Longitudinal Stress
Longitudinal Stress Formula |
||
|
\( \sigma_l \;=\; \dfrac{ p \cdot d }{ 4 \cdot t }\) (Longitudinal Stress) \( p \;=\; \dfrac{ \sigma_l \cdot 4 \cdot t }{ d }\) \( d \;=\; \dfrac{ \sigma_l \cdot 4 \cdot t }{ p }\) \( t \;=\; \dfrac{ p \cdot d }{ \sigma_l \cdot 4 }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \sigma_l \) (Greek symbol sigma) = Longitudinal Stress | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( p \) = Internal Pressure | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( d \) = Mean Pipe Diameter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = Pipe Thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
Longitudinal stress is the stress or force experienced by a material along its longitudinal axis, which is the axis aligned with the length of the object. When a material is subjected to a load or force that acts parallel to its length, it can induce longitudinal stress. In engineering and materials science, longitudinal stress is often associated with tensile or compressive forces applied in the direction of an object's length. Tensile stress occurs when a material is being stretched or pulled apart along its length, while compressive stress arises when the material is being compressed or pushed together along its length.
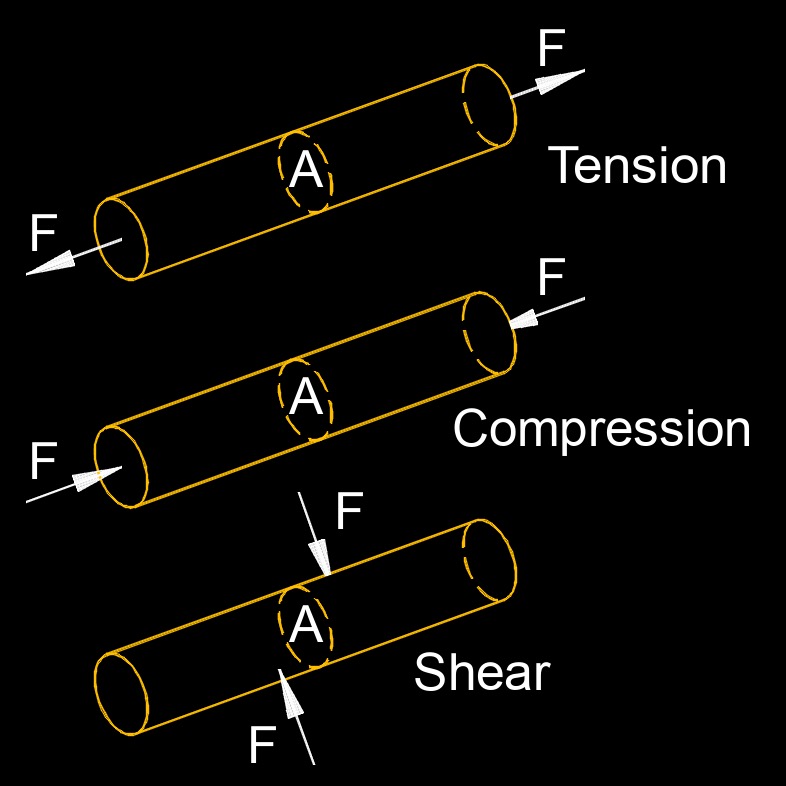
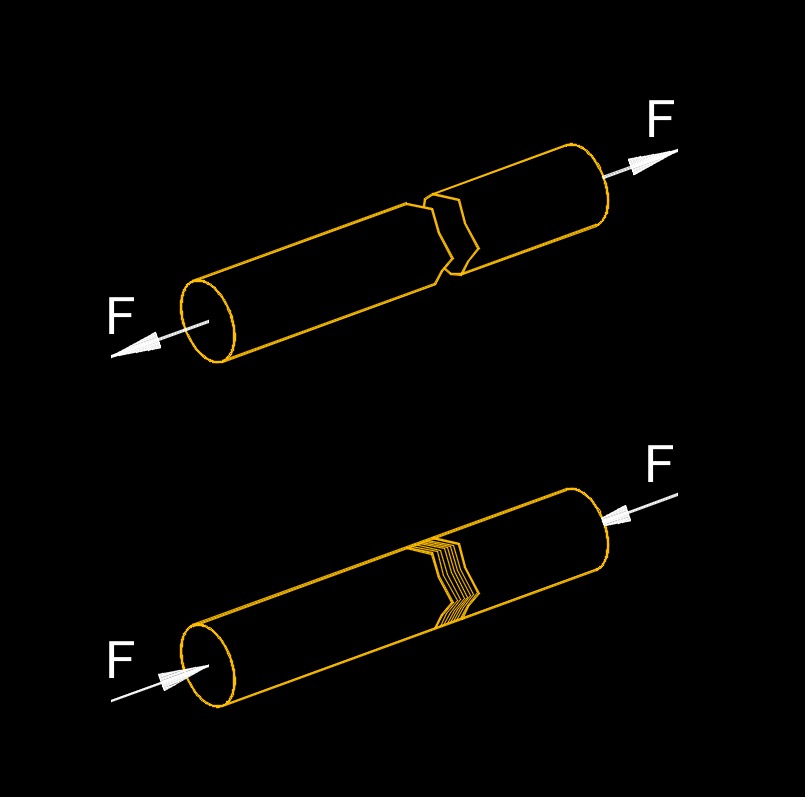
The magnitude of longitudinal stress is typically expressed in units of force per unit area, such as pascals or pounds per square inch (psi). The stress experienced by a material depends on factors such as the applied force, the area cross-section of the material, and its mechanical properties, including its Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio.
Understanding the longitudinal stress in a material is important for evaluating its strength, deformation behavior, and structural integrity. Engineers and designers consider longitudinal stress when designing structures, machinery, and components to ensure they can withstand expected loads and forces without experiencing excessive deformation or failure.

