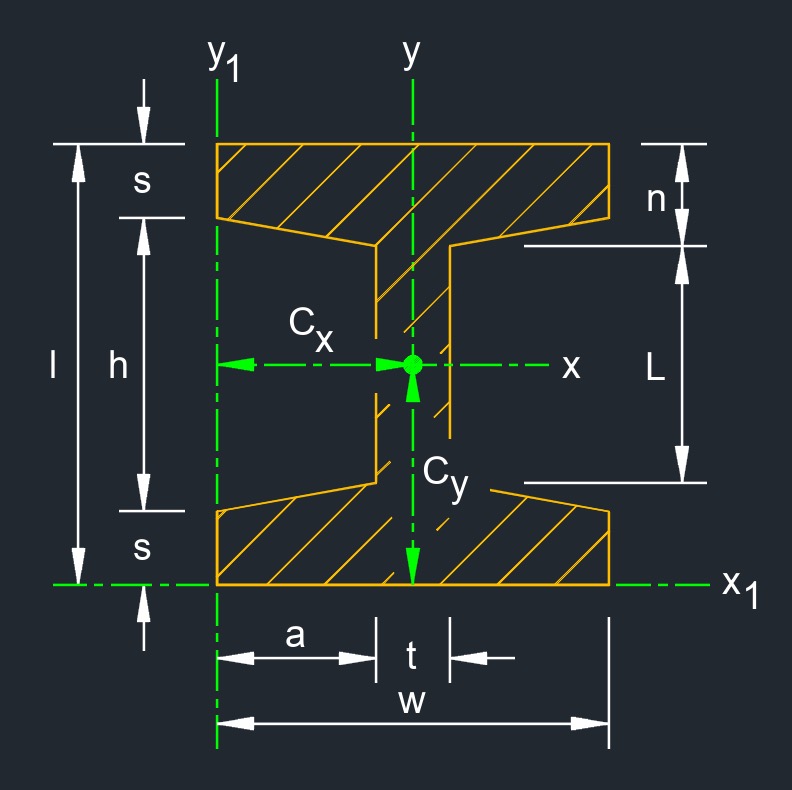
Radius of Gyration of a Tapered I Beam
Radius of Gyration of a Tapered I Beam formulas |
||
|
\( k_x \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ \dfrac{1}{12} \cdot \left[ w\cdot l^3 - \dfrac{1}{4\cdot g} \cdot \left( h^4 - L^4 \right) \right] }{ l \cdot t + 2\cdot a \cdot \left( s + n \right) } } \) \( k_y \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ \dfrac{1}{3} \cdot \left[ w^3 \cdot \left( l - h \right) + L\cdot t^3 + \dfrac{g}{4} \cdot \left( w^4 - t^4 \right) \right] }{ l \cdot t + 2\cdot a \cdot \left( s + n \right) } } \) \( k_z \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x}{^2} + k_{y}{^2} } \) \( k_{x1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ I_{x1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{y1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ I_{y1} }{ A } } \) \( k_{z1} \;=\; \sqrt{ k_{x1}{^2} + k_{y1}{^2} } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = radius of gyration | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( h \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( l \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( L \) = height | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( I \) = moment of inertia | \( in^4 \) | \( mm^4 \) |
| \( n \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( s \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( t \) = thickness | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( a \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( w \) = width | \( in \) | \( mm \) |