Potential Energy
Potential Energy Formula |
||
|
\( PE \;=\; m \cdot g \cdot h \) (Potential Energy) \( m \;=\; \dfrac{ PE }{ g \cdot h } \) \( g \;=\; \dfrac{ PE }{ m \cdot h } \) \( h \;=\; \dfrac{ PE }{ m \cdot g } \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( PE \) = Potential Energy | \( lbf-ft \) | \( J \) |
| \( m \) = Mass | \( lbm \) | \( kg \) |
| \( g \) = Gravity | \(ft \;/\; sec^2\) | \(m \;/\; s^2\) |
| \( h \) = Height | \( ft \) | \( m \) |
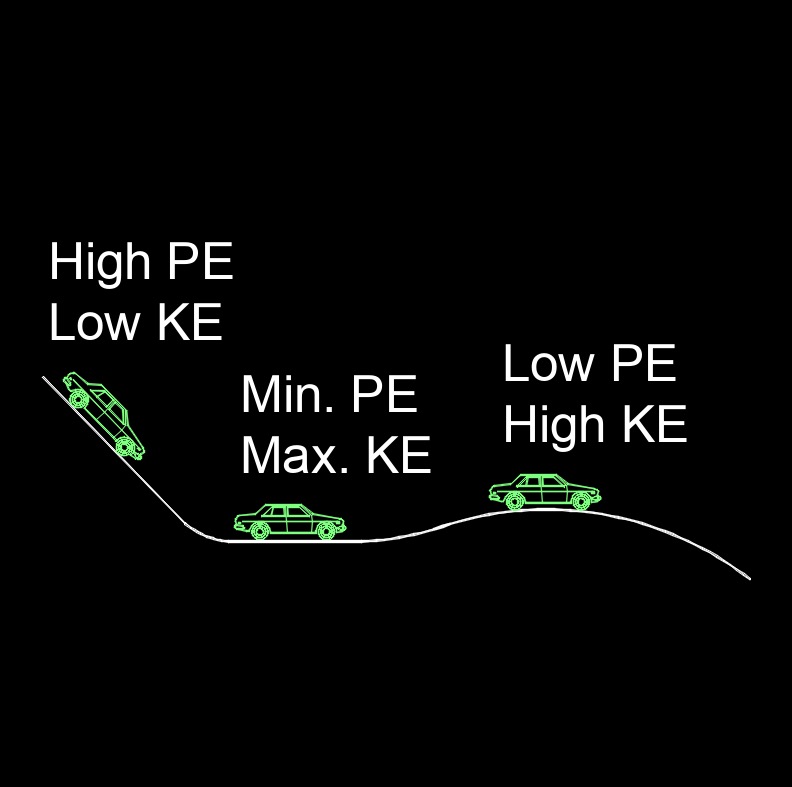 Potential energy, abbreviated as \(PE\), also called stored energy, is the possessed energy by a body due to its relative position in a gravitational field. As the elevation of the body decreases the less potential energy. The energy possessed by an object due to its position or configuration in a force field. It is the energy that is stored within an object as a result of its position or state. The amount of potential energy possessed by an object depends on factors such as its mass, its position relative to other objects or fields, and the strength of the force fields acting on it. The most common example of potential energy is gravitational potential energy, which is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field.
Potential energy, abbreviated as \(PE\), also called stored energy, is the possessed energy by a body due to its relative position in a gravitational field. As the elevation of the body decreases the less potential energy. The energy possessed by an object due to its position or configuration in a force field. It is the energy that is stored within an object as a result of its position or state. The amount of potential energy possessed by an object depends on factors such as its mass, its position relative to other objects or fields, and the strength of the force fields acting on it. The most common example of potential energy is gravitational potential energy, which is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field.

