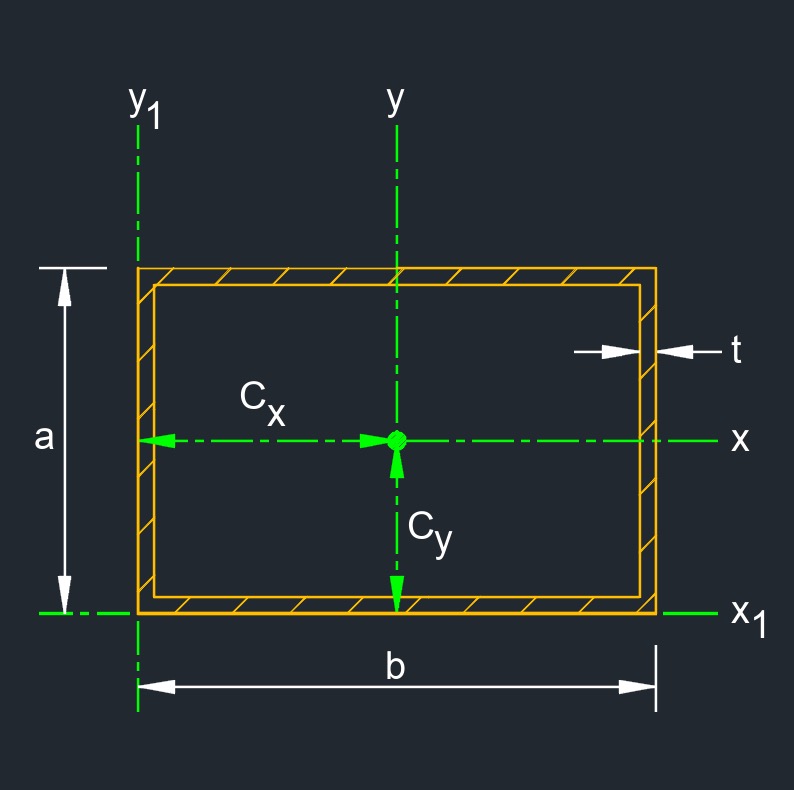
Radius of Gyration of a Thin Wall Rectangle
Radius of Gyration of a Thin Wall Rectangle formulas |
||
|
\( k_{x} \;=\; \left( \sqrt{ \dfrac{ b }{ 6 \cdot ( b + a ) } } \right) \cdot a \) \( k_{y} \;=\; \left( \sqrt{ \dfrac{ a }{ 6 \cdot ( b + a ) } } \right) \cdot b \) \( k_{z} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ a\cdot b }{ 6 } } \) \( k_{x1} \;=\; \left( \sqrt{ \dfrac{ 5\cdot b + 3\cdot a }{ 12 \cdot ( b + a ) } } \right) \cdot a \) \( k_{y1} \;=\; \left( \sqrt{ \dfrac{ 3\cdot b + 5\cdot a }{ 12 \cdot ( b + a ) } } \right) \cdot b \) \( k_{z1} \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ 3 \cdot ( b^3 + a^3 ) + 5\cdot b\cdot a \cdot ( b + a ) }{ 12 \cdot ( b + a ) } } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( k \) = radius of gyration | \(in \) | \(mm \) |
| \( a, b \) = edge | \(in \) | \(mm \) |