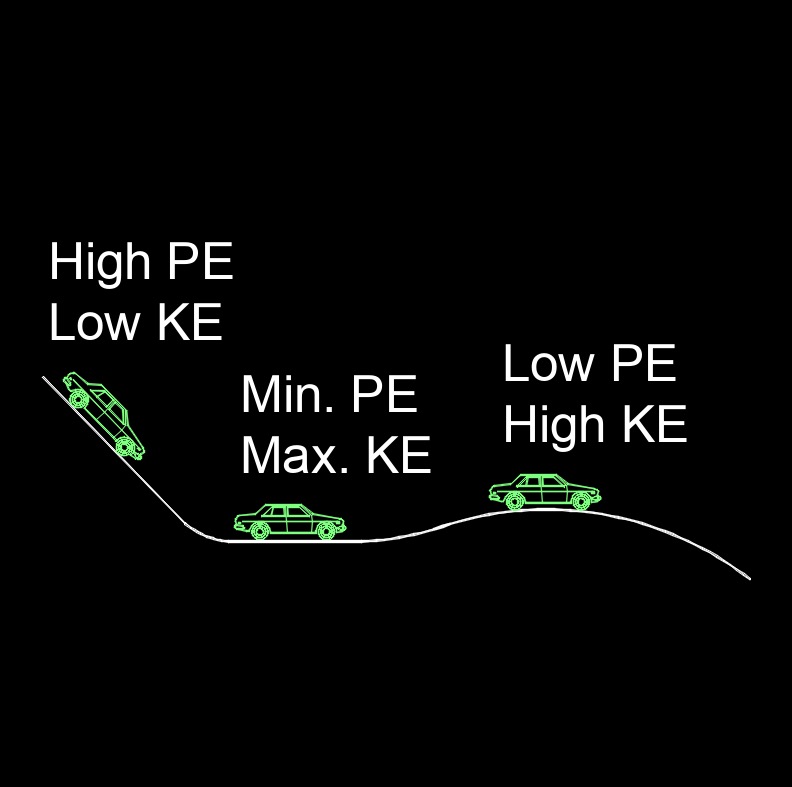
Mechanical Energy - The sum of the change in kinetic energy and potential energy generating from the force of gravity, external forces or the movement released in machine movement.
Radiant Energy (electromagnetic) - Energy transmitted without the movement of mass.
Sound Energy - Energy that we can hear. It is a type of kinetic energy that moves through the air and other matter in the form of sound waves.
Thermal Energy - The exertion of power that is created by heat, or the increase in temperature.
Wind Energy - The kinetic energy of air in motion.
Kinetic Energy Formula |
||
|
\( KE \;=\; \frac{ 1 }{ 2} \cdot m \cdot v^2 \) (Kinetic Energy) \( m \;=\; \dfrac{ 2 \cdot KE }{ v^2 } \) \( v \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ 2 \cdot KE }{ m } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( KE \) = Kinetic Energy | \( lbf-ft \) | \(J\) |
| \( m \) = Mass | \(lbm\) | \(kg\) |
| \( v \) = Velocity | \(ft \;/\; sec\) | \(m \;/\; s\) |

Tags: Energy Kinetic Energy

