Electric Voltage
Electric Voltage Formula |
||
|
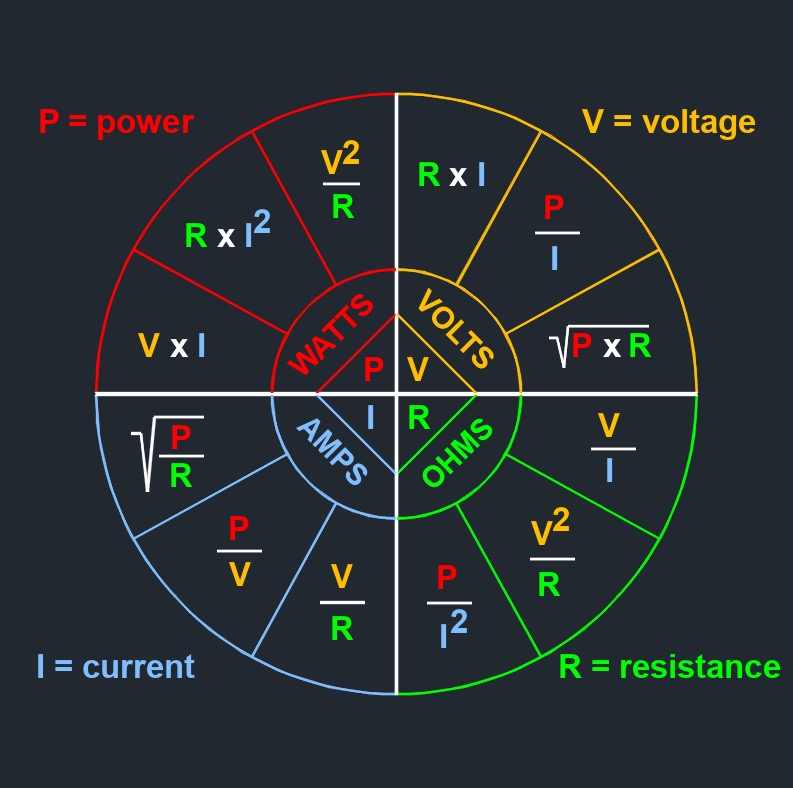
\( V \;=\; I \cdot R \) (Electric Voltage) \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ V }{ R }\) \( R \;=\ \dfrac{ V }{ I }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( V \) = voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( I \) = current | \(A\) | \(A\) |
| \( R \) = resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |
 Electric voltage, abbreviated as \(V\) or \(E\), also called electric potential difference, is the measure of the electric potential energy per unit charge that is required to move a charge from one point to another in an electric field. A unit of electrical pressure. One volt is the amount of pressure that will cause one ampere of current in one ohm of resistance.
Electric voltage, abbreviated as \(V\) or \(E\), also called electric potential difference, is the measure of the electric potential energy per unit charge that is required to move a charge from one point to another in an electric field. A unit of electrical pressure. One volt is the amount of pressure that will cause one ampere of current in one ohm of resistance.
Electric Voltage Formula |
||
|
\( V \;=\; \dfrac{ P }{ I }\) (Electric Voltage) \( P \;=\; V \cdot I \) \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ P }{ V }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( V \) = voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( I \) = current | \(A\) | \(A\) |
| \( P \) = power | \(P\) | \(P\) |
 In simple terms, voltage is the force that drives the electric current through a conductor. It is similar to the pressure that drives water through a pipe. The greater the voltage, the more electric charge will flow through a circuit. Voltage can be calculated using Ohm's Law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.
In simple terms, voltage is the force that drives the electric current through a conductor. It is similar to the pressure that drives water through a pipe. The greater the voltage, the more electric charge will flow through a circuit. Voltage can be calculated using Ohm's Law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.

Electric Voltage Formula |
||
|
\( V \;=\; \sqrt{ P \cdot R } \) (Electric Voltage) \( P \;=\; \dfrac{ V^2 }{ R }\) \( R \;=\; \dfrac{ V^2 }{ P }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( V \) = voltage | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( P \) = power | \(P\) | \(P\) |
| \( R \) = resistance | \(\Omega\) | \(\Omega\) |

Voltage in Series Formula
|
||
| \( V_t \;=\; V_1 + V_2 + V_3 +\; ... \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( V_t \) = voltage total source or drop | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( V_1, V_2, V_3 \) = voltage source or drop | \(V\) | \(V\) |
Voltage in Parallel Formula
|
||
| \( V_t \;=\; V_1 \;=\; V_2 \;=\; V_3 \;=\;\; ... \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( V_t \) = voltage total source or drop | \(V\) | \(V\) |
| \( V_1, V_2, V_3 \) = voltage source or drop | \(V\) | \(V\) |
