Seepage Velocity
Seepage Velocity Formula |
||
|
\( v_s \;=\; \dfrac{ v \cdot A_c }{ A_v }\) (Seepage Velocity) \( v \;=\; \dfrac{ v_s \cdot A_v }{ A_c }\) \( A_c \;=\; \dfrac{ v_s \cdot A_v }{ v }\) \( A_v \;=\; \dfrac{ v \cdot A_c }{ v_s }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( v_s \) = Seepage Velocity | \(ft \;/\; sec\) | \(m \;/\; s\) |
| \( v \) = Darcy Velocity or Flux | \(ft \;/\; sec\) | \(m \;/\; s\) |
| \( A_c \) = Flow Area Cross-section | \(ft^2\) | \(m^2\) |
| \( A_v \) = Voids Area Cross-section | \(ft^2\) | \(m^2\) |
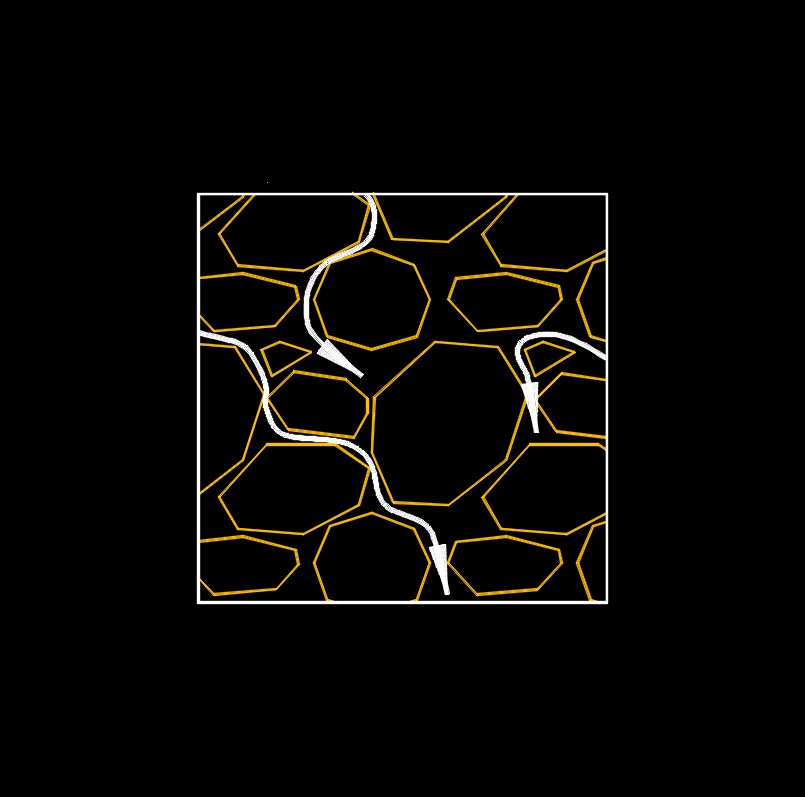 Seepage velocity, abbreviated as \(v_s\), is the velocity at which water or other fluid passes through a porous medium, such as soil or rock. It is a measure of the flow rate or speed of the fluid as it moves through the void spaces within the porous material. Seepage velocity is influenced by several factors, including the hydraulic conductivity of the porous medium, the hydraulic gradient (the change in hydraulic head over a given distance), and the properties of the fluid itself (such as viscosity).
Seepage velocity, abbreviated as \(v_s\), is the velocity at which water or other fluid passes through a porous medium, such as soil or rock. It is a measure of the flow rate or speed of the fluid as it moves through the void spaces within the porous material. Seepage velocity is influenced by several factors, including the hydraulic conductivity of the porous medium, the hydraulic gradient (the change in hydraulic head over a given distance), and the properties of the fluid itself (such as viscosity).
In the context of groundwater flow, seepage velocity is an important parameter for understanding and analyzing the movement of water through an aquifer. It is used in hydrogeology to determine the rate at which groundwater is flowing and to estimate the travel time or distance that water will move within the aquifer.
It's important to note that seepage velocity is a theoretical value and assumes steady state flow conditions. In reality, groundwater flow can be more complex, and factors such as heterogeneity of the porous medium and the presence of boundaries or barriers can influence the actual flow behavior.

