Force Exerted by Contracting or Stretching a Material
Force Exerted by Contracting or Stretching a Material Formula |
||
|
\( F \;=\; \dfrac{ \lambda \cdot A \cdot L_c }{ L_o }\) (Force Exerted by Contracting or Stretching a Material) \( \lambda \;=\; \dfrac{ F \cdot L_o }{ A \cdot L_c }\) \( A \;=\; \dfrac{ F \cdot L_o }{ \lambda \cdot L_c }\) \( L_c \;=\; \dfrac{ F \cdot L_o }{ \lambda \cdot A }\) \( L_o \;=\; \dfrac{ \lambda \cdot A \cdot L_c }{ F }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( F \) = Force Exerted | \(lbf\) | \(N\) |
| \( \lambda \) (Greek symbol lambda) = Modulus of Elasticity | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( A \) = Rigional Area Cross-Section Through Which the Force is Applied | \(ft^2\) | \(m^2\) |
| \( L_c \) = Change in Length | \(ft\) | \(m\) |
| \( L_o \) = Origional Length | \(ft\) | \(m\) |
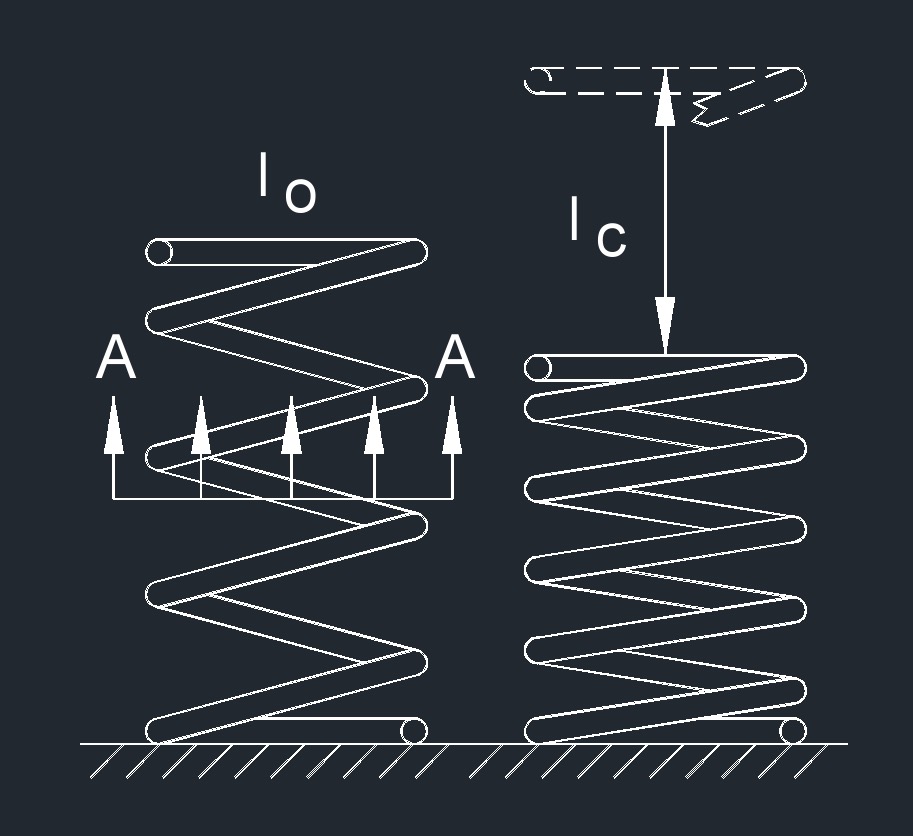 Any strain exerted on a material causes an internal elastic stress. The force applied on a material when contracting or stretching is related to how much the length of the object changes.
Any strain exerted on a material causes an internal elastic stress. The force applied on a material when contracting or stretching is related to how much the length of the object changes.

